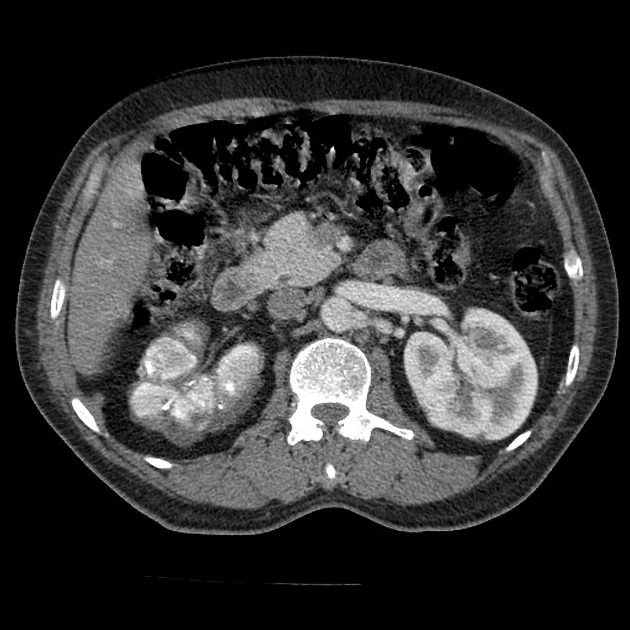
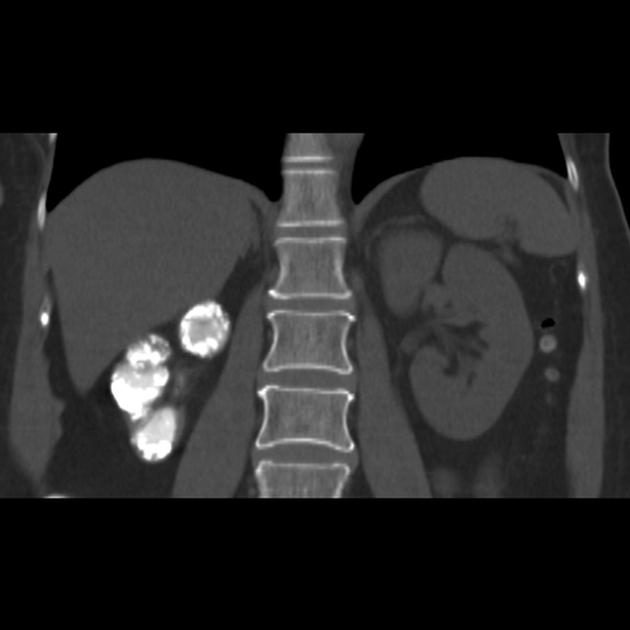
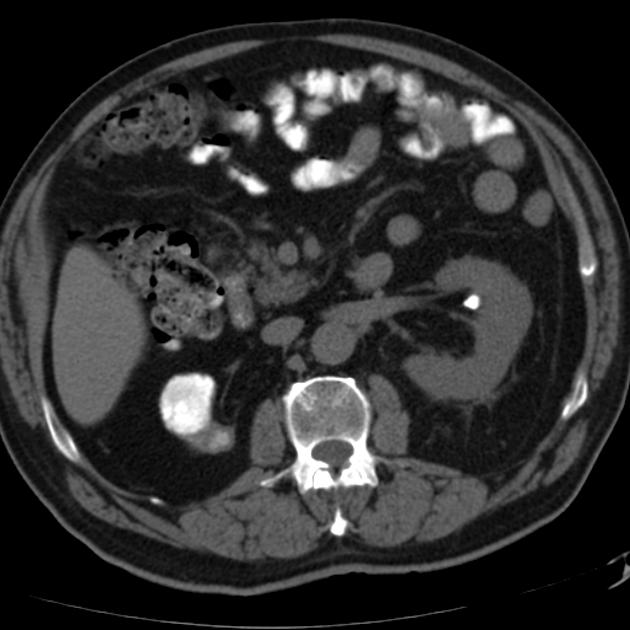
Putty kidney
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Alexandra Stanislavsky had no recorded disclosures.
