Tumor pseudoresponse, also known just as pseudoresponse, refers to the phenomenon of tumors appearing to respond to a specific treatment on imaging criteria when the lesion actually remains stable or has even progressed.
On this page:
Images:
Terminology
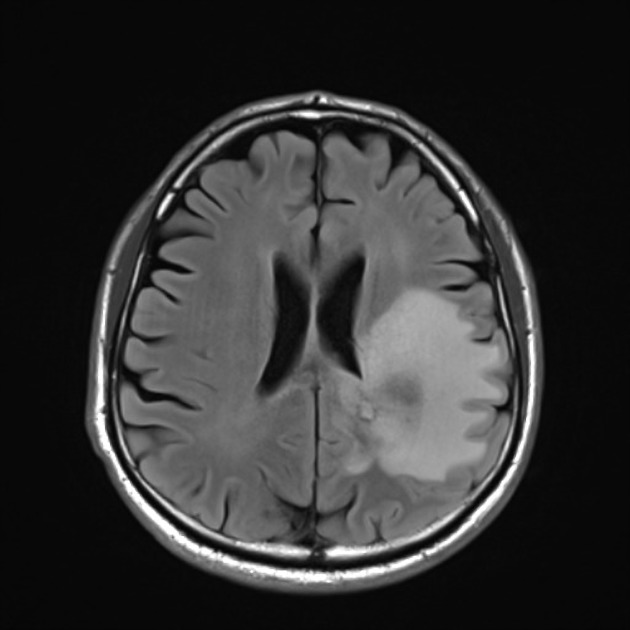
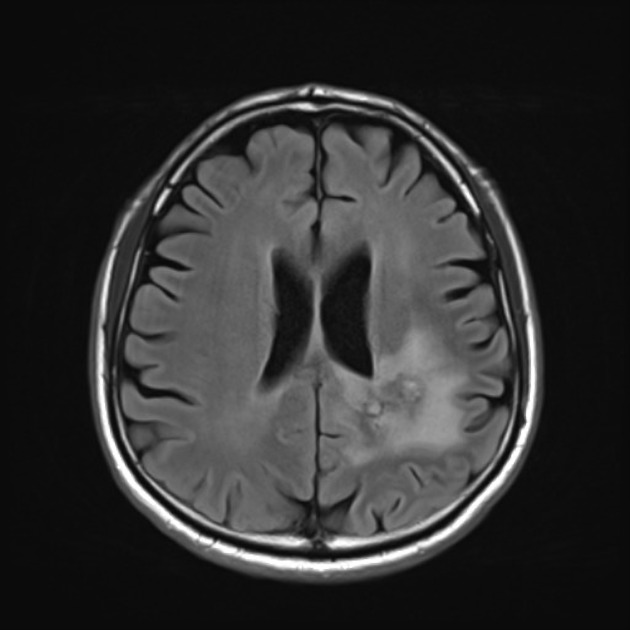
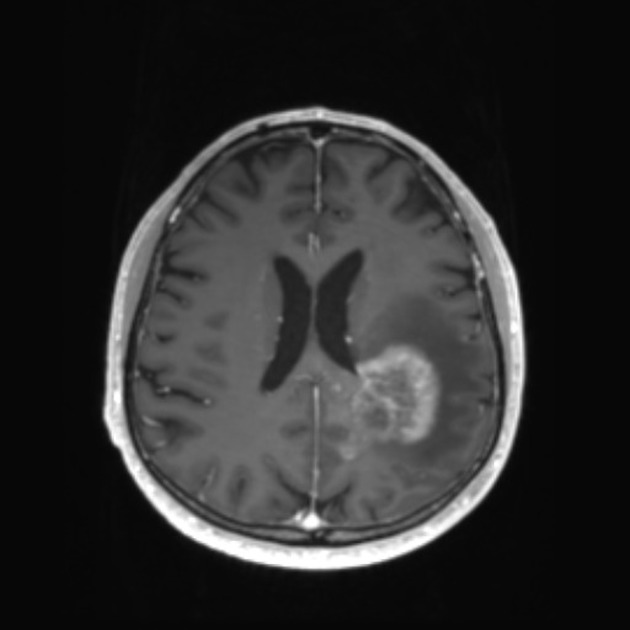
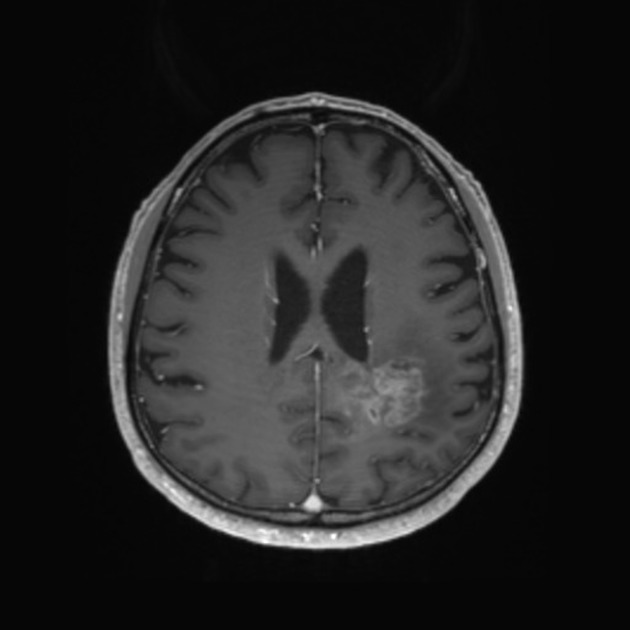
The term is largely used for brain tumors during imaging follow-up, especially for high-grade gliomas (e.g. glioblastoma) in which a rapid decrease in contrast enhancement and edema can be observed in a short period of time after administration of antiangiogenic agents (e.g, bevacizumab and cediranib), often without any significant change in actual tumor size (as visualized on non-contrast sequences) or diffusion/perfusion studies 1-3.
Pathology
Bevacizumab (trade name Avastin), for example, is an inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), aimed at inhibiting the formation of new blood vessels within the tumor (neoangiogenesis). VEGF is produced by the tumors, and not only promotes neoangiogenesis