Disclosures
- updated 15 Jul 2022:
Nothing to disclose
Updates to Article Attributes
Oligohydramnios refers to a situation where the amniotic fluid volume is less than expected for gestational age. Often these fetuses have <500 mL of amniotic fluid. When there is almost no amniotic fluid present, this is termed anhydramnios.
Epidemiology
The estimated prevalence can be up to ~6% of pregnancies 4.
Associations
Pathology
Aetiology
The causes of oligohydramnios are protean and one way to simplify them is by using the mnemonic DRIPPC:
Associations
Radiographic features
Antenatal ultrasound
Several sonographic criteria can be used which include:
Treatment and prognosis
The development of oligohydramnios early in pregnancy is generally a poor prognostic marker. Amnio-infusion can be attempted in severe cases if appropriate.
Complications
See also
-<p><strong>Oligohydramnios</strong> refers to a situation where the <a href="/articles/amniotic-fluid-volume">amniotic fluid volume</a> is less than expected for gestational age. Often these fetuses have <500 mL of amniotic fluid.</p><h4>Epidemiology</h4><p>The estimated prevalence can be up to ~6% of pregnancies <sup>4</sup>.</p><h4>Pathology</h4><h5>Aetiology</h5><p>The causes of oligohydramnios are protean and one way to simplify them is by using the mnemonic <a href="/articles/causes-of-oligohydramnios-mnemonic-1">DRIPPC</a>:</p><ul>-<li>-<strong>D:</strong><ul>-<li><a href="/articles/fetal-death-in-utero-1">demise</a></li>-<li>drugs: e.g. prostaglandin inhibitors (indometacin)</li>- +<p><strong>Oligohydramnios</strong> refers to a situation where the <a href="/articles/amniotic-fluid-volume">amniotic fluid volume</a> is less than expected for gestational age. Often these fetuses have <500 mL of amniotic fluid. When there is almost no amniotic fluid present, this is termed <a href="/articles/anhydramnios" title="Anhydramnios">anhydramnios</a>.</p><h4>Epidemiology</h4><p>The estimated prevalence can be up to ~6% of pregnancies <sup>4</sup>.</p><h5>Associations</h5><ul>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/potter-sequence">Potter sequence</a></p></li>
- +<li><p>underlying <a href="/articles/fetal-hypoxia">fetal hypoxia</a> and<a href="/articles/fetal-cardiovascular-compromise"> fetal cardiovascular compromise</a>: from preferential flow to the fetal brain at the expense of diminished renal blood flow</p></li>
- +<li>
- +<p>twin pregnancy-related complications: </p>
- +<ul><li><p><a href="/articles/twin-to-twin-transfusion-syndrome-1">twin to twin transfusion syndrome</a>: in pump twin </p></li></ul>
- +</li>
- +<li><p>maternal dehydration</p></li>
