Leiomyosarcoma
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Yuranga Weerakkody had no recorded disclosures.
View Yuranga Weerakkody's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Liz Silverstone had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Liz Silverstone's current disclosures- Leiomyosarcoma (LMS)
- Leiomyosarcomata
- Leiomyosarcomas
Leiomyosarcomas are extremely rare malignant neoplasms that originate from smooth muscle cells and may be considered the malignant counterpart of a leiomyoma. They are classified as soft tissue tumours and account for ~8% of malignant soft tissue tumours 10.
On this page:
Pathology
Location
Leiomyosarcomas can potentially occur anywhere there is smooth muscle. Commonly described sites include the following 14:
uterine leiomyosarcoma: most common, accounting for up to one-third of uterine sarcomas 8
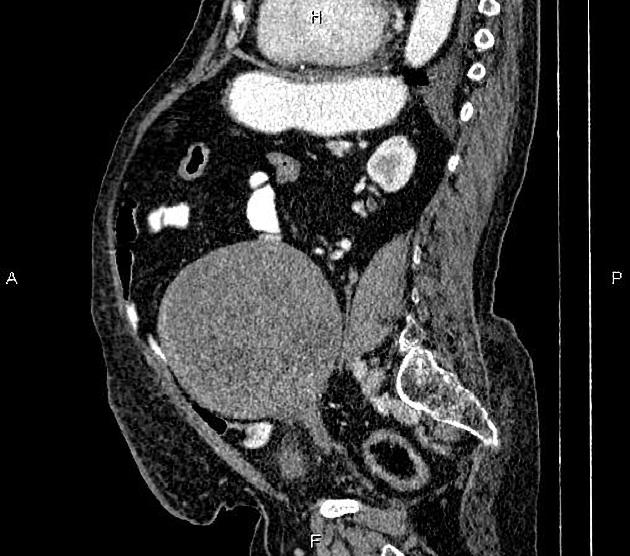
retroperitoneal leiomyosarcoma: most common extra-uterine site 11
Less common sites include:
liver: hepatic leiomyosarcoma
bladder
nasopharynx
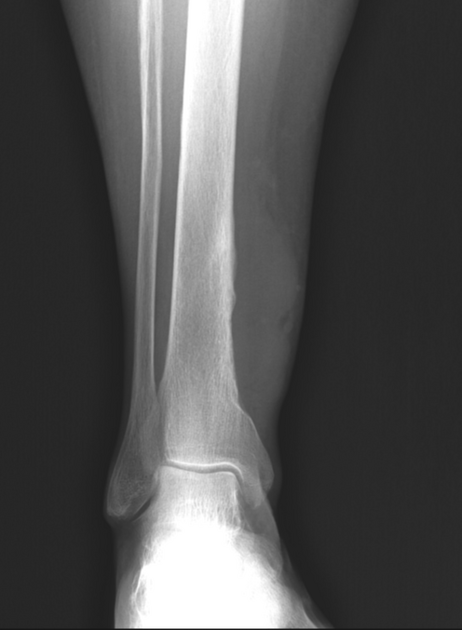
bone 6: primary leiomyosarcoma of bone
-
blood vessels (~2 % of leiomyosarcomas 14)
-
veins: 5x more common than arteries for vascular leiomyosarcomas 14
-
arteries
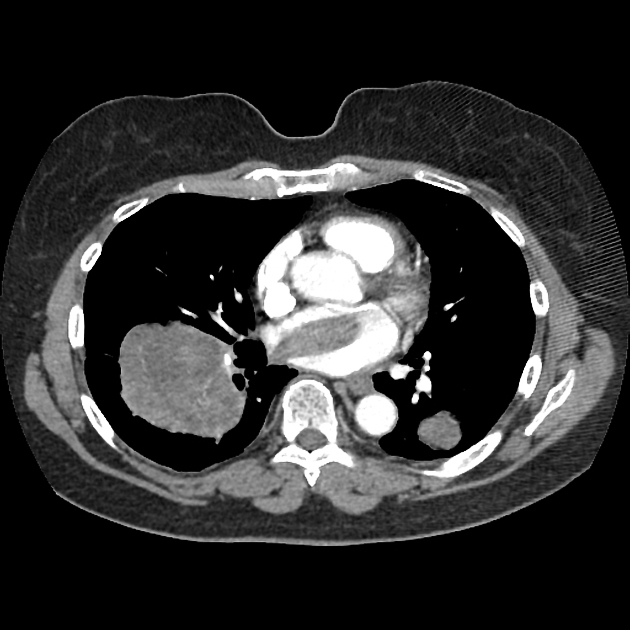
primary pulmonary artery leiomyosarcoma: most common arterial site 14
other sites include aorta, carotid, subclavian, renal, splenic, iliac, femoral (common and superficial), and popliteal arteries 14
-
central nervous system: primary intracranial leiomyosarcoma
skin: cutaneous leiomyosarcoma 13
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Radiographic features
Morphological imaging features would be invariably dependent on the site (refer to individual articles). Generally, they tend to be large masses, especially in cases of abdominopelvic lesions ref.