View Alexandra Stanislavsky's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Arlene Campos had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Arlene Campos's current disclosures- Putty kidneys
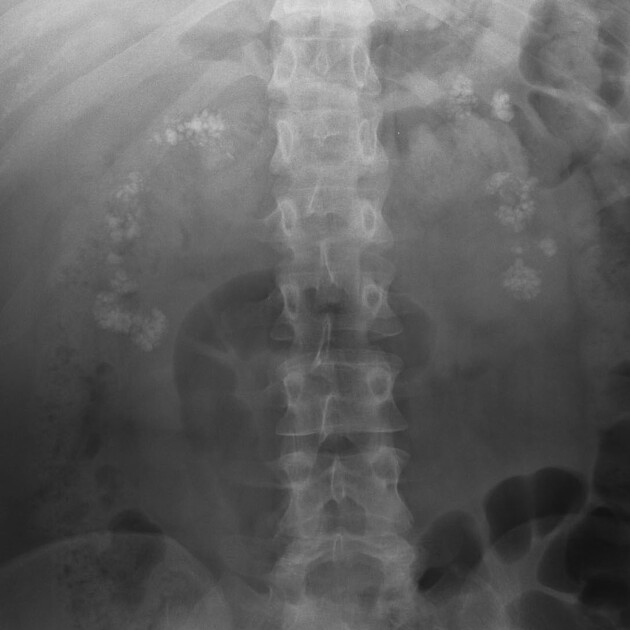
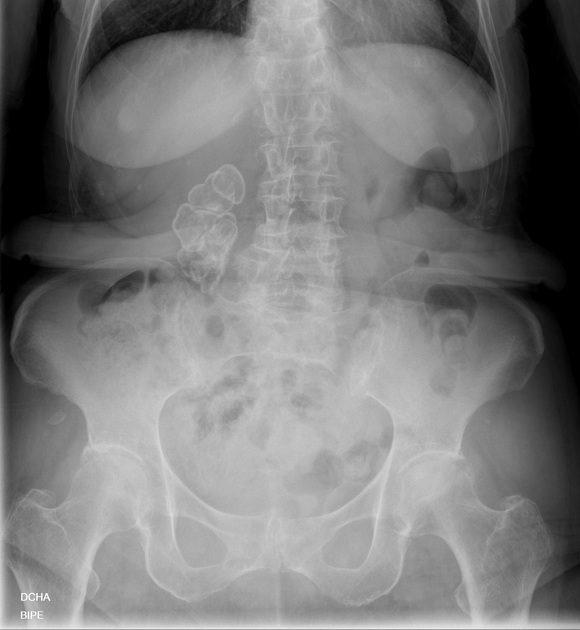
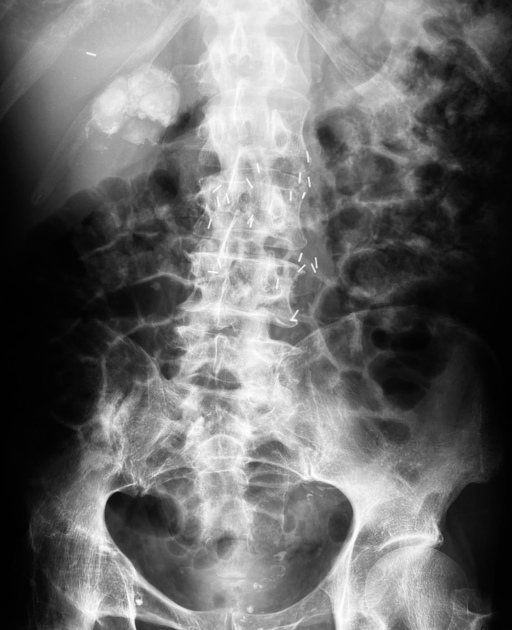
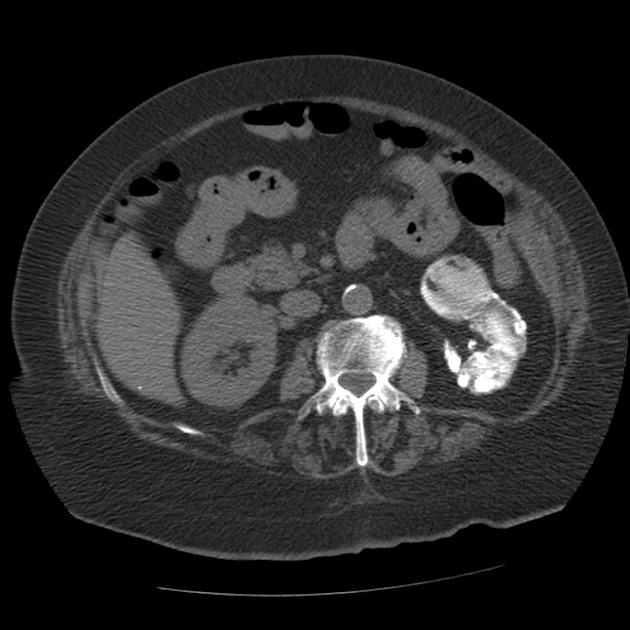
A putty kidney refers to a pattern of renal calcification associated with renal tuberculosis conventionally described on plain radiography. The calcification can be large, round or oval, dense or very homogeneous and ground glass-like, representing calcified caseous tissue within dilated calyces 3,4.
This condition is due to the superimposition of ureteral obstruction on renal parenchymal tuberculosis.
Premkumar et al. labeled calcification 'putty-like' if any faint area of uniform calcification was more than 1 cm in diameter 4. Putty calcification needs to be differentiated from a lobar pattern of calcification, wherein dense calcific rims outline the periphery of distorted renal lobes. Lobar calcification represents an end-stage appearance, associated with autonephrectomy.
References
- 1. Dyer R, Chen M, Zagoria R. Classic Signs in Uroradiology. Radiographics. 2004;24 Suppl 1(suppl_1):S247-80. doi:10.1148/rg.24si045509 - Pubmed
- 2. Gibson M, Puckett M, Shelly M. Renal Tuberculosis. Radiographics. 2004;24(1):251-6. doi:10.1148/rg.241035071 - Pubmed
- 3. Merchant S, Bharati A, Merchant N. Tuberculosis of the Genitourinary System-Urinary Tract Tuberculosis: Renal Tuberculosis-Part I. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2013;23(1):46-63. doi:10.4103/0971-3026.113615 - Pubmed
