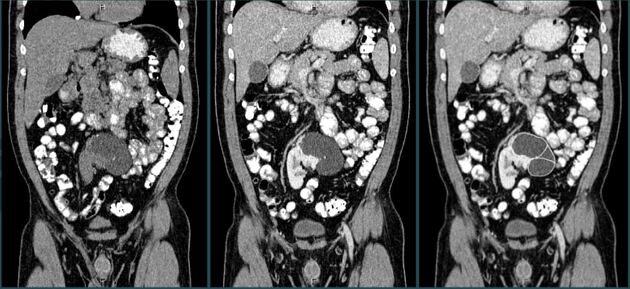
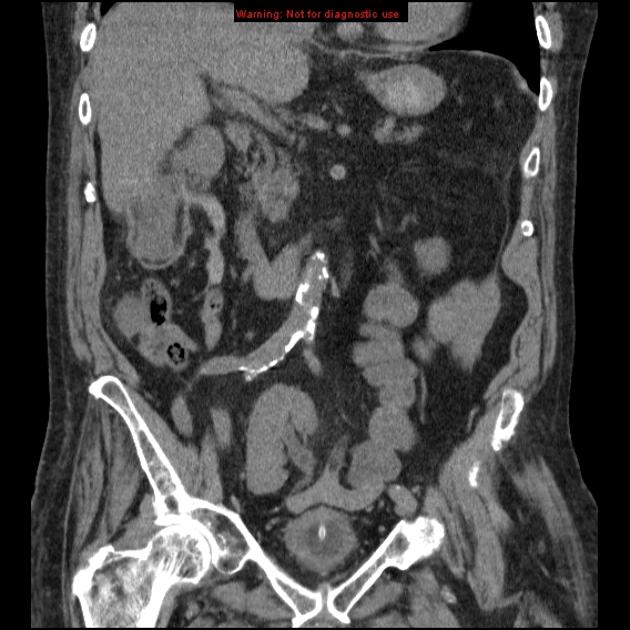
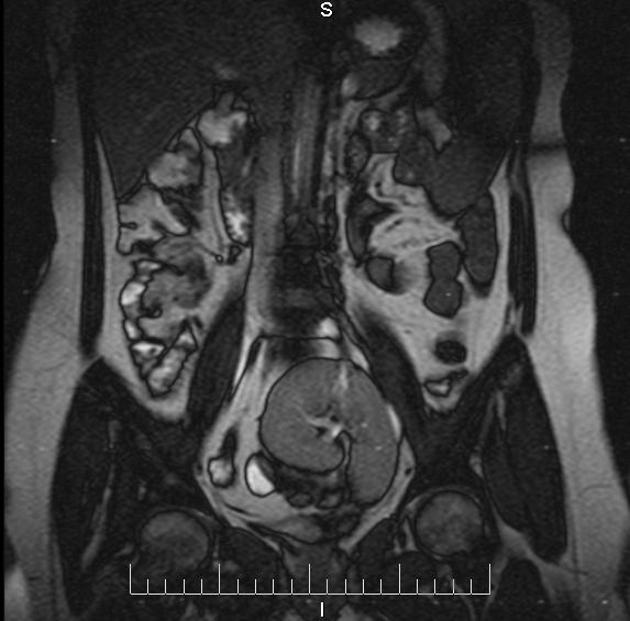
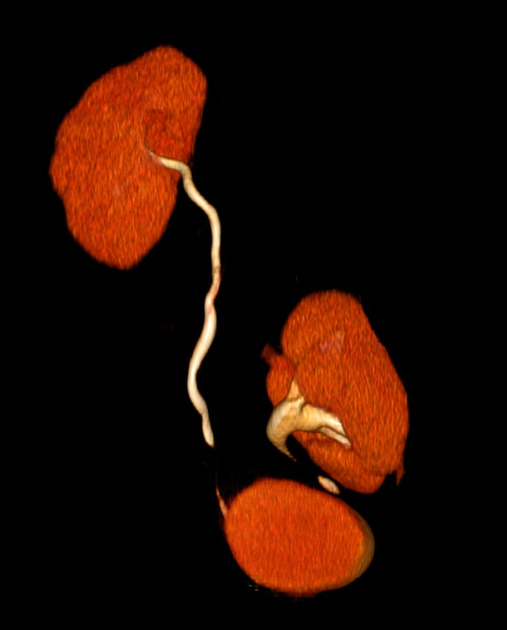