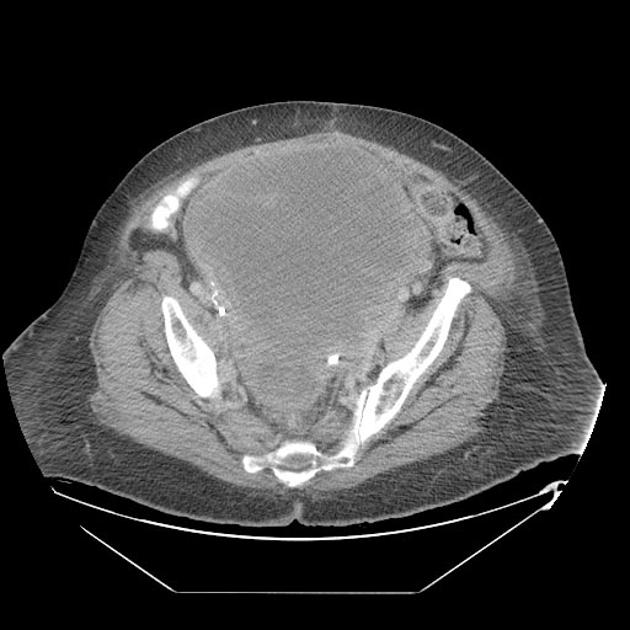
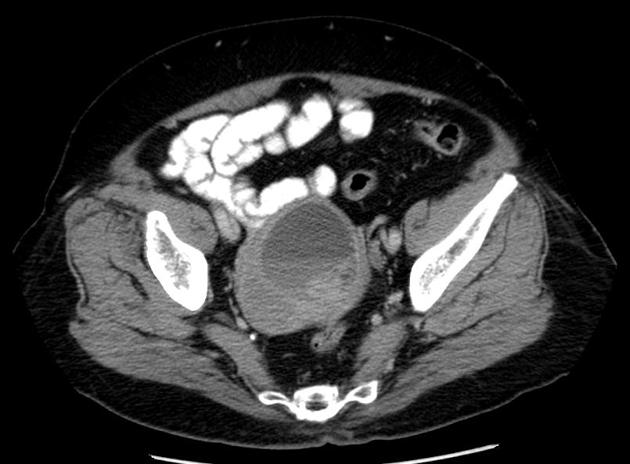
CT
generally heterogeneous ref
commonly demonstrate central low attenuation representing necrosis 12
calcification exceedingly rare ref
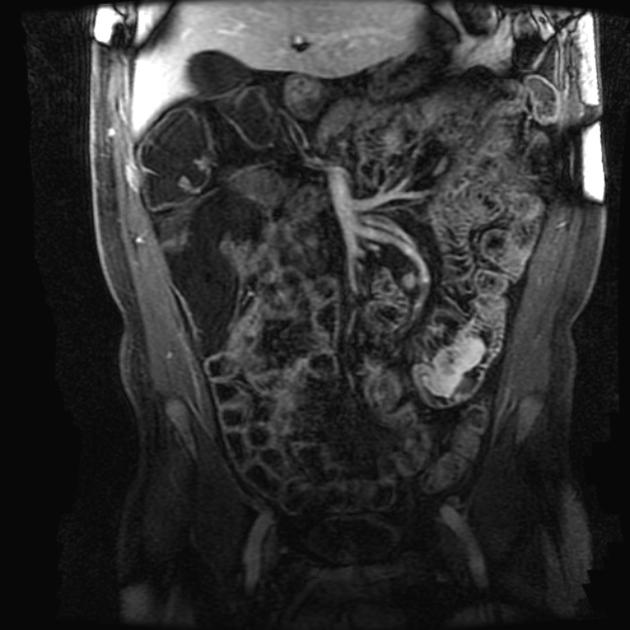
MRI
The tumour frequently demonstrates cystic foci. Signal characteristics include ref:
T1: isointense to muscle
T2: intermediate to hypointense to neighbouring fat
T2 FS: predominantly hyperintense
Differential diagnosis
For a meaningful differential, it is necessary to consider site-specific tumours.