- 4. Premkumar A, Lattimer J, Newhouse J. CT and Sonography of Advanced Urinary Tract Tuberculosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987;148(1):65-9. doi:10.2214/ajr.148.1.65 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Infections
- bacterial
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Streptococcus anginosus group
- Staphylococcus aureus
- group A Streptococcus
- Klebsiella pneumonia
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Moraxella catarrhalis
- atypical
-
tuberculosis
- causative agent
- tuberculoma (tuberculous granuloma)
- tuberculous abscess
- miliary tuberculosis
- pulmonary tuberculosis
-
extrapulmonary tuberculosis
- intracranial tuberculosis
- tuberculous otomastoiditis
- tuberculous lymphadenopathy
- cardiac tuberculosis
- tuberculous mastitis
-
abdominal tuberculosis
- gastrointestinal tuberculosis
- tuberculous peritonitis
- visceral tuberculosis
- hepatic tuberculosis
- gallbladder tuberculosis
- pancreatic tuberculosis
- splenic tuberculosis
-
genitourinary tuberculosis
- renal tuberculosis
- bladder and ureteric tuberculosis
- prostatic tuberculosis
- scrotal tuberculosis (testes, epididymis, seminal vesicles, vas deferens)
- tuberculous pelvic inflammatory disease (female)
- skeletal tuberculosis
-
tuberculosis
- viral
- fungal
- Aspergillus
-
aspergillosis
- CNS aspergillosis
-
fungal sinusitis
- non-invasive: hyphae do not invade mucosa
- invasive: hyphae seen invading mucosa +/- beyond
- pulmonary aspergillosis




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.