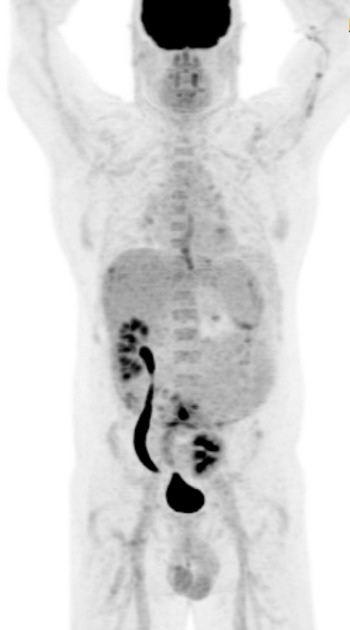
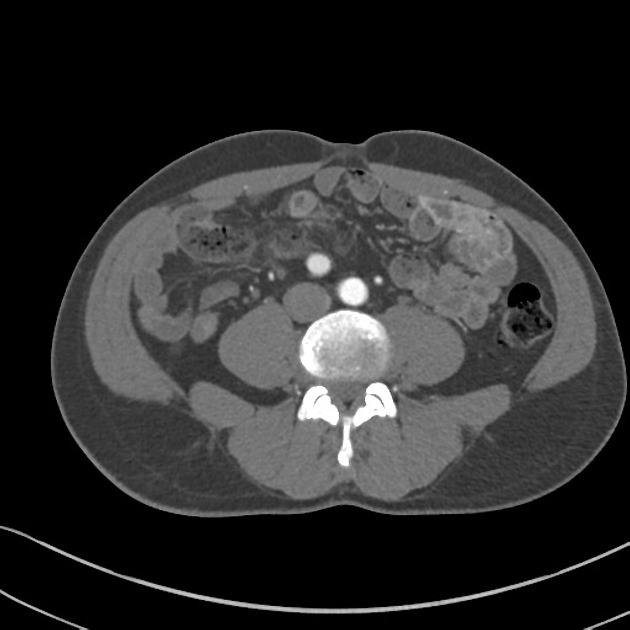
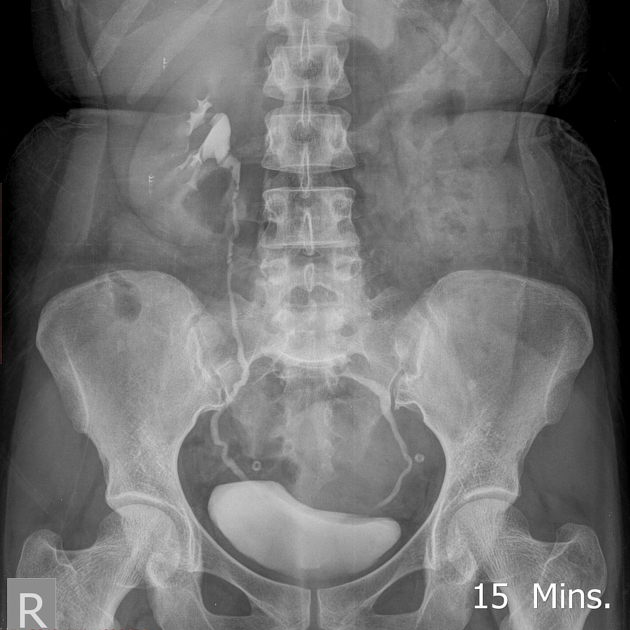
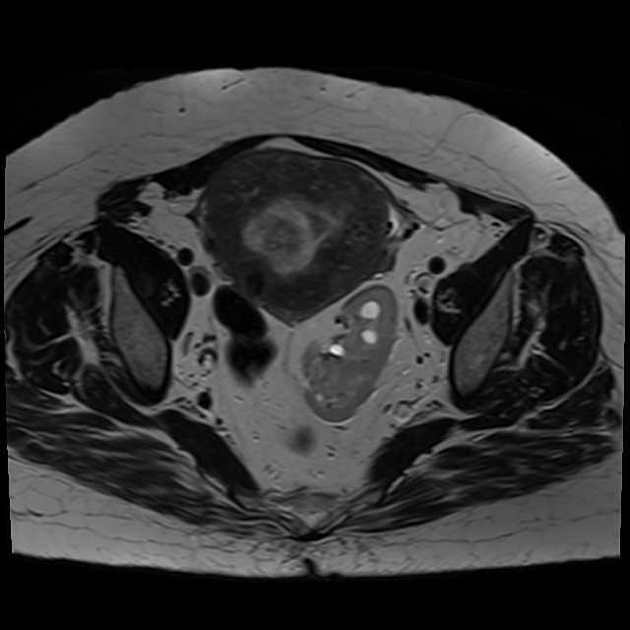
