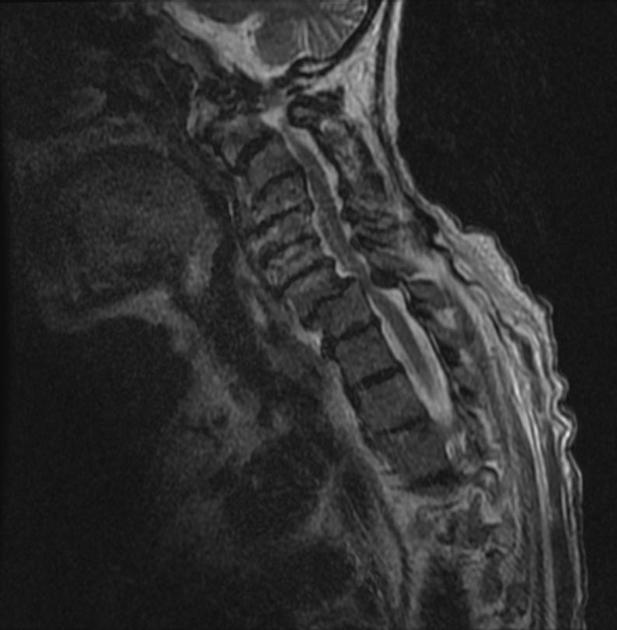
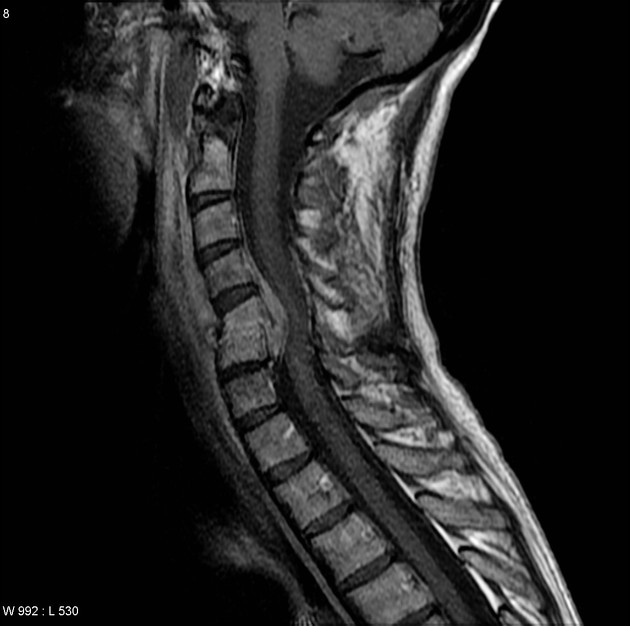
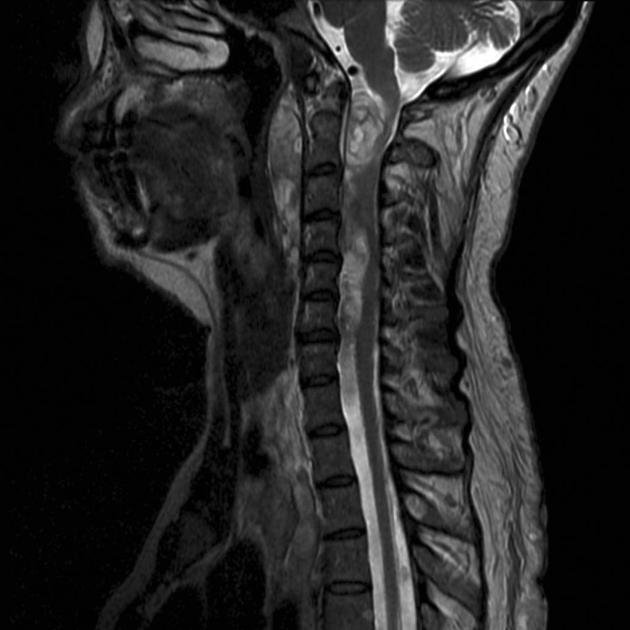
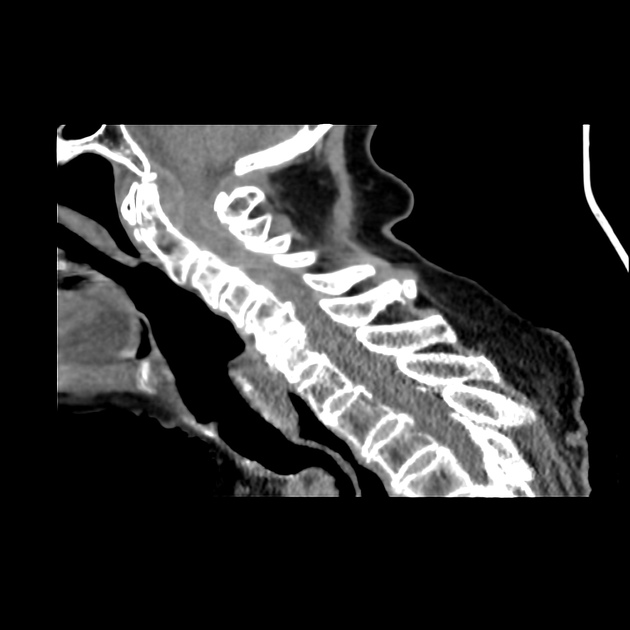
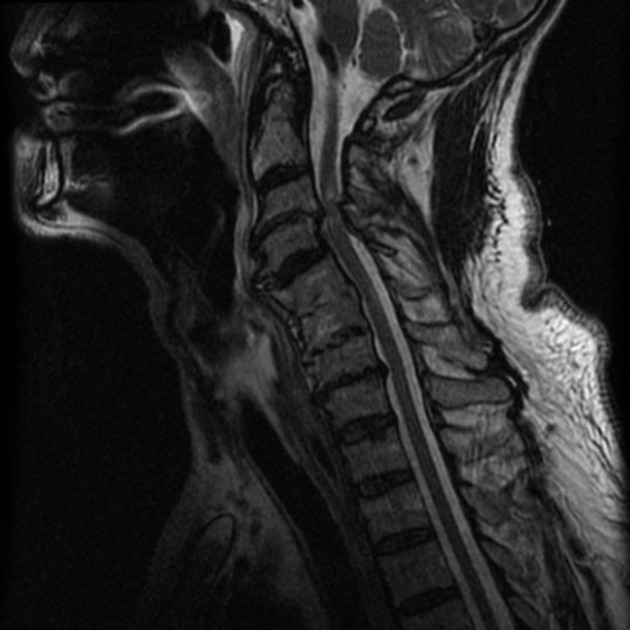
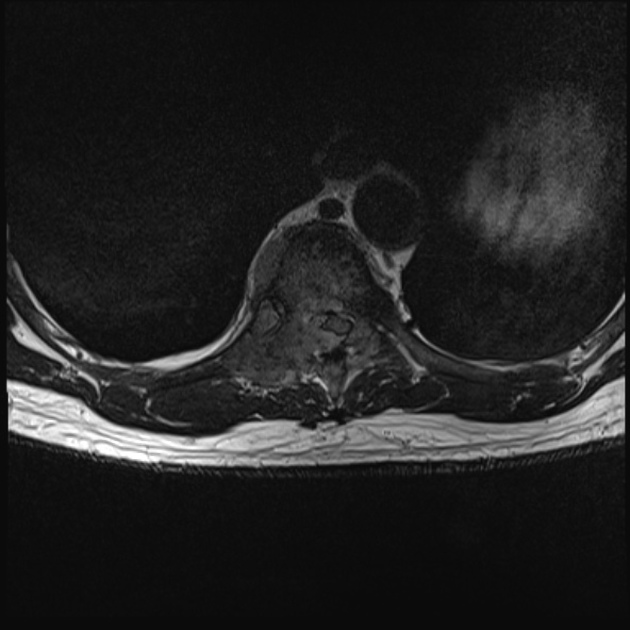
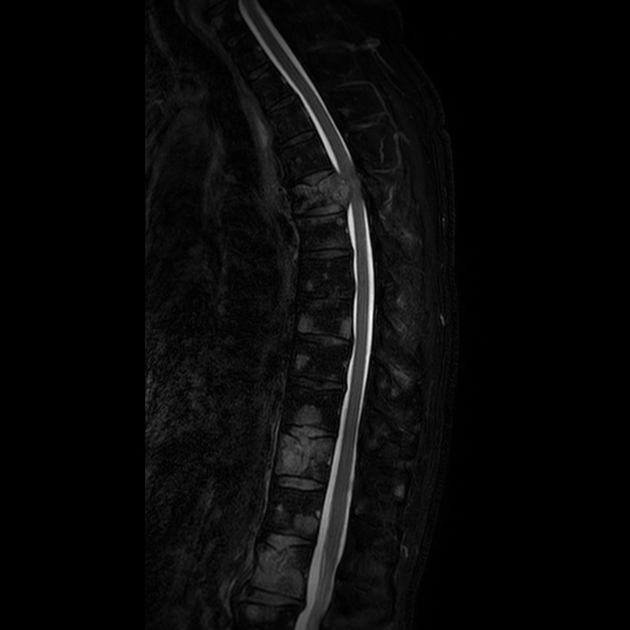
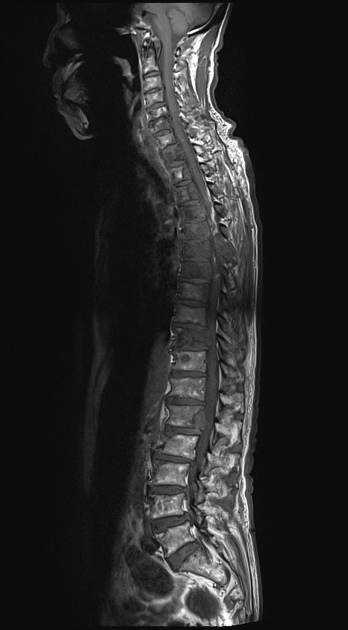
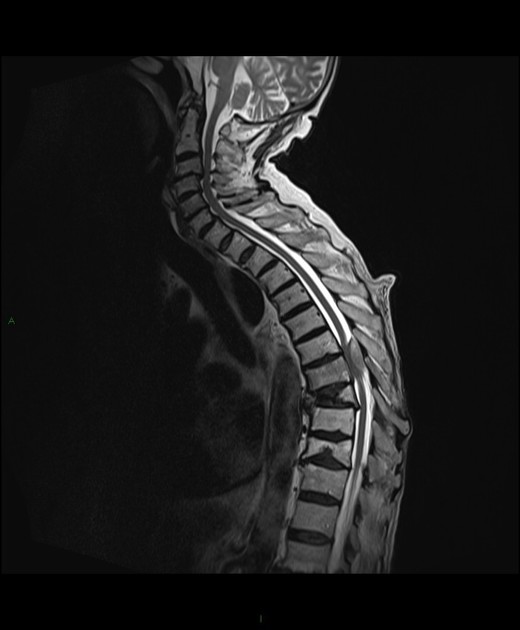
Spinal cord compression (SCC) is a surgical emergency, usually requiring prompt surgical decompression to prevent permanent neurological impairment. If the spinal roots below the conus medullaris are involved, and there are characteristic symptoms and signs, it is termed cauda equina syndrome.
Pathology
Etiology
There are numerous causes of cord compression. These can be divided according to the location of the compressing mass:
-
discitis osteomyelitis (usually associated with an epidural abscess)
degenerative anterolisthesis/spondylosis
-
vertebral
-
trauma
vertebral fracture (e.g. burst fracture)
fracture-dislocation
-
tumor
iatrogenic
cement leakage following vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty
-
-
epidural space
-
dura
-
intradural space
Lesions of the cord itself can present in a similar manner to extrinsic cord compression but are usually considered separately (e.g. spinal cord tumors, spinal cord abscess).








 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.