Oligohydramnios
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Mohamed Refaey had no recorded disclosures.
View Mohamed Refaey's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Grace Carpenter had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Grace Carpenter's current disclosuresOligohydramnios refers to a situation where the amniotic fluid volume is less than expected for gestational age. Often these fetuses have <500 mL of amniotic fluid. When there is almost no amniotic fluid present, this is termed anhydramnios.
On this page:
Epidemiology
The estimated prevalence can be up to ~6% of pregnancies 4.
Associations
underlying fetal hypoxia and fetal cardiovascular compromise: from preferential flow to the fetal brain at the expense of diminished renal blood flow
-
twin pregnancy-related complications:
twin to twin transfusion syndrome: in pump twin
maternal dehydration
Pathology
Etiology
The causes of oligohydramnios are protean and one way to simplify them is by using the mnemonic DRIPPC:
-
D:
drugs: e.g. prostaglandin inhibitors (indomethacin)
-
R: renal abnormalities (from decreased urine output)
I: IUGR (intra-uterine growth restriction): 80% may occur from decreased renal perfusion due to sparing effect
-
P: premature rupture of membranes
P: post dates
-
C: chromosomal anomalies (especially if other anomalies are found)
Radiographic features
Ultrasound
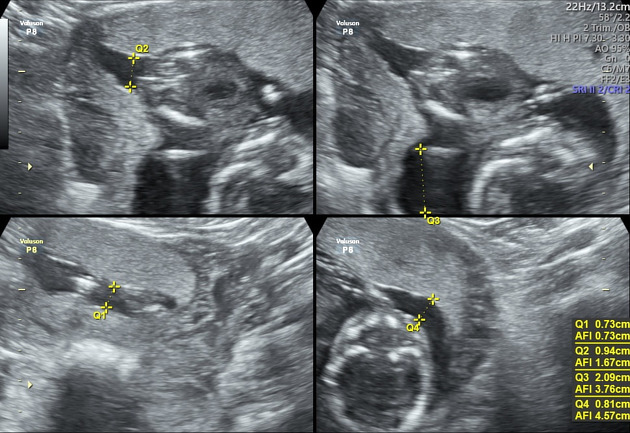
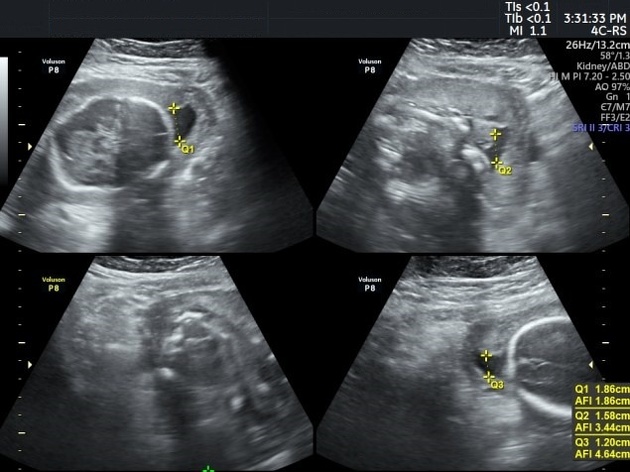
Several sonographic criteria can be used which include:
four quadrants amniotic fluid index (AFI): <5 cm
two diameter pocket method: <1 x 1 cm or <15 cm2
Treatment and prognosis
The development of oligohydramnios early in pregnancy is generally a poor prognostic marker. Amnio-infusion can be attempted in severe cases if appropriate.