but also reduces the effectiveness of gap junctions and creates fenestrations in the endothelium of existing brain capillaries, leading to edema and enhancement 4. The amount of VEGF produced has been shown to correlate with tumor grade.
The changes seen in pseudoresponse (rapid reduction in enhancement and vasogenic edema) are largely mediated by changes in blood-brain barrier permeability rather than antiangiogenic effects.
Radiographic features
MRI
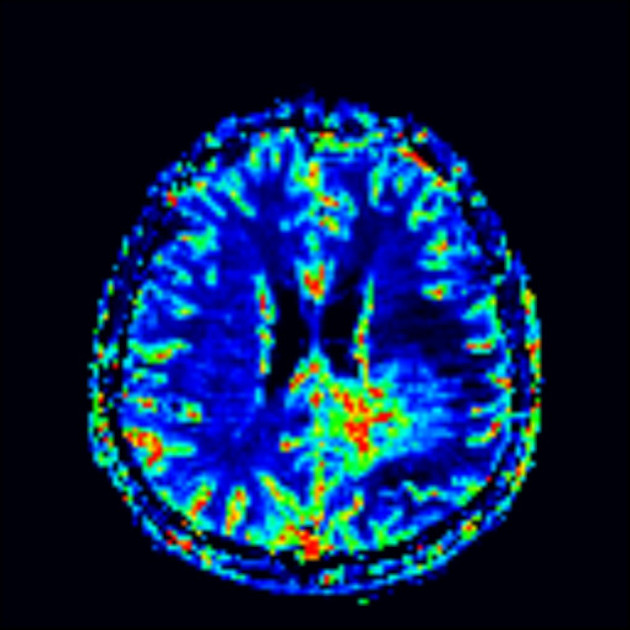
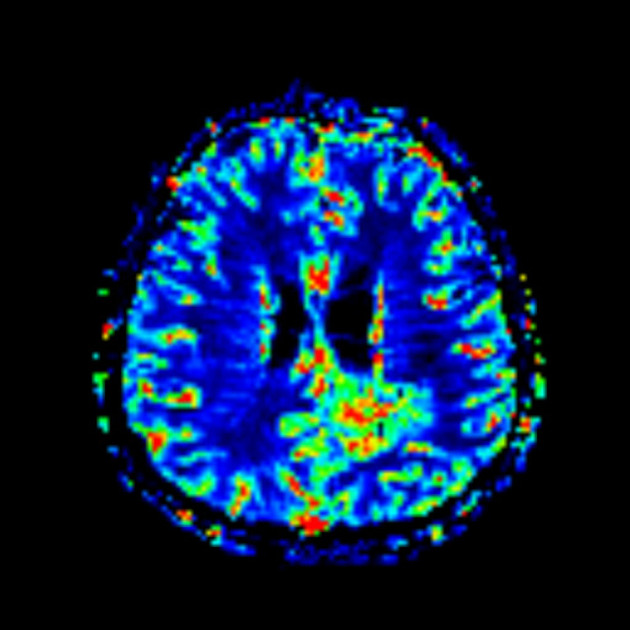
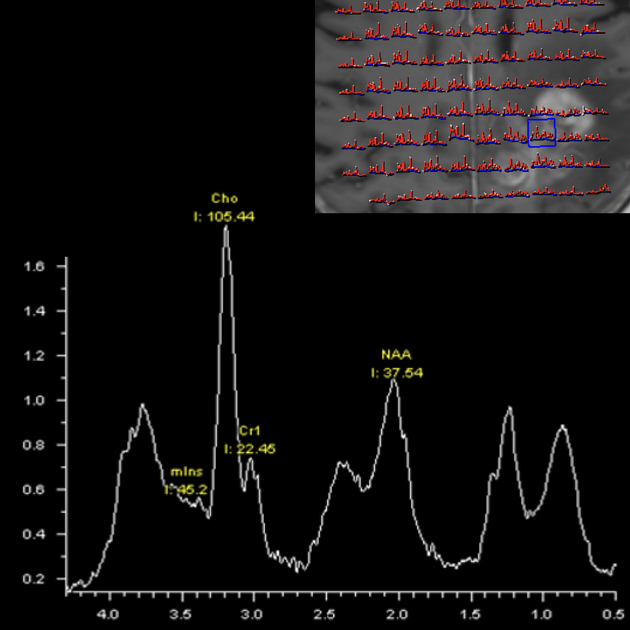
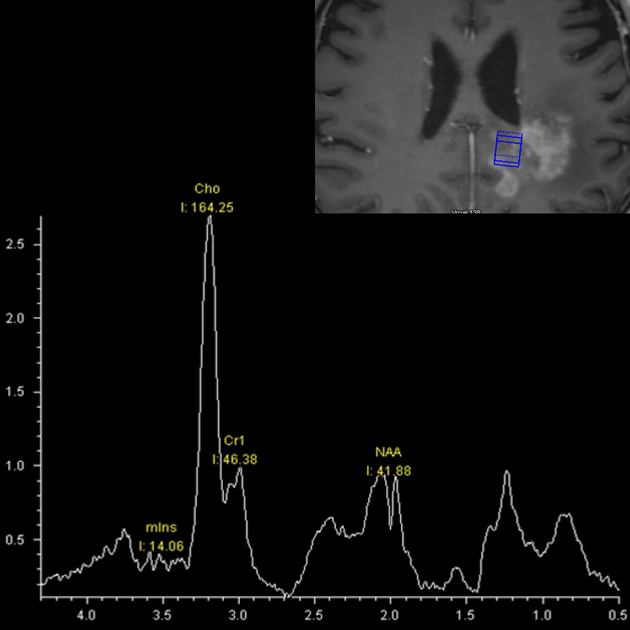
MRI is the modality of choice for the routine follow-up of gliomas. MR spectroscopy, MR perfusion (particularly cerebral blood volume) and diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) are particularly important in this setting to assess for the presence of residual viable, but now non-enhancing, tumor, as relying on enhancement and T2 signal change can be misleading due to the aforementioned changes in blood-brain barrier permeability 4.
Essential to correct interpretation is the availability of multiple previous imaging studies and information relating to the type and timing of therapy.
Typical features of pseudoresponse when compared to pre-treatment scans:
reduction in vasogenic edema
reduction in enhancement
persistent low ADC values
persistent tumor trace
persistent elevation of rCBV
Despite the fact that these advanced MRI sequences have helped in differentiating pseudoresponse from a true response, imaging follow-up is still required 1.
Coagulative necrosis
In a small percentage of patients treated with bevacizumab, areas of the tumor will undergo coagulative necrosis and appear bright on DWI and profoundly dark on ADC with or without surrounding enhancement. The significance of this finding, that can be mistaken for infarction or hypercellular tumor, depends on whether this area of diffusion restriction remains stable or increases in size. In the former it is a relatively good prognostic sign, suggesting an improvement in overall survival. In contrast, when the size of these regions increases on follow-up imaging, it suggests a worse prognosis 5.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.