Clavicle (AP cephalic view)
Updates to Article Attributes
Body
was changed:
The clavicle AP cephalic angulation view is a standard projection part of the clavicle series. Often and is often used in conjunction with the AP clavicle, this view.
Indication
This projection straightens out the clavicle and projects most of it above overlaying anatomythe scapula and second and third rib. It can help to determine angulation of fractures and dislocation 1.
Patient position
- patient is preferably erect
- midcoronal plane of the patient is parallel to the image receptor, in other words, the patient's back is against the image receptor
- the clavicle of the affected side is at the
centrecenter of the image receptor - affected arm is in a neutral position
by the patient side
Technical factors
- anteroposterior projection
-
centringcentering point- just below mid clavicle
- angled cephalic 15-30°
-
collimation
- superior to the skin margins
- inferior to include mid scapula
- lateral to include the skin margin
- medial to include the sternoclavicular joint
-
orientation
- landscape
-
detector size
- 18 cm x 24 cm
-
exposure
- 60-70 kVp
- 10-18 mAs
-
SID
- 100 cm
-
grid
- yes (this can vary departmentally)
Image technical evaluation
- the clavicle is 'flattened out' projecting above the shoulder girdle
- a slight overlap of the humeral head
withwithin the glenoid
Practical points
Remember to move your detector to compensate for the cephalic angulation. This projection can often better demonstrate subtle clavicle fractures, if you can't see anything on the AP projection, this should be your next point of call.
-<p>The clavicle<strong> AP cephalic angulation view </strong>is a standard projection part of the <a href="/articles/clavicle-series">clavicle series</a>. Often used in conjunction with the AP clavicle, this projection straightens out the clavicle and projects it above overlaying anatomy.</p><h4>Patient position</h4><ul>- +<p>The clavicle<strong> AP cephalic angulation view </strong>is a standard projection part of the <a href="/articles/clavicle-series">clavicle series</a> and is often used in conjunction with the AP clavicle view.</p><h4>Indication</h4><p>This projection straightens out the clavicle and projects most of it above the scapula and second and third rib. It can help to determine angulation of fractures and dislocation <sup>1</sup>. </p><h4>Patient position</h4><ul>
-<li>the clavicle of the affected side is at the centre of the image receptor</li>-<li>affected arm is in a neutral position by the patient side</li>- +<li>the clavicle of the affected side is at the center of the image receptor</li>
- +<li>affected arm is in a neutral position</li>
-<strong>centring point</strong><ul>- +<strong>centering point</strong><ul>
-<li>a slight overlap of the humeral head with the glenoid</li>- +<li>a slight overlap of the humeral head within the glenoid</li>
References changed:
- 1. John Lampignano, Leslie E. Kendrick. Bontrager's Textbook of Radiographic Positioning and Related Anatomy. (2017) <a href="https://books.google.co.uk/books?vid=ISBN9780323399661">ISBN: 9780323399661</a><span class="ref_v4"></span>
Images Changes:
Image ( destroy )
Ddx
was set to
.
Caption
was removed:
Position
was set to
.
Image 1 X-ray (AP 20 deg cephalad) ( update )

Caption
was changed:
Image 2 X-ray (Frontal cephalic angulation) ( create )
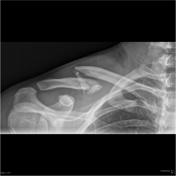
Image 3 X-ray (Frontal cephalic angulation) ( create )








 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.