Complications
-
first-trimester oligohydramnios can result in failure of pregnancy in up to 95% from complications such as
pulmonary hypoplasia: implies a very poor prognosis
See also
References
- 1. Ralph Weissleder, Jack Wittenberg, Mukesh G. Harisinghani. Primer of Diagnostic Imaging. (2003) ISBN: 0323023282 - Google Books
- 2. Sivit C, Hill M, Larsen J, Kent S, Lande I. The Sonographic Evaluation of Fetal Anomalies in Oligohydramnios Between 16 and 30 Weeks Gestation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1986;146(6):1277-81. doi:10.2214/ajr.146.6.1277 - Pubmed
- 3. Levine D, Goldstein R, Callen P, Damato N, Kilpatrick S. The Effect of Oligohydramnios on Detection of Fetal Anomalies with Sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997;168(6):1609-11. doi:10.2214/ajr.168.6.9168737 - Pubmed
- 4. Chauhan S, Taylor M, Shields D, Parker D, Scardo J, Magann E. Intrauterine Growth Restriction and Oligohydramnios Among High-Risk Patients. Amer J Perinatol. 2007;24(4):215-21. doi:10.1055/s-2007-972926 - Pubmed
- 5. Nabhan A & Abdelmoula Y. Amniotic Fluid Index Versus Single Deepest Vertical Pocket as a Screening Test for Preventing Adverse Pregnancy Outcome. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2008. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd006593.pub2
- 6. Johnson J, Chauhan S, Ennen C, Niederhauser A, Magann E. A Comparison of 3 Criteria of Oligohydramnios in Identifying Peripartum Complications: A Secondary Analysis. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 2007;197(2):207.e1-8. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2007.04.048 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Hypertensive states in pregnancy
- Preterm premature rupture of membranes
- Urethral agenesis
- Congenital limb amputation
- Meckel-Gruber syndrome
- Trisomy 22
- Placental insufficiency
- Wharton jelly
- Triploidy
- Fetal hydronephrosis
- Patau syndrome
- Amniotic fluid index
- Fetal megacystis
- Demise of a twin
- Pseudo-omphalocele
- Obstetric curriculum
- Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease
- In utero infection
- Polyhydramnios
- Umbilical arterial Doppler assessment
- Intrauterine fetal demise
- Uterine arteries flow notching
- Congenital high airways obstruction syndrome (CHAOS)
- Thalamomegaly - fetal
- Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease
- Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) - antenatal
- Inevitable miscarriage
- Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome
- Echogenic fetal kidneys and megacystis
- Asymmetrical intrauterine growth restriction with fetal distress
- Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease - antenatal
- Acardiac twin
- Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease - antenatal
- Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease - antenatal
- Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease - antenatal
- Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease associated with severe hydrocephalus
- Twin-twin transfusion syndrome - stage 1
- Fetal cardiac failure - acardiac twin - monochorial pregnancy
- Posterior urethral valve (antenatal ultrasound)
- Posterior urethral valve - antenatal ultrasound
Related articles: Pathology: Genitourinary
- obstetrics
-
first trimester
- ultrasound findings in early pregnancy
- embryo/fetus
- beta-hCG levels
- confirming intrauterine gestation
- pregnancy of unknown location (PUL)
- first trimester vaginal bleeding
- early structural scan
- aneuploidy testing
-
second trimester
- fetal biometry
- amniotic fluid volume
- fetal morphology assessment
- soft markers
- amnioreduction
- Doppler ultrasound
- nuchal translucency
- 11-13 weeks antenatal scan
- chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis
- other
- placenta
- placental anatomy
- placental developmental abnormalities
- placenta previa
- spectrum of abnormal placental villous adherence
- abnormalities of cord insertion
- abruptio placentae
- placental pathology
- vascular pathologies of placenta
- placental infections
- placental masses
- molar pregnancy
- twin placenta
- miscellaneous
-
first trimester
- gynecology
- acute pelvic pain
- chronic pelvic pain
- uterus
- ovaries
- ovarian follicle
- ovarian torsion
- pelvic inflammatory disease
- ovarian cysts and masses
- paraovarian cyst
- polycystic ovaries
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- post-hysterectomy ovary
- cervix
- fallopian tube
- other
- male genital tract
- prostate gland
- transrectal ultrasound
- prostate tumors
- infections of the prostate
-
prostatitis
- acute bacterial prostatitis
-
chronic prostatitis
- chronic bacterial prostatitis
- chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)
- asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
- granulomatous prostatitis
- emphysematous prostatitis
- prostatic abscess
-
prostatitis
- benign prostatic hypertrophy
- cystic lesions of the prostate
- prostatic calcification
- prostatic infarction
- testes
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- testicular torsion
- orchitis
- testicular trauma
-
germ cell tumors of the testis
- testicular seminoma
-
non seminomatous germ cell tumors
- mixed germ cell tumor
- yolk sac tumor (endodermal sinus tumor)
- embryonal cell carcinoma
- choriocarcinoma
- testicular teratoma
- testicular epidermoid (teratoma with ectodermal elements only)
- burned out testis tumor
- sex cord / stromal tumors of the testis
- testicular cyst
- testicular lymphoma
- bilateral testicular lesion
- paratesticular lesions
- epididymis
- other
- polyorchidism
- cryptorchidism
- tubular ectasia of the rete testis
- cystadenoma of the rete testis
- testicular sarcoidosis
- testicular tuberculosis
- spermatic cord
- fibrous pseudotumor of the scrotum
- scrotal leiomyosarcoma
- testicular adrenal rest tumors (TARTs)
- tunica vaginalis testis mesothelioma
- splenogonadal fusion
- testicular vasculitis
- abnormal testicular Doppler flow (differential)
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- penis
- prostate gland
- KUB
- kidneys
- normal renal anatomy
- hydronephrosis
- urolithiasis
- renal masses
- renal cystic disease
- renal infection
- vascular
- trauma
- ureter
- normal ureter anatomy
- ureteral stricture
- ureteral dilatation
- ureteral anomalies
- ureteral tumors
- ureteral trauma
- other
- bladder
- kidneys







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.