Lobar nephronia, also known as acute focal nephritis, refers to an intermediate stage between acute pyelonephritis and renal abscess, and is a focal region of interstitial nephritis.
The condition is discussed further as part of the article on acute pyelonephritis.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Acute lobar nephronia is commonly found in children. However, immunosuppressed adults, those with abnormalities in the genitourinary tract, or have other underlying systemic conditions (e.g. diabetes mellitus and cirrhosis) may also be affected 2.
Clinical presentation
Clinical features for lobar nephronia are similar to acute pyelonephritis and renal abscess 2:
fever
flank pain
leukocytosis
pyuria
elevated C-reactive protein
Radiographic features
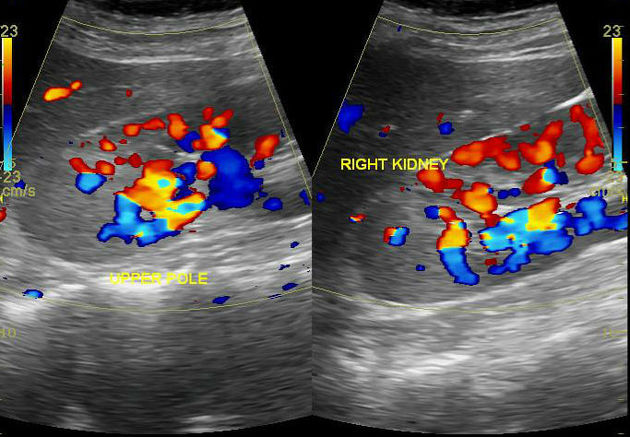
Ultrasound
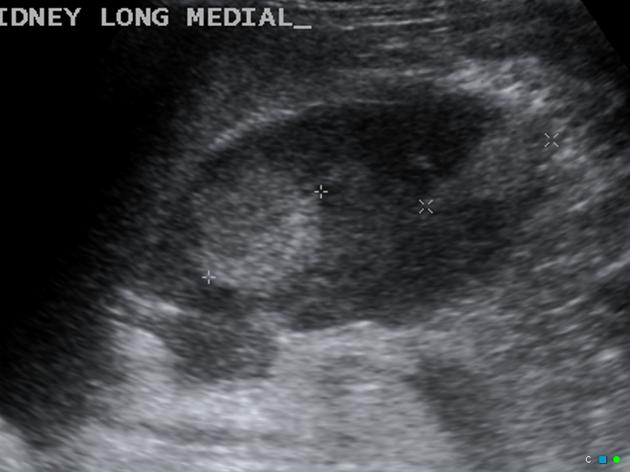
focal hyperechogenicity 3
diffuse nephromegaly 3
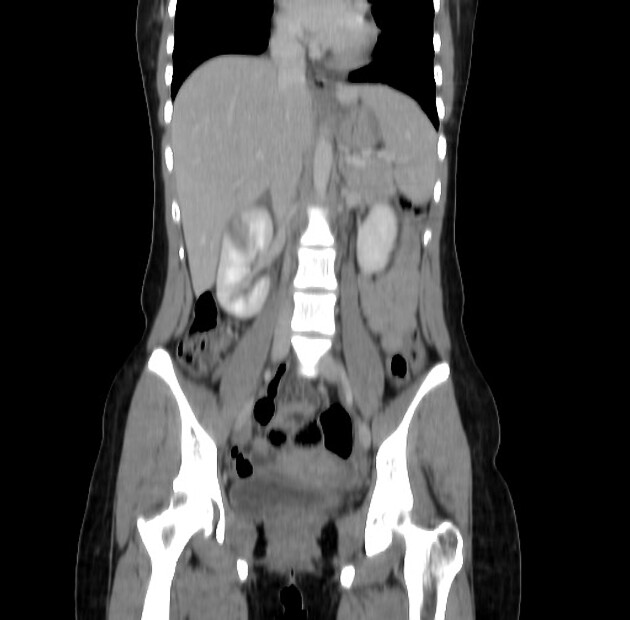
CT
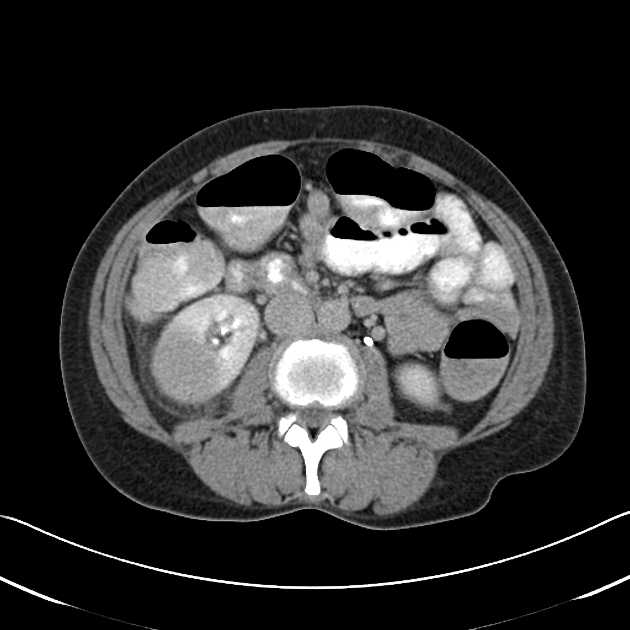
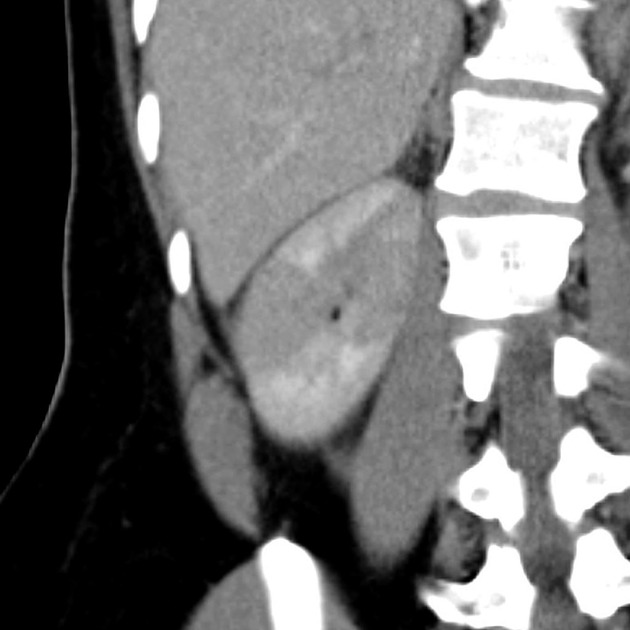
CT with intravenous contrast is the gold standard for diagnosing lobar nephronia. It appears as a wedge of poorly perfused renal parenchyma with ill-defined borders, without a cortical rim sign 2.
History and etymology
Lobar nephronia was first described by Rosenfield et al. in 1978 2.
Differential diagnosis
renal infarction: in these patients the cortical rim sign is present, and clinical presentation is different, without inflammatory/infectious symptoms




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.