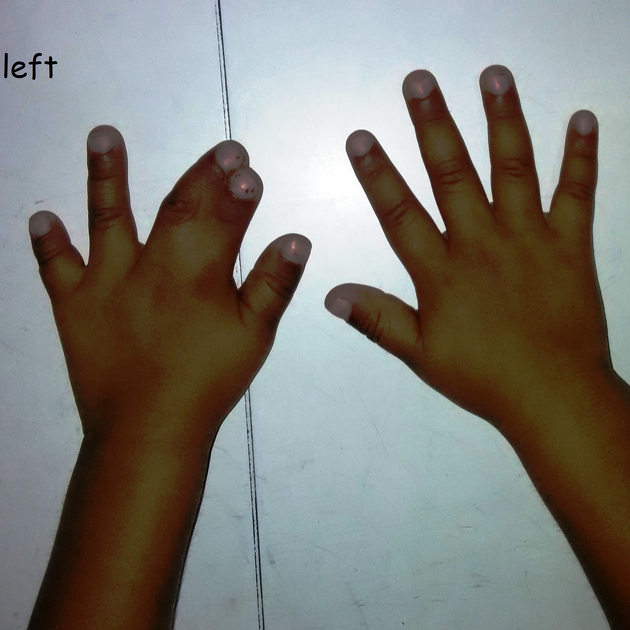
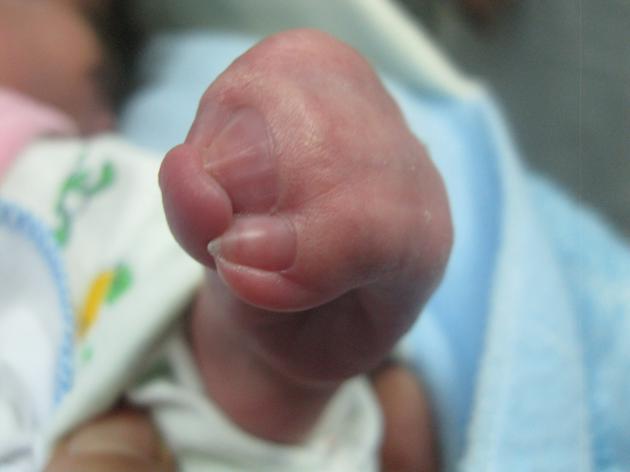
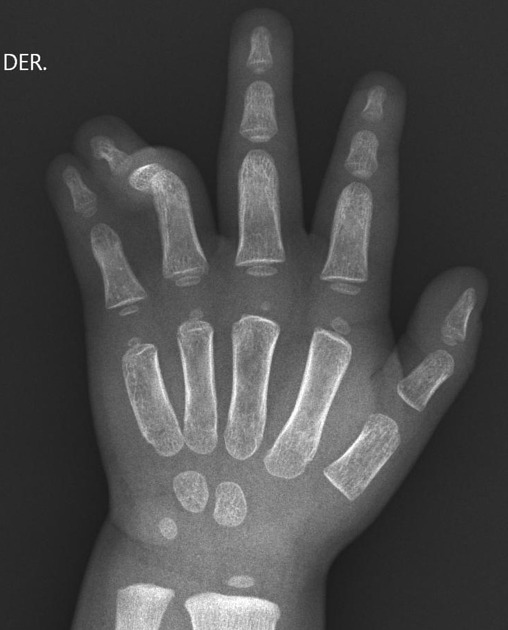
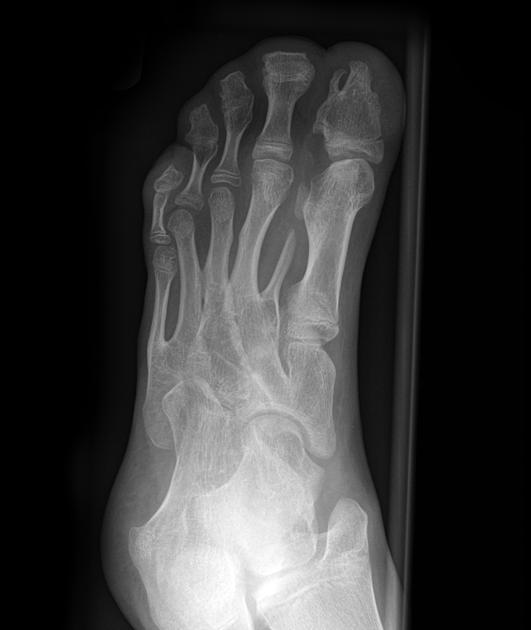
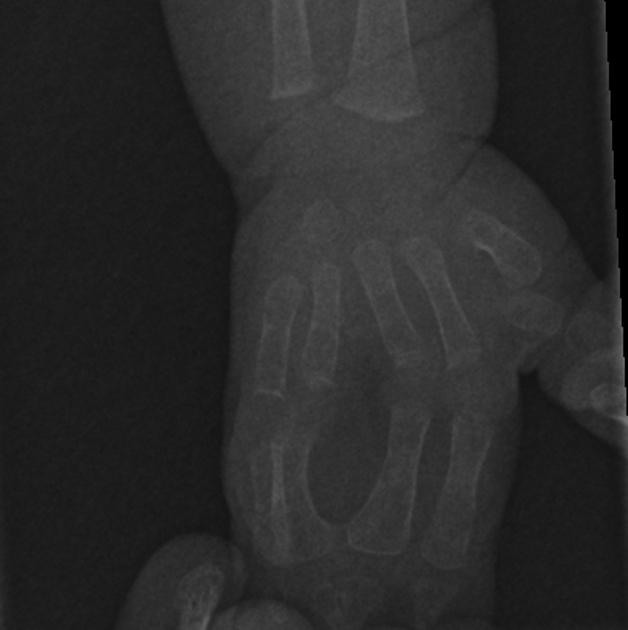
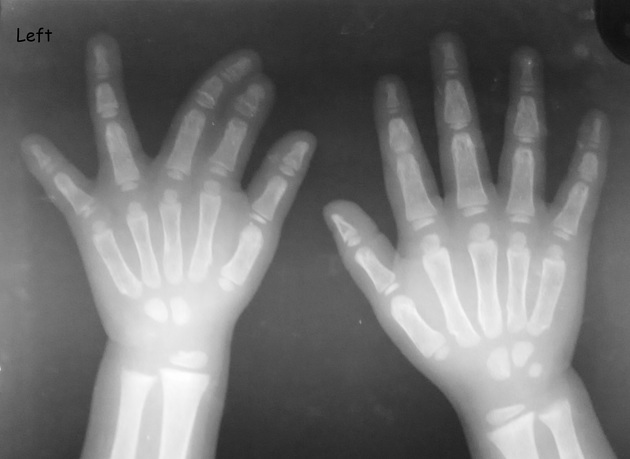
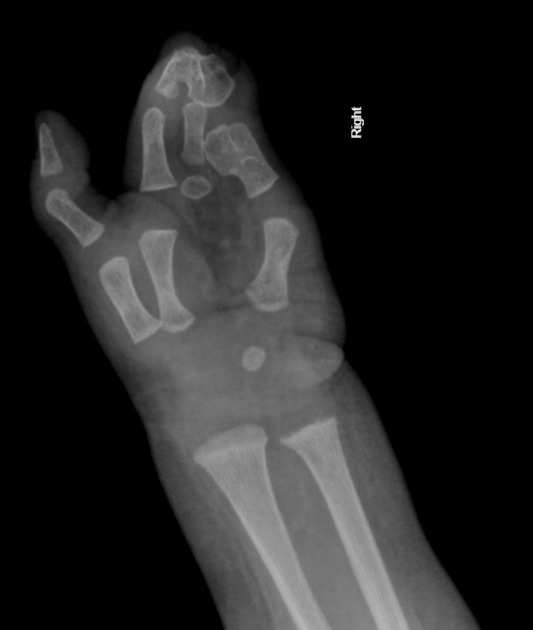
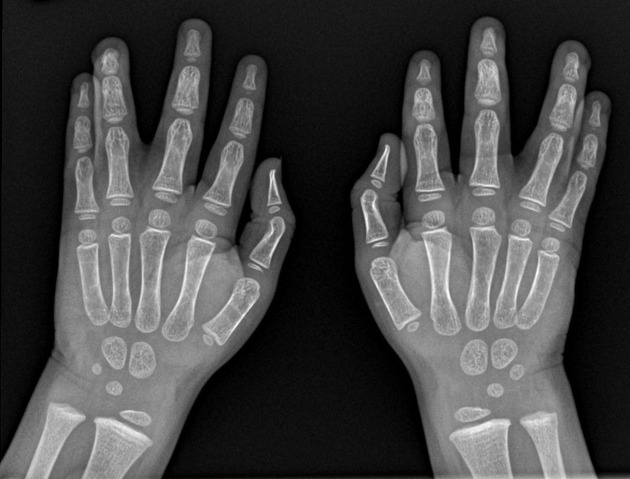
Syndactyly (plural: syndactylies) refers to a congenital fusion of two or more digits. It may be confined to soft tissue (soft tissue syndactyly / simple syndactyly) or may involve bone (bony syndactyly / complex syndactyly).
On this page:
Epidemiology
The overall estimated incidence is at ~1 per 2500 to 5000 live births 6,8. There may be a greater male predilection.
Associations
Syndactyly can occur as an isolated phenomenon or can be associated with numerous other entities. Isolated cases can be either sporadic or familial.
-
aneuploidic syndromic
triploidy: tend to affect the 3rd and 4th digits of the hands
-
non-aneuploidic syndromic
-
type I: Apert syndrome
type II: Crouzon syndrome
type III: Saethre-Chotzen syndrome
type V: Pfeiffer syndrome
-
type I: Noack syndrome
type II: Carpenter syndrome: typically gives soft tissue syndactyly
type III: Sakati-Nyhan syndrome
type IV: Goodman syndrome
-
-
non-syndromic
isolated polydactyly, a.k.a. polysyndactyly
isolated brachydactyly, a.k.a. brachysyndactyly
isolated ectrodactyly
Pathology
There is a very wide spectrum of syndactyly ranging from partial to complete.
Location
Overall, the 2nd and 3rd digits tend to be most frequently associated 6. May involve the toes more than the fingers.
Radiographic features
Plain radiograph
Postnatally the type and degree of bony syndactyly can be easily diagnosed on plain film.
Ultrasound
Often difficult to diagnose on ultrasound (especially with soft tissue syndactyly). The diagnosis may be suggested if the digits appear to constantly move together 7. The fingers may appear constantly deformed with complex syndactyly 6.
Treatment and prognosis
The overall prognosis can be extremely variable depending on the presence of other associated anomalies.
History and etymology
The term syndactyly is derived from the Greek words "syn" meaning together and "daktulos" meaning fingers.






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.