- +</ul><h4>Pathology</h4><h5>Aetiology</h5><p>The causes of oligohydramnios are protean and one way to simplify them is by using the mnemonic <a href="/articles/causes-of-oligohydramnios-mnemonic-1">DRIPPC</a>:</p><ul>
- +<li>
- +<p><strong>D:</strong></p>
- +<ul>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/fetal-death-in-utero-1">demise</a></p></li>
- +<li><p>drugs: e.g. prostaglandin inhibitors (indometacin)</p></li>
-<strong>R: </strong>renal abnormalities (from decreased urine output)<ul>-<li><a href="/articles/renal-agenesis">renal agenesis</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/renal-dysgenesis">renal dysplasia</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/posterior-urethral-valves">posterior urethral valves</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/polycystic-kidneys">polycystic kidneys</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/multicystic-dysplastic-kidney">multicystic dysplastic kidney (MCDK)</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/urethral-atresia">urethral atresia</a></li>- +<p><strong>R: </strong>renal abnormalities (from decreased urine output)</p>
- +<ul>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/renal-agenesis">renal agenesis</a></p></li>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/renal-dysgenesis">renal dysplasia</a></p></li>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/posterior-urethral-valves">posterior urethral valves</a></p></li>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/polycystic-kidneys">polycystic kidneys</a></p></li>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/multicystic-dysplastic-kidney">multicystic dysplastic kidney (MCDK)</a></p></li>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/urethral-atresia">urethral atresia</a></p></li>
- +<li><p><strong>I:</strong> IUGR (<a href="/articles/intrauterine-growth-restriction">intra-uterine growth restriction</a>): 80% may occur from decreased renal perfusion due to sparing effect</p></li>
-<strong>I:</strong> IUGR (<a href="/articles/intrauterine-growth-restriction">intra-uterine growth restriction</a>): 80% may occur from decreased renal perfusion due to sparing effect</li>-<li>-<strong>P:</strong> premature rupture of membranes<ul>-<li><a href="/articles/premature-rupture-of-membranes-prom">premature rupture of membranes (PROM)</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/pre-term-premature-rupture-of-membranes-pprom">preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM)</a></li>- +<p><strong>P:</strong> premature rupture of membranes</p>
