Milwaukee shoulder refers to a destructive arthropathy associated with advanced rotator cuff tears and deposition of basic calcium phosphate crystals including hydroxyapatite crystals.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Milwaukee shoulder frequently affects older women with an age range of 50 - 90 years, often with a history of trauma to the region.
Clinical presentation
Symptoms are usually comparatively mild, despite rapid and marked progression of radiographic features. Other joints can be affected by a similar process.
Pathology
Alizarin red S stain identifies clumped calcium hydroxyapatite crystals which produce a “halo” of orange-red stain.
Radiographic features
Plain radiograph
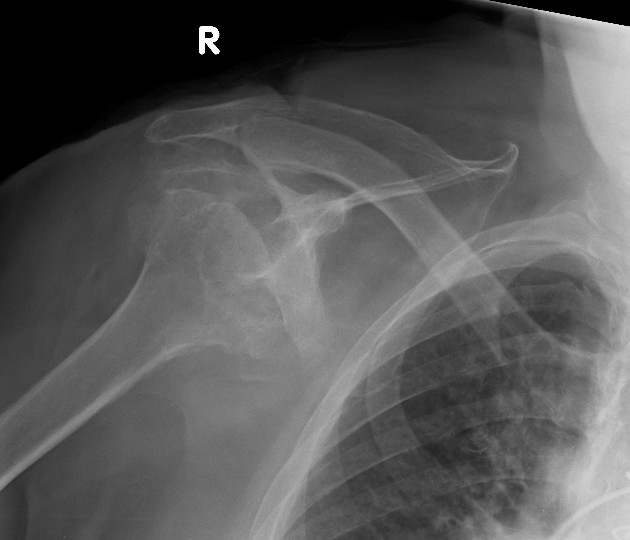
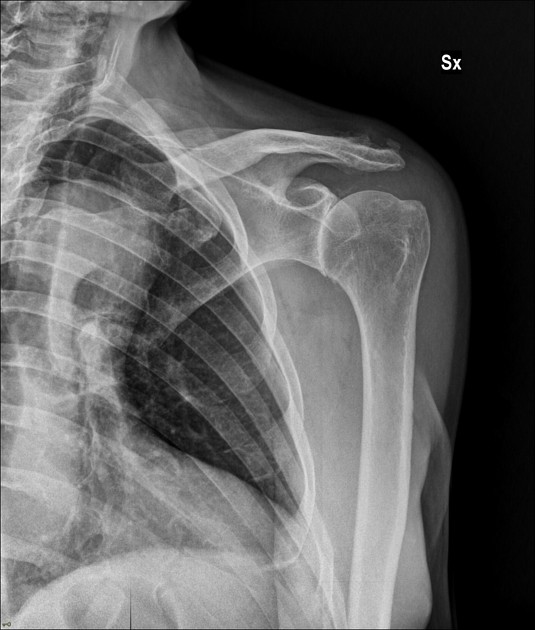
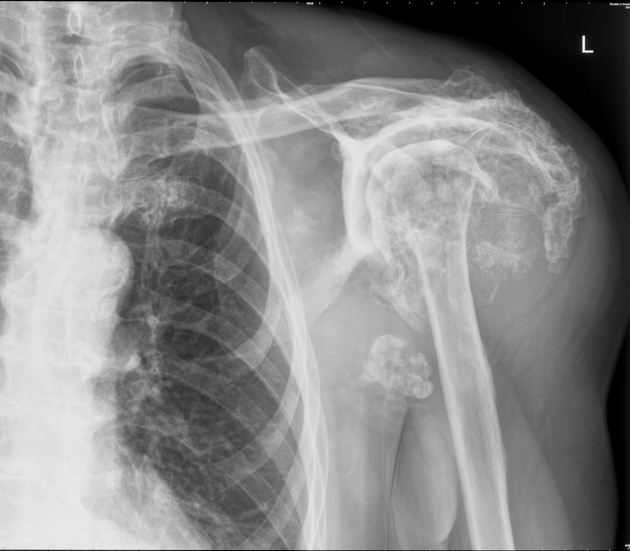
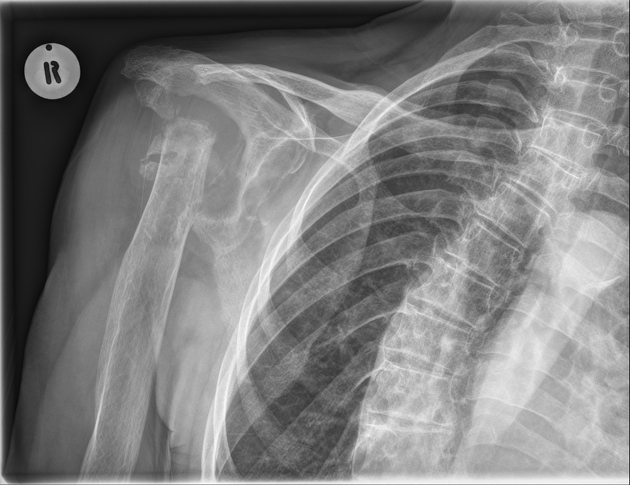
Radiographic findings are striking and resemble a neuropathic joint, with advanced articular surface destruction with intra-articular loose bodies, subchondral sclerosis, soft tissue swelling and rotator cuff disruption. Cases often demonstrate superior subluxation of the humeral head in relation to the glenoid fossa 4. The superior subluxation can also result in pseudoarthrosis with the distal clavicle and/or acromion 7.
MRI
MRI findings mirror those of the plain radiographs and include:
large shoulder joint effusion
complete rotator cuff tear
narrowing of the glenohumeral joint
thinning of cartilage
destruction of subchondral bone
Treatment and prognosis
No specific treatment is available, only supportive treatment for symptom relief 3.
History and etymology
Regius Professor of Surgery, Dr Robert Adams (1791-1875) was an Irish surgeon who first described this pathology in his own textbook published in 1857 5. In 1981, a group of Milwaukee-based researchers encountered four cases of rotator cuff loss, shoulder arthropathy and joint effusions containing calcium phosphate crystals and hence coined the term "Milwaukee shoulder" 6.
Differential diagnosis
General imaging differential considerations include:
-
advanced secondary osteoarthritis
previous trauma
previous septic arthritis





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.