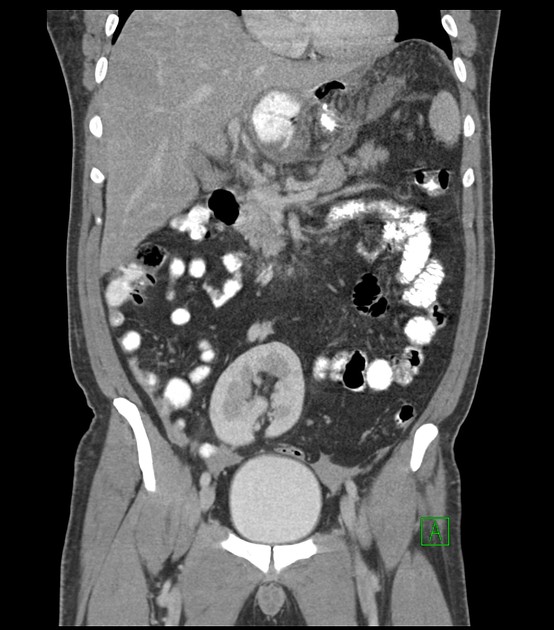
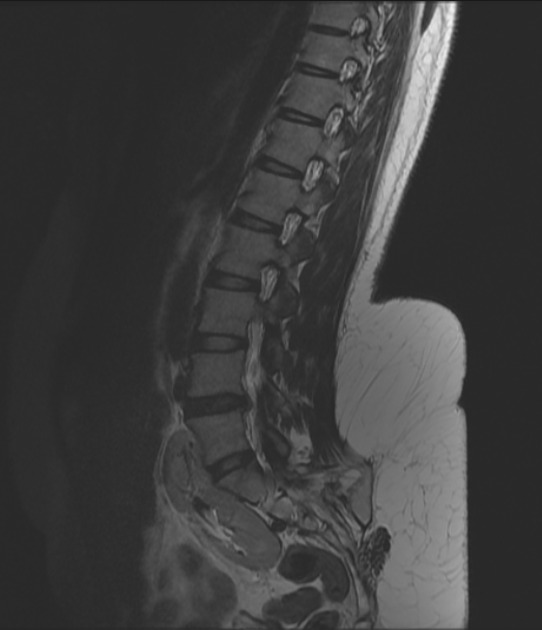
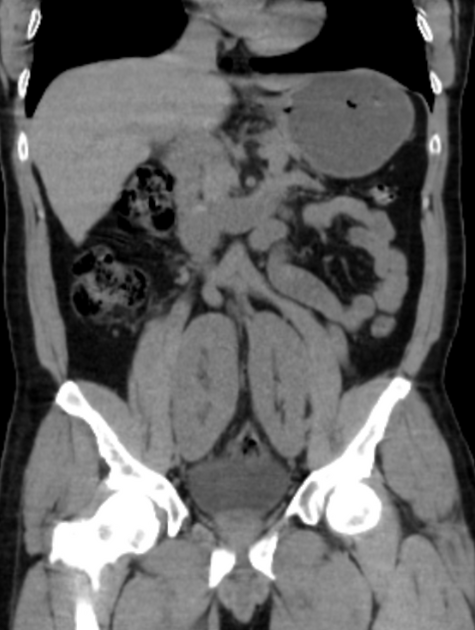
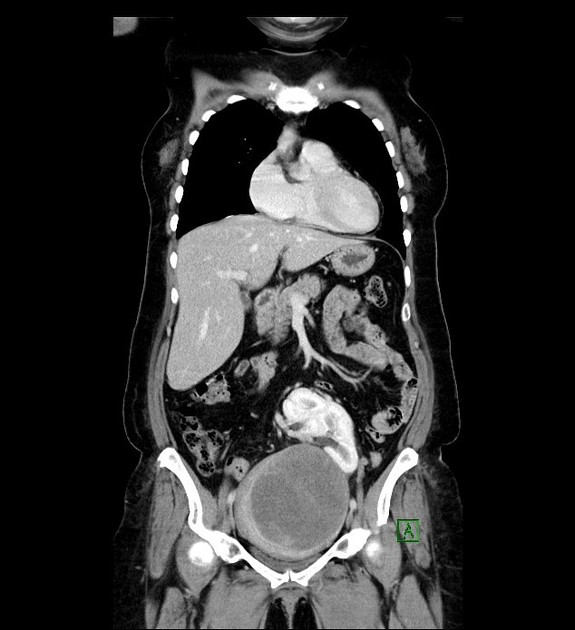
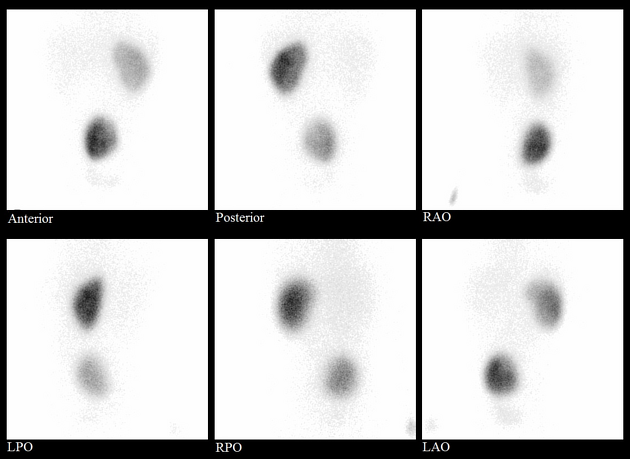
