Kienböck disease is the eponymous name given to osteonecrosis involving the lunate. It is often referred to as lunatomalacia.
On this page:
Epidemiology
The age distribution for Kienböck disease depends on gender. The condition is most common within the dominant wrist of young adult men where it appears to be due to repeated loading of the lunate. In women, Kienböck disease typically occurs in middle age and is equally divided between the dominant and non-dominant wrist 1.
Associations
There is a significant association between negative ulnar variance and Kienböck disease, although the majority of people with negative ulnar variance do not have the condition. A causal association is difficult to prove, however, the effectiveness of decompressive procedures such as radial shortening or ulnar lengthening in relieving pain and preventing further collapse of the lunate is supportive 2. Overall, the negative ulnar variance is present as a predisposing factor in around 75% of cases of Kienböck disease.
Pathology
The pathologic changes are equivalent to those of osteonecrosis of other bones. There is disruption of critical blood supply leading to bone infarction, central necrosis, and surrounding hyperemia. Microfractures ensue resulting in flattening and deformity of the bone surface.
The vascular supply of the lunate greatly contributes to formation of Kienböck disease. In 70% of patients, multiple vessels supply both volar and dorsally. On the volar surface, these include branches from the anterior interosseous artery in 70% and a branch of the palmar intercarpal arch in 70% of patients. On the dorsal surface, dorsal perforating branches of the anterior interosseous artery are seen in 86% of patients and dorsal branch from the dorsal intercarpal arch in 50% of patients 3.
In the remaining ~30%, only a single vessel is present volar and dorsally, which predisposes to osteonecrosis of the lunate 1.
Classification
Several classifications systems are used to assess Kienböck disease, the most commonly used are 5,6:
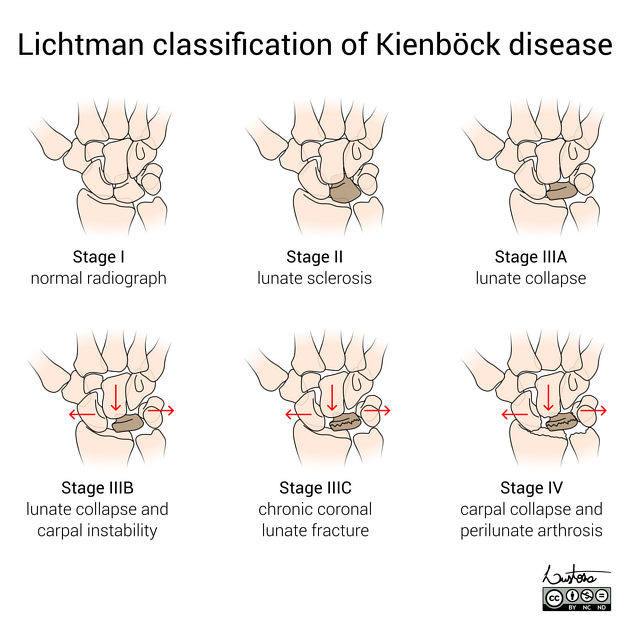
Lichtman classification - radiographic
Schmitt classification - MRI
Bain classification - arthroscopic
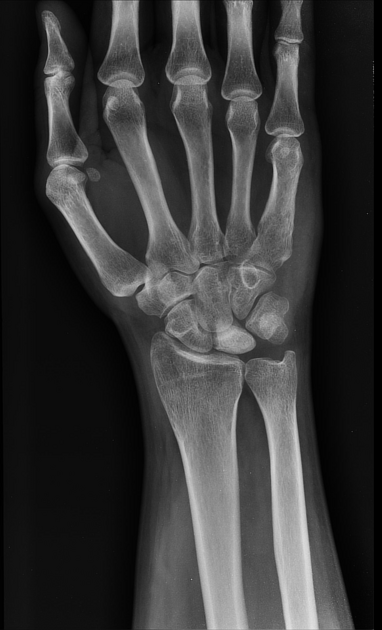