- +<ul>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/premature-rupture-of-membranes-prom">premature rupture of membranes (PROM)</a></p></li>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/pre-term-premature-rupture-of-membranes-pprom">preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM)</a></p></li>
- +<li><p><strong>P: </strong><a href="/articles/post-dates-fetus">post dates</a></p></li>
-<strong>P: </strong><a href="/articles/post-dates-fetus">post dates</a>-</li>-<li>-<strong>C: </strong><a href="/articles/chromosomal-anomalies">chromosomal anomalies</a> (especially if other anomalies are found)<ul>-<li><a href="/articles/edwards-syndrome-1">trisomy 18</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/patau-syndrome">trisomy 13</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/triploidy">triploidy</a></li>- +<p><strong>C: </strong><a href="/articles/chromosomal-anomalies">chromosomal anomalies</a> (especially if other anomalies are found)</p>
- +<ul>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/edwards-syndrome-1">trisomy 18</a></p></li>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/patau-syndrome">trisomy 13</a></p></li>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/triploidy">triploidy</a></p></li>
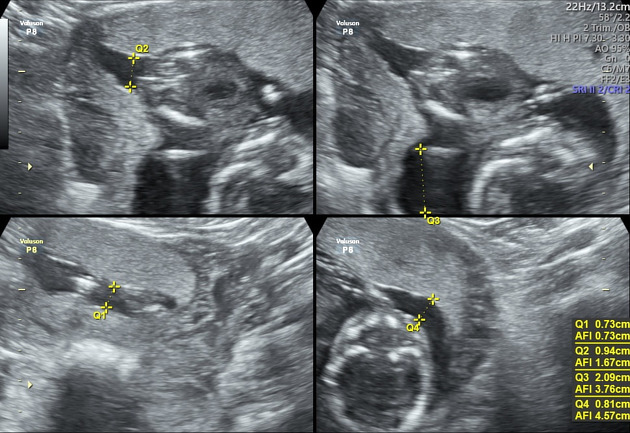
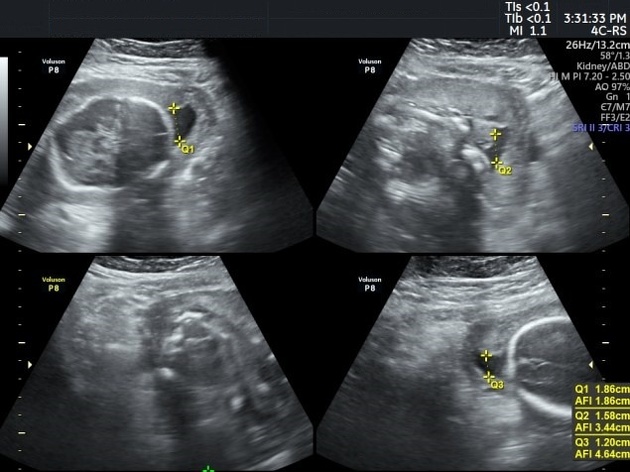
-</ul><h5>Associations</h5><ul>-<li><a href="/articles/potter-sequence">Potter sequence</a></li>-<li>underlying <a href="/articles/fetal-hypoxia">fetal hypoxia</a> and<a href="/articles/fetal-cardiovascular-compromise"> fetal cardiovascular compromise</a>: from preferential flow to the fetal brain at the expense of diminished renal blood flow</li>-<li>twin pregnancy-related complications: <ul><li>-<a href="/articles/twin-to-twin-transfusion-syndrome-1">twin to twin transfusion syndrome</a>: in pump twin </li></ul>-</li>-<li>maternal dehydration </li>-<li>four quadrants <a href="/articles/amniotic-fluid-index">amniotic fluid index</a> (AFI): <5 cm</li>-<li>-<a href="/articles/two-diameter-pocket-method">two diameter pocket method</a>: <1 x 1 cm or <15 cm<sup>2</sup>-</li>-<li>-<a href="/articles/deepest-vertical-pocket-method">maximum vertical pocket depth</a>: <2 cm</li>-</ul><h4>Treatment and prognosis</h4><p>The development of oligohydramnios early in pregnancy is generally a poor prognostic marker. <a href="/articles/amnio-infusion">Amnio-infusion</a> can be attempted in severe cases if appropriate.