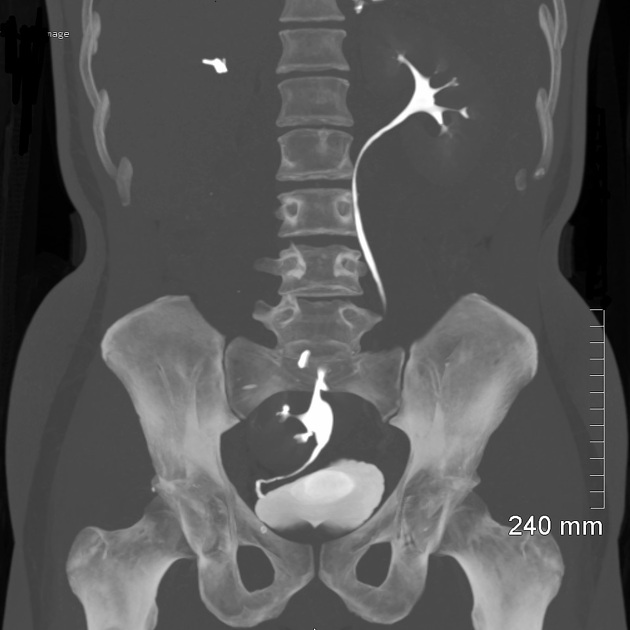
Pelvic kidney
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Avni K P Skandhan had no recorded disclosures.