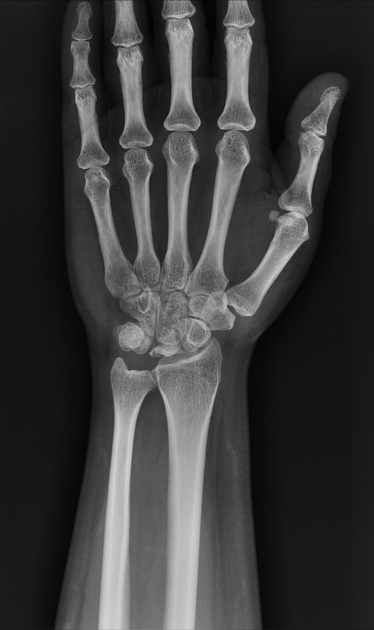
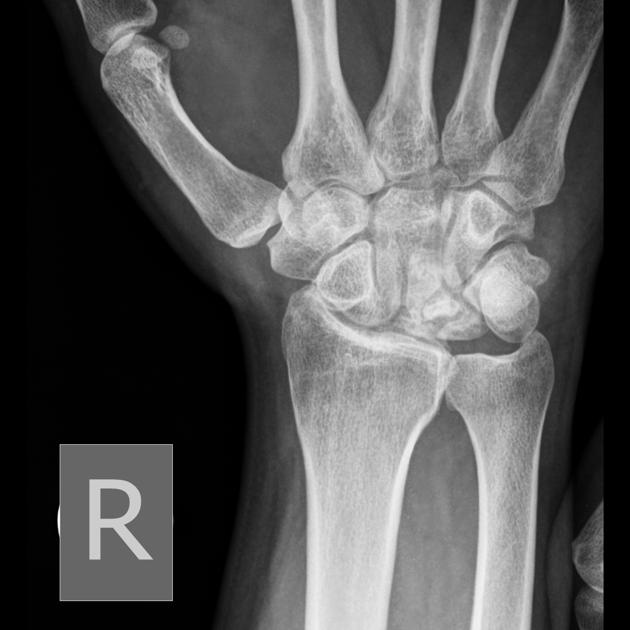
Radiographic features
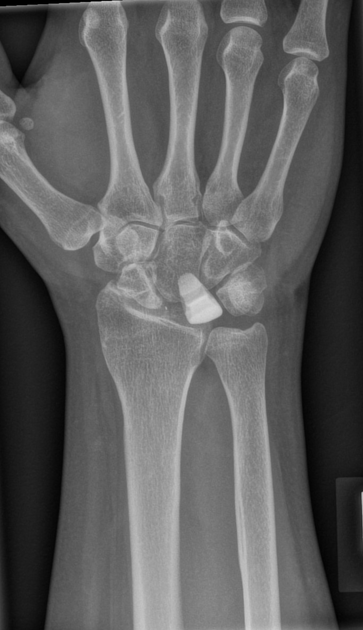
Plain radiograph
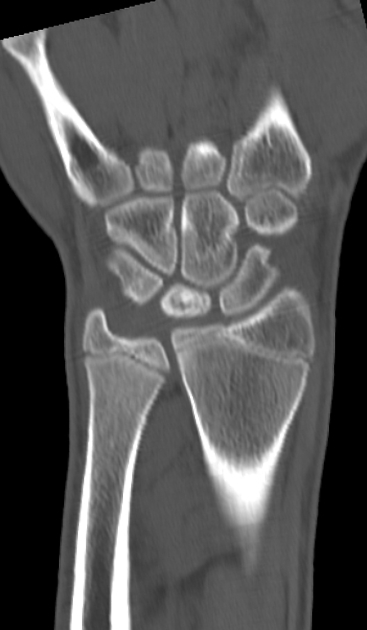
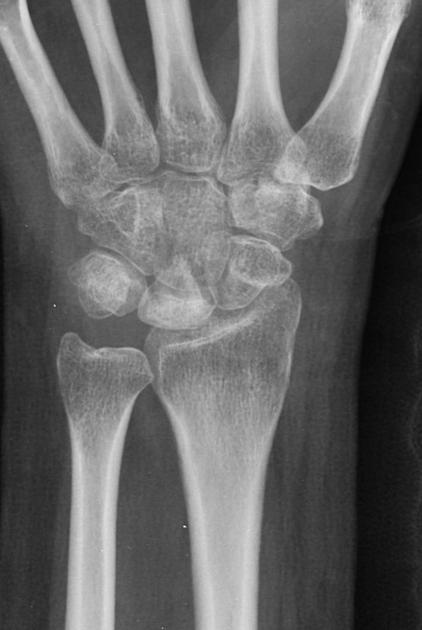
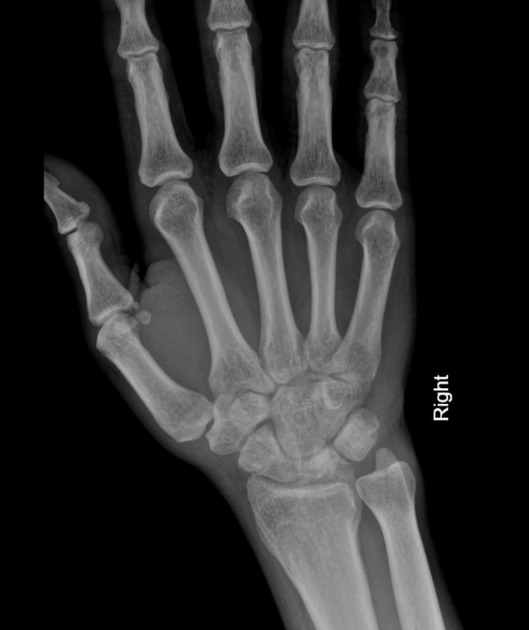
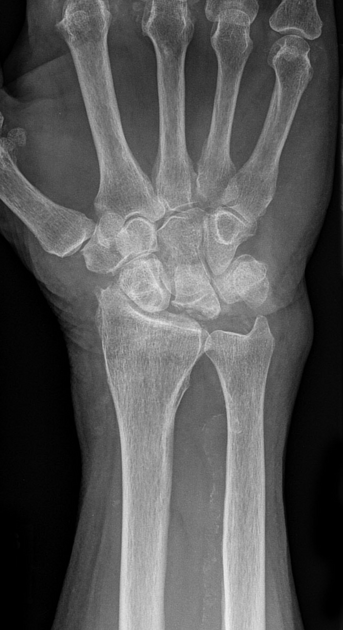
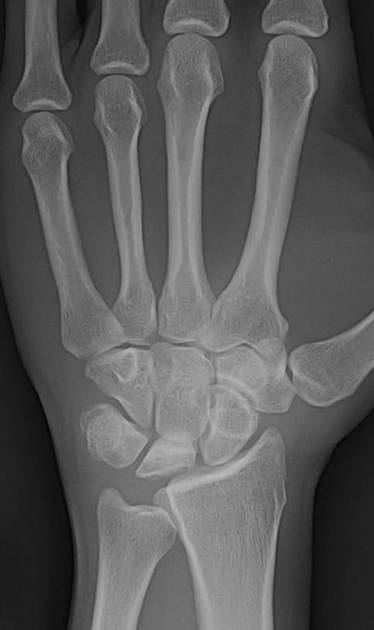
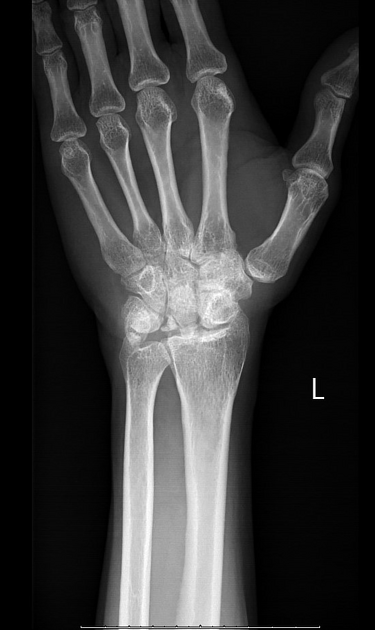
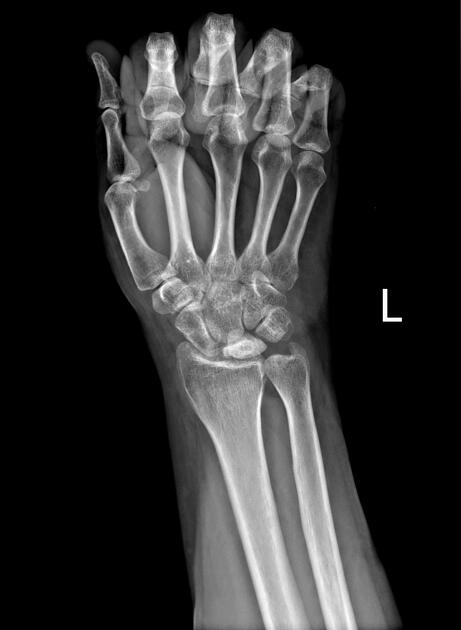
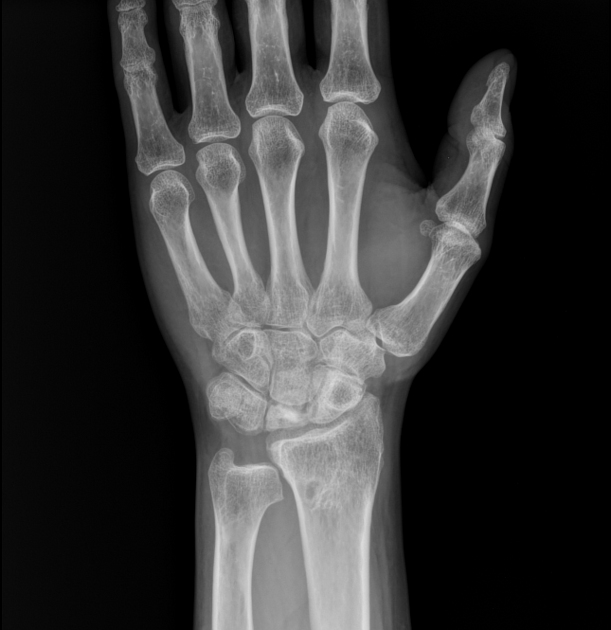
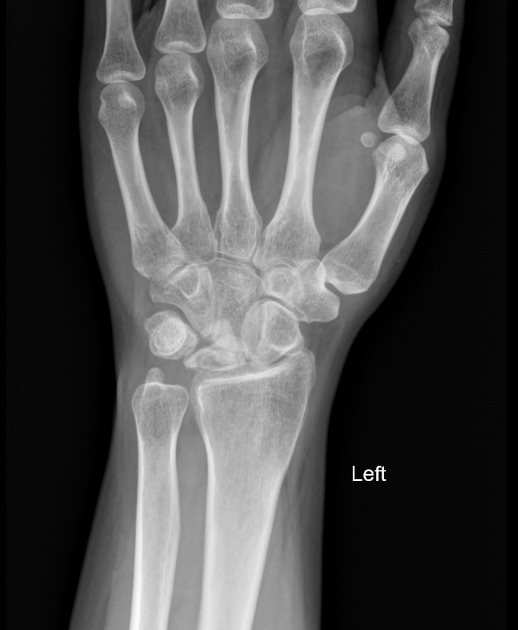
Sclerosis and flattening of the lunate. When flattening is marked there is rotation of the scaphoid which further adds to the stress on the lunate. Fragmentation of the lunate and secondary degenerative disease may develop later.