References
- 1. Disler DG, Chew FS. Gastric leiomyosarcoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1992;159 (1): 58. AJR Am J Roentgenol (citation) - Pubmed citation
- 2. Bush CH, Reith JD, Spanier SS. Mineralization in musculoskeletal leiomyosarcoma: radiologic-pathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003;180 (1): 109-13. AJR Am J Roentgenol (full text) - Pubmed citation
- 3. Rha SE, Byun JY, Jung SE et-al. CT and MRI of uterine sarcomas and their mimickers. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003;181 (5): 1369-74. AJR Am J Roentgenol (full text) - Pubmed citation
- 4. Kaushik S, Neifeld JP. Leiomyosarcoma of the renal vein: imaging and surgical reconstruction. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002;179 (1): 276-7. AJR Am J Roentgenol (full text) - Pubmed citation
- 5. Levine MS, Buck JL, Pantongrag-brown L et-al. Leiomyosarcoma of the esophagus: radiographic findings in 10 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996;167 (1): 27-32. AJR Am J Roentgenol (abstract) - Pubmed citation
- 6. Bush C, Reith J, Spanier S. Mineralization in Musculoskeletal Leiomyosarcoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003;180(1):109-13. doi:10.2214/ajr.180.1.1800109 - Pubmed
- 7. Davies CE, Davies AM, Kindblom LG et-al. Soft tissue tumors with muscle differentiation. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2010;14 (2): 245-56. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1253165 - Pubmed citation
- 8. Rha SE, Byun JY, Jung SE et-al. CT and MRI of uterine sarcomas and their mimickers. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003;181 (5): 1369-74. AJR Am J Roentgenol (full text) - Pubmed citation
- 9. Matsuyama A, Hisaoka M, Hashimoto H. Vascular Leiomyosarcoma: Clinicopathology and Immunohistochemistry with Special Reference to a Unique Smooth Muscle Phenotype. Pathol Int. 2010;60(3):212-6. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1827.2009.02508.x - Pubmed
- 10 .Kransdorf MJ. Malignant soft-tissue tumors in a large referral population: distribution of diagnoses by age, sex, and location. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1995;164 (1): 129-34. AJR Am J Roentgenol (abstract) - Pubmed citation
- 11. O'Sullivan P, Harris A, Munk P. Radiological Imaging Features of Non-Uterine Leiomyosarcoma. Br J Radiol. 2008;81(961):73-81. doi:10.1259/bjr/18595145 - Pubmed
- 12. McLeod A, Zornoza J, Shirkhoda A. Leiomyosarcoma: Computed Tomographic Findings. Radiology. 1984;152(1):133-6. doi:10.1148/radiology.152.1.6729102 - Pubmed
- 13. Juan Y, Saboo S, Tirumani S et al. Malignant Skin and Subcutaneous Neoplasms in Adults: Multimodality Imaging with CT, MRI, and 18F-FDG PET/CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014;202(5):W422-38. doi:10.2214/AJR.13.11424 - Pubmed
- 14. Nguyen D, Leon L, Pacanowski J, Berman S. A Case of Leiomyosarcoma of the Common Femoral Artery. J Vasc Surg Cases Innov Tech. 2021;7(2):291-4. doi:10.1016/j.jvscit.2021.02.004 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- WHO classification of breast tumours (5th ed.)
