Niemann-Pick disease type C
Updates to Case Attributes
This patient was homozygous for the most common mutation in NPC, I1061T. Whilst this case is normally associated with juvenile onset and death before adulthood, this patient lived well into middle-adulthood adulthood. He presented initially with hepatosplenomegaly and cholestatic jaundice at birth, which slowly resolved, and his genetic diagnosis was not made until clear learning difficulties presented in his pre-teen years.
He later presented in young adulthood with a psychotic mood disorder, consistent with a rapid-cycling bipolar disorder. At this time he also demonstrated clear vertical supranuclear gaze palsy and cerebellar ataxia, consistent with a diagnosis of NPC. His presentation did not respond to antipsychotics but responded to sodium valproate. The development of cognitive impairment responded for a time to the addition of donepezil.
-<p>This patient was homozygous for the most common mutation in NPC, I1061T. Whilst this case is normally associated with juvenile onset and death before adulthood, this patient lived well into middle-adulthood. He presented initially with hepatosplenomegaly and cholestatic jaundice at birth, which slowly resolved, and his genetic diagnosis was not made until clear learning difficulties presented in his pre-teen years.</p><p>He later presented in young adulthood with a psychotic mood disorder, consistent with a rapid-cycling bipolar disorder. At this time he also demonstrated clear vertical supranuclear gaze palsy and cerebellar ataxia, consistent with a diagnosis of NPC. His presentation did not respond to antipsychotics but responded to sodium valproate. The development of cognitive impairment responded for a time to the addition of donepezil.</p>- +<p>This patient was homozygous for the most common mutation in NPC, I1061T. Whilst this case is normally associated with juvenile onset and death before adulthood, this patient lived well into middle adulthood. He presented initially with hepatosplenomegaly and cholestatic jaundice at birth, which slowly resolved, and his genetic diagnosis was not made until clear learning difficulties presented in his pre-teen years.</p><p>He later presented in young adulthood with a psychotic mood disorder, consistent with a rapid-cycling bipolar disorder. At this time he also demonstrated clear vertical supranuclear gaze palsy and cerebellar ataxia, consistent with a diagnosis of NPC. His presentation did not respond to antipsychotics but responded to sodium valproate. The development of cognitive impairment responded for a time to the addition of donepezil.</p>
References changed:
- 1. Walterfang, M, Fietz, M, Fahey, M, Sullivan, D, Leane, P, Lubman, DI, & Velakoulis, D. The Neuropsychiatry of Niemann-Pick Type C Disease in Adulthood. (2006) The Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences,18(2), pp 158-70. <a href="https://doi.org/10.1176/jnp.2006.18.2.158">doi:10.1176/jnp.2006.18.2.158</a> <span class="ref_v4"></span>
- 2. Walterfang, M, Fahey, M, Sullivan, D, Leane, P, Desmond, P, Wood, A, Seal, ML, Steward, C, Adamson, C, Kokkinos, C, Fietz, M & Velakoulis, D. White and gray matter alterations in adults with Niemann-Pick disease type C: a cross-sectional study. (2010) Neurology, 75, pp 49-56. <a href="https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181e6210e">doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181e6210e</a> - <a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20484681">Pubmed</a> <span class="ref_v4"></span>
- 1. Walterfang, M, Fietz, M, Fahey, M, Sullivan, D, Leane, P, Lubman, DI, & Velakoulis, D (2006). The Neuropsychiatry of Niemann-Pick Type C Disease in Adulthood. The Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 18(2), pp 158 - 170.
- 2. Walterfang, M, Fahey, M, Sullivan, D, Leane, P, Desmond, P, Wood, A, Seal, ML, Steward, C, Adamson, C, Kokkinos, C, Fietz, M & Velakoulis, D (2010). White and gray matter alterations in adults with Niemann-Pick disease type C: A cross-sectional study. Neurology, 75, pp 49 - 56.
Updates to Freetext Attributes
Niemann-Pick disease, type C (NPC) is a neurovisceral storage disease occuringoccurring as a result of defective intracellular (chole)sterol trafficking, caused by mutations in the NPC1 and NPC2 genes. Approximately 1/3 of cases present in adulthood, often with major mental illness, comorbid with ataxia, dysarthria, cognitive impairment and vertical gaze palsy (affecting saccadic movements with pursuit movements preserved until late). It should be considered in any patient with an undiagnosed ataxia or a chronic treatment-resistant mental illness associated with atypical neurological signs, gaze palsy, or cognitive impairment. Neurons are most affected in the cerebellum, followed by subcortical regions such as thalamus, basal ganglia, and hippocampus. White matter is diffusely affected.
Common imaging findings in adult NPC include ventricular enlargement, mild sulcal widening (often with an anterior localization), and cerebellar hemisphere and vermis atrophy. Some patients show hippocampal atrophy, and younger patients often show hyperintensity of periventricular white matter due to more fulminant white matter pathology.
Updates to Study Attributes
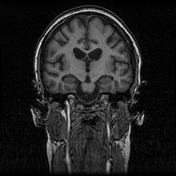
Mild cerebral atrophy with no appreciable lobar predominance and hippocampal size not disproportionate. Moderate cerebellar atrophy, most prominently involving the superior vermis/cerebellar hemispheres. Mild periventricular T2 FLAIR hyperintensity. A more focal small area of T2 FLAIR hyperintensity is in the right anterior centrum semiovale and similarly immediately to the left of the inferior cerebellar vermis. No restricted diffusion.
Normal flow voids within the imaged intracranial arteries. Findings in keeping with known Niemann Pick's disease.
Image MRI (T1) ( update )
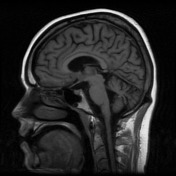
Image MRI (T2) ( update )
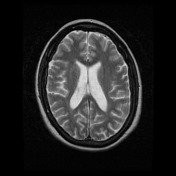
Image MRI (T1) ( update )







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.