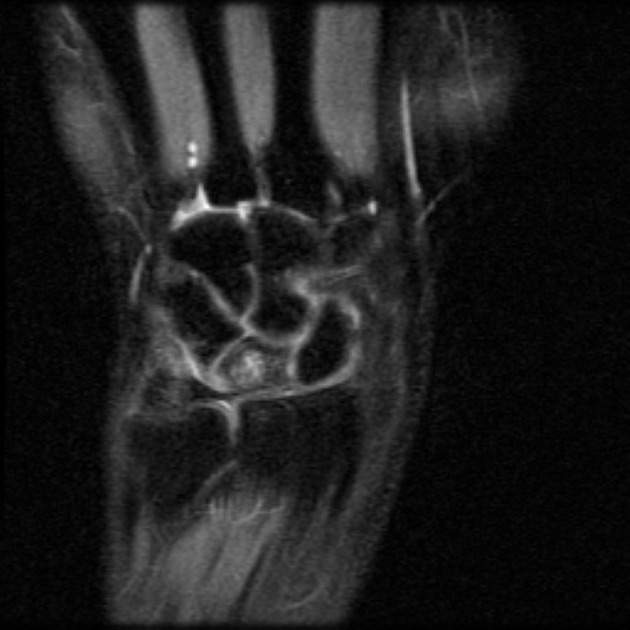
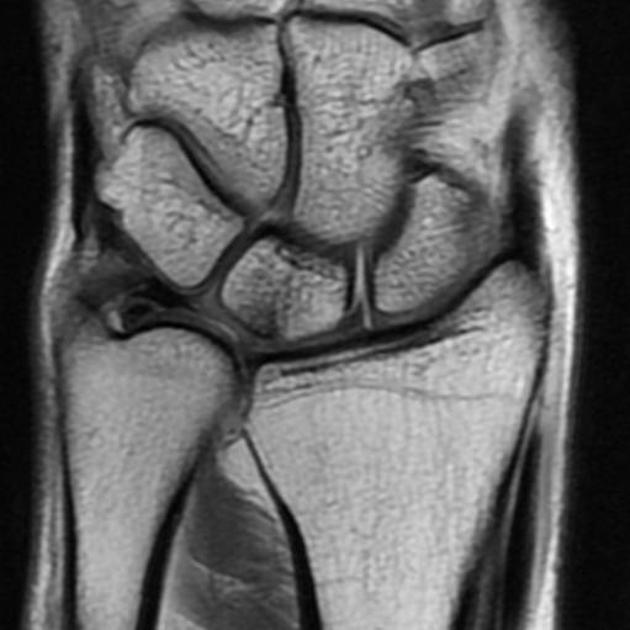
MRI
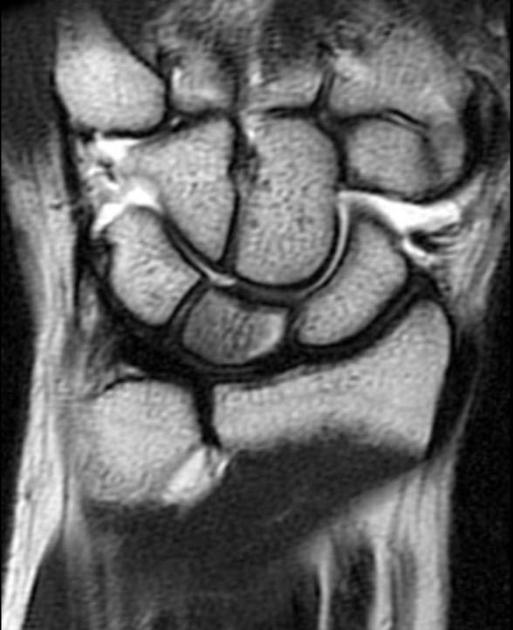
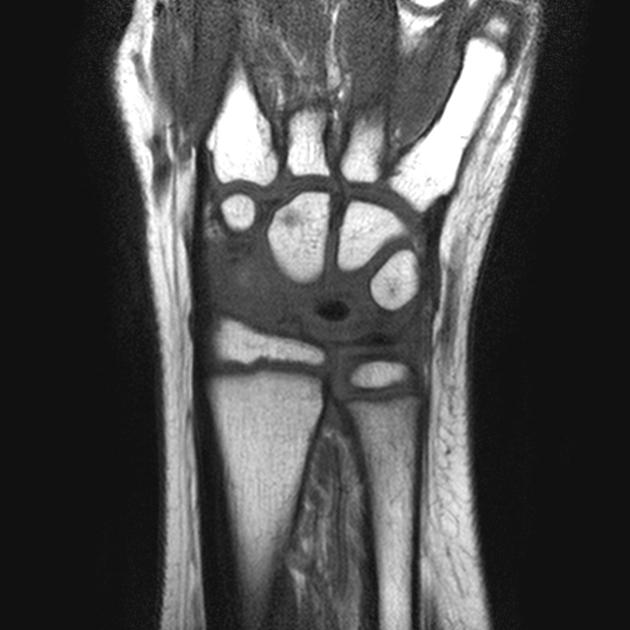
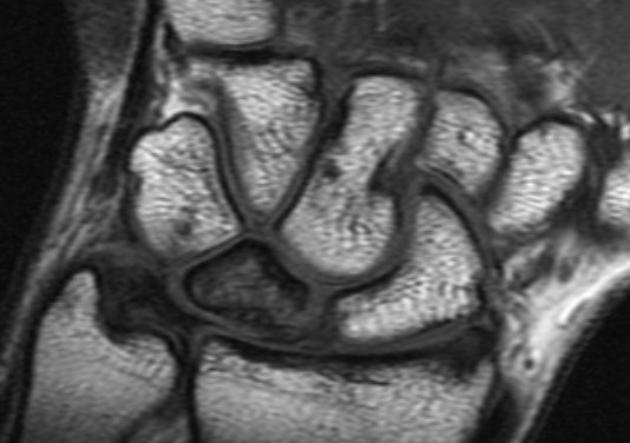
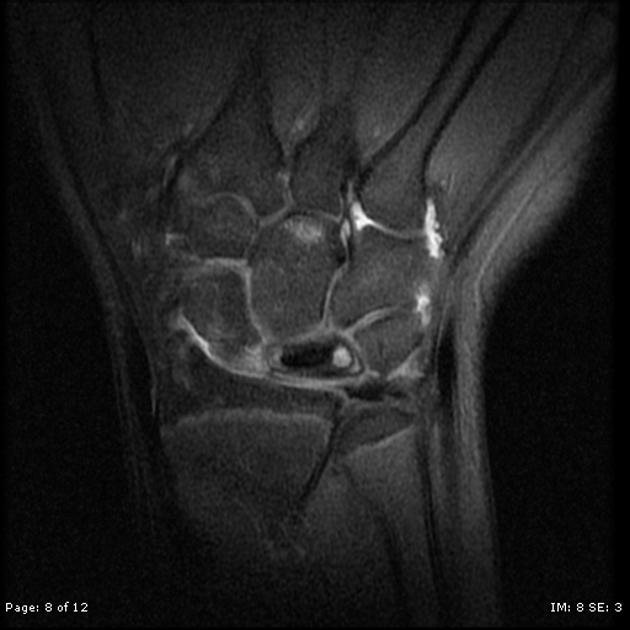
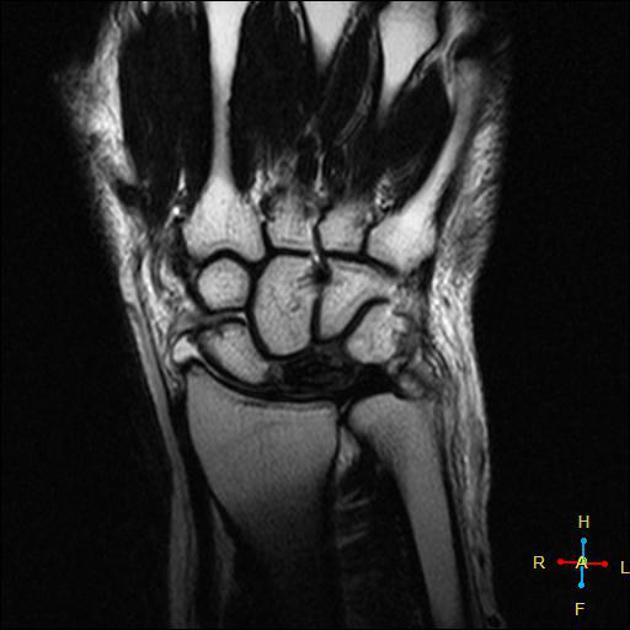
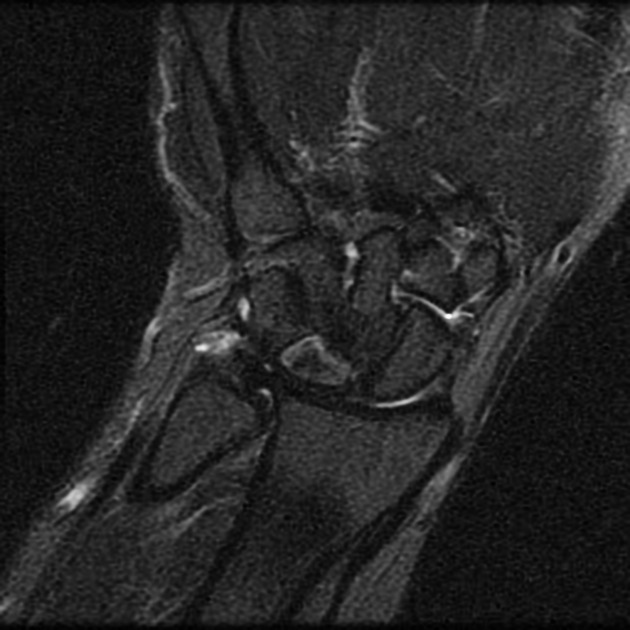
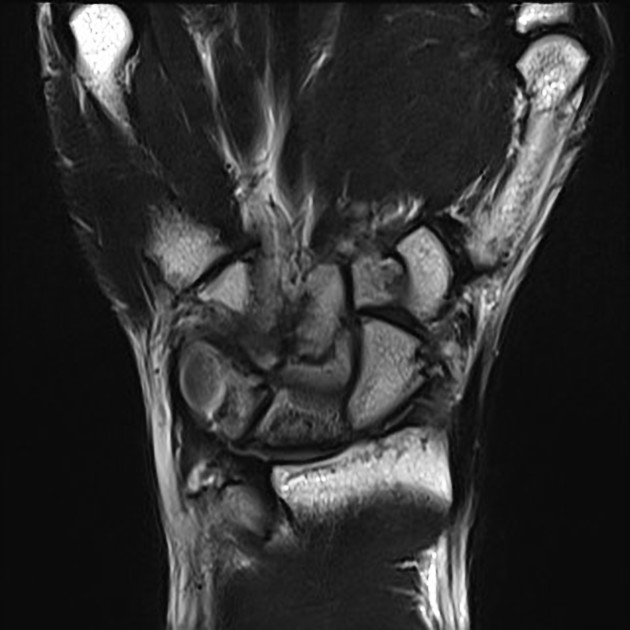
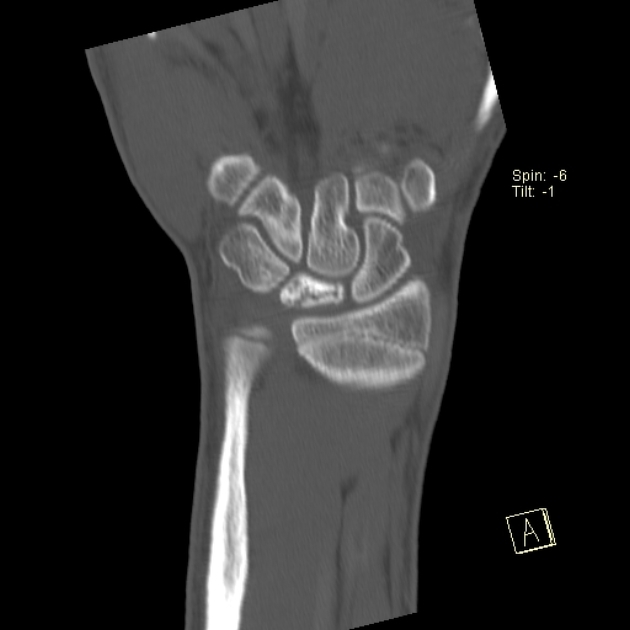
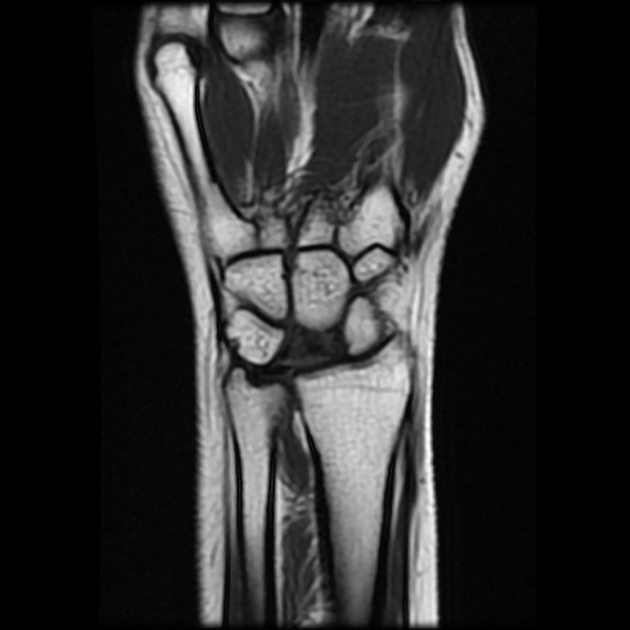
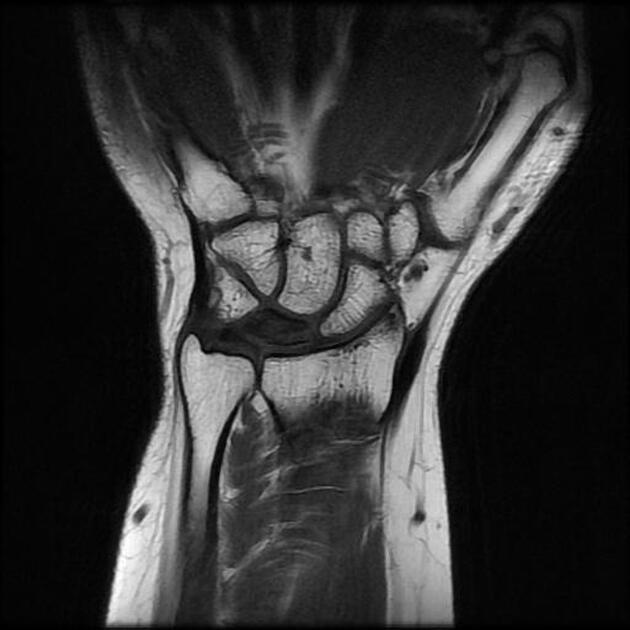
Is the most sensitive and specific test and may detect very early disease. The pattern of lunate bone signal change allows the condition to be differentiated from ulnar impaction syndrome: the major differential diagnosis. Sclerosis (low T1 and T2) is usually seen centrally and within the radial aspect of the lunate. Sclerosis can be diffuse. Bone edema (high T2, intermediate T1) may be seen in the acute phase, particularly on the radial side.
Nuclear medicine
Negative bone scintigraphy can be useful to exclude the disease, however, a positive scan is not specific enough for the diagnosis.
Treatment and prognosis
Conservative management with rest, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and immobilization in mild cases is often very effective. Radial shortening to correct negative ulnar variance is the most common surgical therapy with good results. Other operative procedures include ulnar lengthening, revascularization, lunate excision with or without prosthetic replacement, and intercarpal fusion. Proximal row carpectomy is used as a salvage procedure in refractory cases 1.
History and etymology
The condition is named after Austrian radiologist Robert Kienböck (1871-1953), who described the condition in 1910 4.
Differential diagnosis
On imaging consider
-
sclerosis/signal change is at the proximal ulnar aspect of lunate
more commonly associated with positive ulnar variance





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.