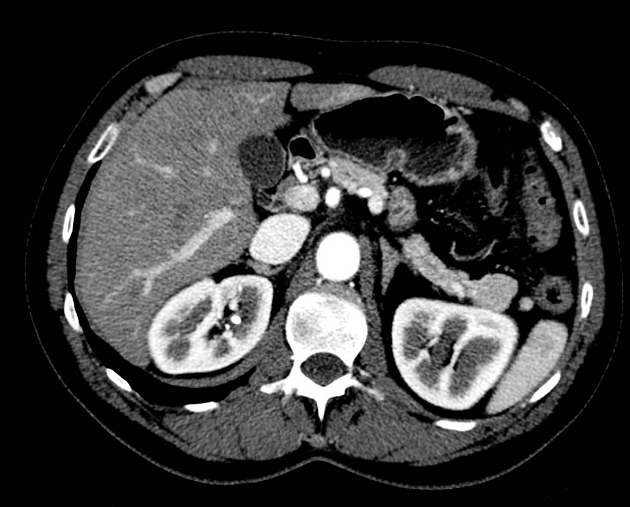
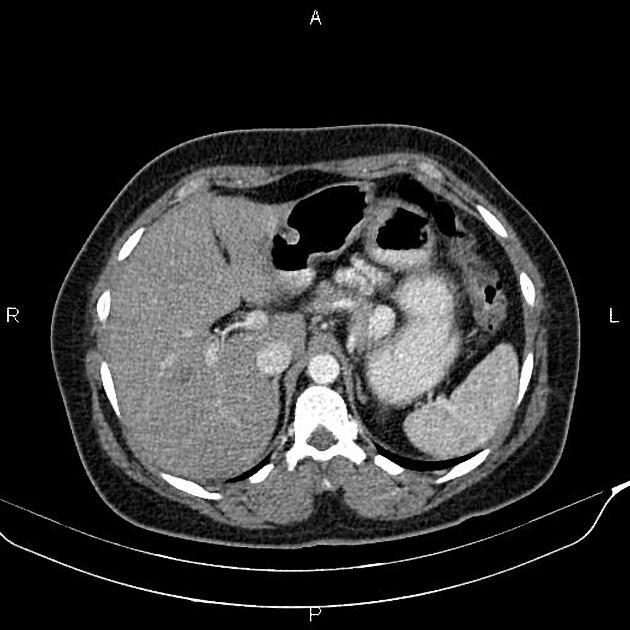
An intrapancreatic accessory spleen is a splenunculus within the pancreatic parenchyma.
Differentiating this finding from other pancreatic neoplasms is important to avoid unnecessary surgery.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Intrapancreatic splenunculi are not as rare as previously thought and their incidence rate is estimated to 17% of those with accessory spleens in an autopsy series 2,4.
Radiographic features
CT
An intrapancreatic splenunculus presents as a well-circumscribed rounded or ovoid homogeneous, hyperdense nodule 1. The enhancement pattern follows that of the spleen.
MRI
The signal and enhancement pattern of intrapancreatic accessory spleens are identical to the splenic parenchyma 1.
Differential diagnosis
The differential on CT and MRI is that of hypervascular pancreatic lesions.
The diagnosis can be confirmed by:
- single-photon emission CT with technetium 99–labeled red blood cells or sulfur colloid granules 2,4
- contrast-enhanced ultrasound using microgranules; in the late phase, granules are retained almost exclusively by the hepatic and splenic parenchyma 2









 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.