</p><h4>Complications</h4><ul><li>first-trimester oligohydramnios can result in failure of pregnancy in up to 95% from complications such as<ul>-<li>-<a href="/articles/pulmonary-hypoplasia">pulmonary hypoplasia</a>: implies a very poor prognosis</li>-<li><a href="/articles/fetal-limb-contractures">fetal limb contractures</a></li>- +<li><p>four quadrants <a href="/articles/amniotic-fluid-index">amniotic fluid index</a> (AFI): <5 cm</p></li>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/two-diameter-pocket-method">two diameter pocket method</a>: <1 x 1 cm or <15 cm<sup>2</sup></p></li>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/deepest-vertical-pocket-method">maximum vertical pocket depth</a>: <2 cm</p></li>
- +</ul><h4>Treatment and prognosis</h4><p>The development of oligohydramnios early in pregnancy is generally a poor prognostic marker. <a href="/articles/amnio-infusion">Amnio-infusion</a> can be attempted in severe cases if appropriate.</p><h5>Complications</h5><ul><li>
- +<p>first-trimester oligohydramnios can result in failure of pregnancy in up to 95% from complications such as</p>
- +<ul>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/pulmonary-hypoplasia">pulmonary hypoplasia</a>: implies a very poor prognosis</p></li>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/fetal-limb-contractures">fetal limb contractures</a></p></li>
-<li><a href="/articles/polyhydramnios">polyhydramnios</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/anhydramnios">anhydramnios</a></li>- +<li><p><a href="/articles/polyhydramnios">polyhydramnios</a></p></li>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/anhydramnios">anhydramnios</a></p></li>
Image
1
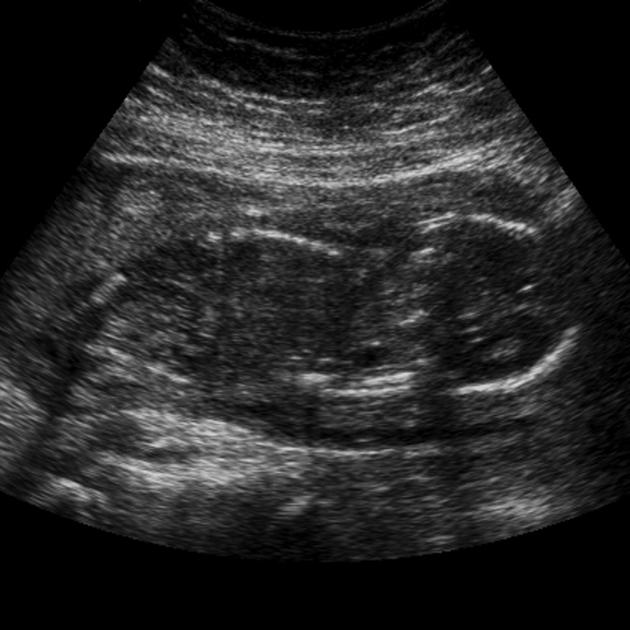
Ultrasound (Longitudinal)
(
update
)
Image
2
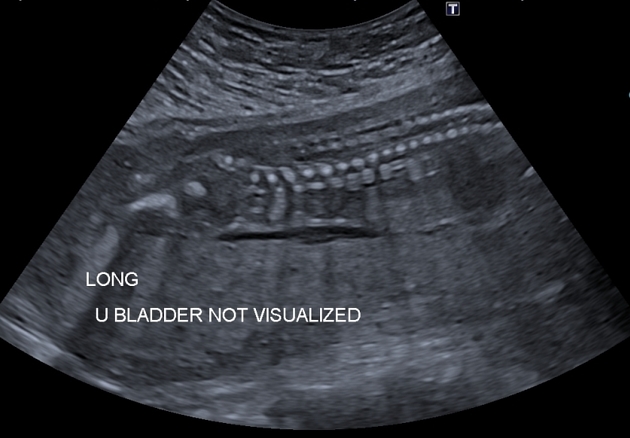
Ultrasound
(
update
)
Image
3
Ultrasound
(
update
)
Image
4
Ultrasound
(
update
)
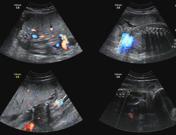
Caption
was changed:
OligohydramniosCase 4: with autosomal recessive polycystic kidney diseaseARPKD
Image
5
Ultrasound
(
update
)
Image
6
Ultrasound (Longitudinal)
(
update
)
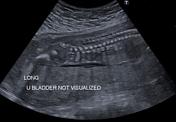
Caption
was changed:
With ARPCKDCase 6: with ARPKD
Image
7
Ultrasound
(
update
)
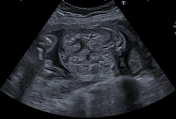
Caption
was changed:
With ARPCKDCase 7: with ARPKD
Image
8
Ultrasound
(
update
)
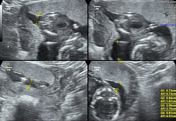
Caption
was changed:
WithCase 8: with megacystis
Image
9
Ultrasound
(
update
)
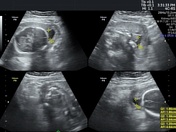
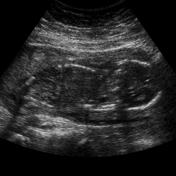
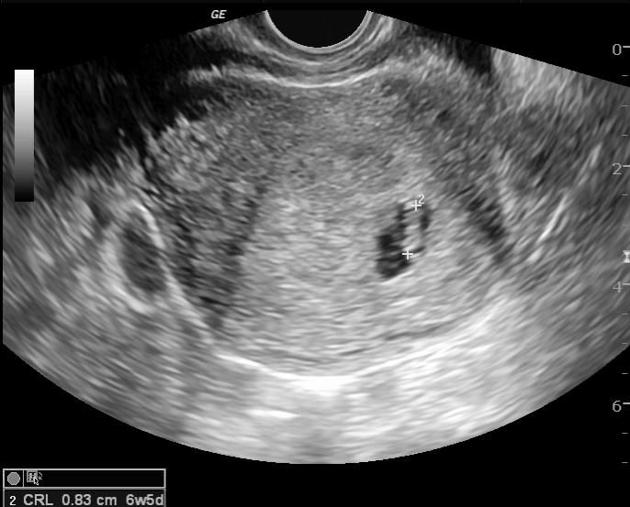
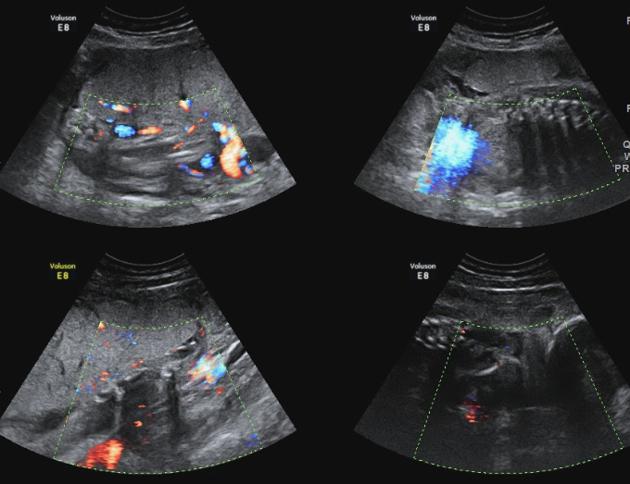
Caption
was changed:
With asymmetrical intrauterine growth restrictionCase 9: with asymmetric IUGR















 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.