View Avni K P Skandhan's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Mohammad Taghi Niknejad had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Mohammad Taghi Niknejad's current disclosures- Pelvic ectopic kidney
- Pelvic kidneys
- Pelvic ectopic kidneys
- Sacral kidneys
- Sacral kidney
Pelvic kidneys, sometimes known as a sacral kidney, are kidneys that are fixed in the bony pelvis or across the spine and are an anatomic variant 1.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Pelvic ectopia is seen in 1 in 2,100-3,000 autopsies. It is considered the most common form of renal ectopia 4.
Associations
Ectopic kidneys are often associated with other abnormalities such as agenesis of the opposite kidney, vascular malformations and genital anomalies.
Other uncommon associations include:
Clinical presentation
These patients tend to be asymptomatic and often the diagnosis is incidental on an imaging test performed for a reason unrelated to the renal tract.
Renal tract pathology (e.g., infection, calculus) can affect pelvic kidneys; thus, the referred pain is not typical for the renal tract and may be confused for other abdominopelvic pathology, e.g., appendicitis or pelvic inflammatory disease.
Other signs and symptoms of ectopic kidneys include:
incontinence
palpable abdominal or pelvic mass
renovascular hypertension secondary to an anomalous blood supply (from the iliac (common/external/iliac) arteries)
dystocia from a pelvic kidney
Gross anatomy
The vascular supply of pelvic kidneys is highly variable, mainly because they retain their fetal blood supply. Single, dual and triple supply have been reported originating from the aortic bifurcation, the common iliac and the internal iliac arteries 5.
Differential diagnosis
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Thomas G, BARTON JC. Ectopic pelvic kidney. JAMA. 1936;106(3):197-201
- 2. Kakitsubata Y, Kakitsubata S, Watanabe K, Natsuda Y, Miyanaga I. Pelvic Kidney Associated with Other Congenital Anomalies: US and CT Manifestations. Radiat Med. 1993;11(3):107-9. - Pubmed
- 3. William E. Erkonen, Wilbur L. Smith. Radiology 101. (2005) ISBN: 9780781751988 - Google Books
- 4. Zoran L. Barbaric. Principles of Genitourinary Radiology. (1991) ISBN: 9780865773479 - Google Books
- 5. Eid S, Iwanaga J, Loukas M, Oskouian R, Tubbs R. Pelvic Kidney: A Review of the Literature. Cureus. 2018;10(6):e2775. doi:10.7759/cureus.2775 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Zinner syndrome
- Ureteroinguinal hernia
- Pelvic kidney with obstructing ureteric calculus
- Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma
- Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser syndrome
- Pelvic kidney
- Bilateral pelvic kidneys
- Gallbladder dysfunction
- Bilateral pelvic kidneys with PUJ obstruction, fusion and right-sided duplex system
- Ectopic pregnancy
- COVID-19 induced mesenteric venous infarction with small bowel obstruction
- Bilateral pelvic kidneys with fusion and malrotation
- Lying down adrenal sign
- Ovarian torsion - Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser Syndrome
- Leiomyosarcoma of the uterus
- Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser syndrome
- Pelvic kidney
- Pelvic kidney with ureterocele
- Uterine adenomyosis with incidental pelvic kidney
- Ectopic pelvic kidney
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- celiac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses








 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.