- Primary intracranial leiomyosarcoma
- Small bowel lymphoma
- WHO classification of tumours of bone
- Dedifferentiated chondrosarcoma
- Tracheal masses
- Hypervascular metastases
- Skin cancer
- Hypervascular liver lesions
- Deep fibrous histiocytoma
- Urinary bladder wall or lumen calcification (differential)
- Broad ligament
- Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma
- Parasitic leiomyoma
- Unilateral hypertransradiant hemithorax
- Tumours of the small intestine
- Oesophageal leiomyosarcoma
- Soft tissue sarcoma
- Inferior vena cava leiomyosarcoma
- Leiomyoma
- Thigh leiomyosarcoma (FDG PET-CT)
- Leiomyosarcoma with tumor thrombus in left atrium
- Retroperitoneal liposarcoma
- Inferior vena cava leiomyosarcoma
- Lung metastases from a leiomyosarcoma
- Leiomyosarcoma of the left ovarian vein
- Retroperitoneal leiomyosarcoma
- Pulmonary Metastasis
- HIV-associated leiomyosarcoma - intracranial
Related articles: Pathology: Genitourinary
- obstetrics
-
first trimester
- ultrasound findings in early pregnancy
- embryo/fetus
- beta-hCG levels
- confirming intrauterine gestation
- pregnancy of unknown location (PUL)
- first trimester vaginal bleeding
- early structural scan
- aneuploidy testing
-
second trimester
- fetal biometry
- amniotic fluid volume
- fetal morphology assessment
- soft markers
- amnioreduction
- Doppler ultrasound
- nuchal translucency
- 11-13 weeks antenatal scan
- chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis
- other
- placenta
- placental anatomy
- placental developmental abnormalities
- placenta praevia
- spectrum of abnormal placental villous adherence
- abnormalities of cord insertion
- abruptio placentae
- placental pathology
- vascular pathologies of placenta
- placental infections
- placental masses
- molar pregnancy
- twin placenta
- miscellaneous
-
first trimester
- gynaecology
- acute pelvic pain
- chronic pelvic pain
- uterus
- ovaries
- ovarian follicle
- ovarian torsion
- pelvic inflammatory disease
- ovarian cysts and masses
- paraovarian cyst
- polycystic ovaries
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- post-hysterectomy ovary
- cervix
- fallopian tube
- other
- male genital tract
- prostate gland
- transrectal ultrasound
- prostate tumours
- infections of the prostate
-
prostatitis
- acute bacterial prostatitis
-
chronic prostatitis
- chronic bacterial prostatitis
- chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)
- asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
- granulomatous prostatitis
- emphysematous prostatitis
- prostatic abscess
-
prostatitis
- benign prostatic hypertrophy
- cystic lesions of the prostate
- prostatic calcification
- prostatic infarction
- testes
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- testicular torsion
- orchitis
- testicular trauma
-
germ cell tumours of the testis
- testicular seminoma
-
non seminomatous germ cell tumours
- mixed germ cell tumour
- yolk sac tumour (endodermal sinus tumour)
- embryonal cell carcinoma
- choriocarcinoma
- testicular teratoma
- testicular epidermoid (teratoma with ectodermal elements only)
- burned out testis tumour
- sex cord / stromal tumours of the testis
- testicular cyst
- testicular lymphoma
- bilateral testicular lesion
- paratesticular lesions
- epididymis
- other
- polyorchidism
- cryptorchidism
- tubular ectasia of the rete testis
- cystadenoma of the rete testis
- testicular sarcoidosis
- testicular tuberculosis
- spermatic cord
- fibrous pseudotumour of the scrotum
- scrotal leiomyosarcoma
- testicular adrenal rest tumours (TARTs)
- tunica vaginalis testis mesothelioma
- splenogonadal fusion
- testicular vasculitis
- abnormal testicular Doppler flow (differential)
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- penis
- prostate gland
- KUB
- kidneys
- normal renal anatomy
- hydronephrosis
- urolithiasis
- renal masses
- renal cystic disease
- renal infection
- vascular
- trauma
- ureter
- normal ureter anatomy
- ureteral stricture
- ureteral dilatation
- ureteral anomalies
- ureteral tumours
- ureteral trauma
- other
- bladder
- kidneys




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.