Mucinous adenocarcinomas of the prostate or colloid adenocarcinomas of the prostate are a variant of acinar adenocarcinoma and characterized by mucinous features.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Mucinous adenocarcinomas of the prostate are rare and account for less than 0.5% of prostate cancers 1-4.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of mucinous adenocarcinomas of the prostate is based on typical histological features.
Clinical presentation
Clinical features of mucinous adenocarcinoma of the prostate are not different from conventional prostatic adenocarcinoma with most patients presenting with elevated prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels 1.
Pathology
Mucinous adenocarcinomas of the prostate are characterized by a mucinous extracellular stroma in more than one-fourth of the tumor that is not caused by a non-prostatic source e.g. a mucinous rectal tumor with prostatic invasion 1-5.
Mucinous carcinomas are assigned a Gleason grade based on the architectural pattern as other forms of prostate carcinoma 2.
Macroscopic appearance
The cut surface of mucinous prostatic adenocarcinomas has been described as gelatinous or opalescent 1.
Microscopic appearance
Microscopically mucinous prostatic adenocarcinomas by the following histological features 1:
- pools of mucin ranging from 25% to 90%
- cord-like, microglandular, tubular or cribriform growth patterns
- associated collagenous micronodules
- rarely signet ring cells
Immunophenotype
Mucinous adenocarcinomas usually express prostatic markers as the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) and prostate-specific acid phosphatase (PSAP) 1 and MUC2 2. Immunohistochemistry stains for CK7, CK20 or CDX2 tend to be negative otherwise another origin as urethral carcinoma or colonic adenocarcinoma should be favored 1.
Radiographic features
MRI
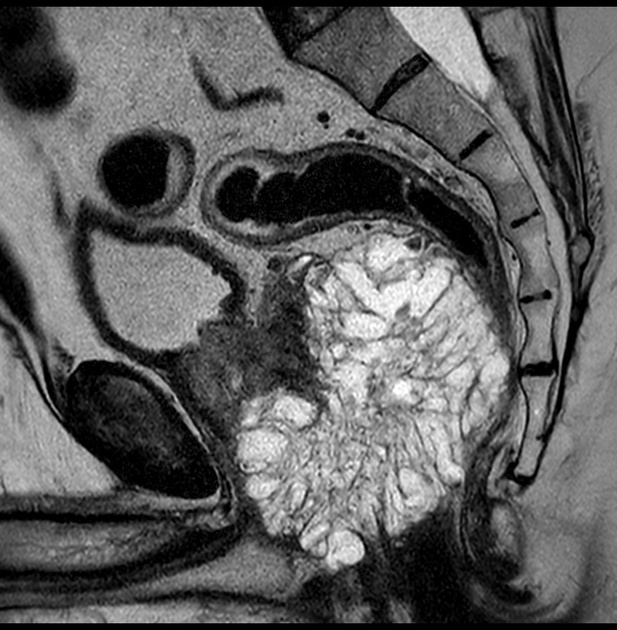
Due to the mucinous content mucinous adenocarcinomas of the prostate feature a different appearance on prostate MRI, which can aid in the diagnosis. They typically appear hyperintense in both T1w and T2w images and the high signal in T2w images might make it indistinguishable from the normal peripheral zone of the prostate and pose difficulties for their detection 3-6. Also different to typical adenocarcinoma, there might not be any diffusion restriction 3,6.
In addition, mucinous carcinomas do not seem to show any malignant metabolism on spectroscopy 4.
Signal characteristics
- T1: hyperintense
- T2: hyperintense
- DWI: might not show any diffusion restriction (hyperintense on b-1000, but isointense on ADC)
- DCE (Gd): early or late enhancement
Radiology report
The radiological report should include a description of the following:
- form, location and size
- tumor margins
- extraprostatic extension
- seminal vesicle invasion
- bladder or rectal invasion
- suspicious or enlarged lymph nodes
Treatment and prognosis
The prognosis of mucinous adenocarcinoma is considered to be comparable if not favorable to conventional adenocarcinoma even though it has been believed to be more aggressive in the past 1,3.
Radical prostatectomy seems to be associated with favorable outcomes 2,3. They also seem to respond to hormonal therapy.
Differential diagnosis
Conditions mimicking the imaging appearance of mucinous prostatic adenocarcinoma include 5:
- rhabdomyosarcoma of the prostate
- cystic prostatic hyperplasia
- cystadenoma
- prostatic abscess
- neuroendocrine tumors of the prostate




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.