1,189 results found
Article
Thoracic plane
The thoracic plane, also known as the transthoracic plane or the plane of Ludwig is an artificial horizontal plane used to divide the mediastinum into the superior mediastinum and the inferior mediastinum.
It is defined as a horizontal line that runs from the manubriosternal joint (sternal angl...
Article
Plane joint
Plane joints, also known as gliding joints, are a type of synovial joint between flat or near-flat articular surfaces.
Movements
Under normal conditions plane joints only permit sliding movement in the same plane as the articular surfaces, and do not allow movement in any other plane. The de...
Article
Transpyloric plane
The transpyloric plane, also known as Addison's plane, is an imaginary axial plane located midway between the jugular notch and superior border of pubic symphysis, at approximately the level of L1 vertebral body. It an important landmark as many key structures are visualised at this level, altho...
Article
Cardiac imaging planes
Cardiac imaging planes are standard orientations for displaying the heart on MRI, CT, SPECT, and PET, similar to those used in echocardiography. The planes are defined in reference to the long axis of the left ventricle, which is the line that connects the ventricular apex to the centre of the m...
Article
Avascular plane of Brodel
The avascular plane of Brodel is the section of renal parenchyma between 2/3 anterior and 1/3 posterior kidney on the cross-section that is relatively avascular. The reason for its relative avascularity is that it represents the plane where the anterior and posterior segmental renal artery branc...
Article
Thoracic plane (mnemonic)
A handy mnemonic to remember the structures found at the level of the thoracic plane (also known as the plane of Ludwig) is:
CLAPTRAP
RAT PLANT
Mnemonic
CLAPTRAP
C: cardiac plexus
L: ligamentum arteriosum
A: aortic arch (inner concavity)
P: pulmonary trunk
T: tracheal bifurcation (carin...
Article
Axial plane for imaging of the brain
A consistent axial plane for imaging of the brain needs to be chosen to allow for reproducible image acquisition and comparison. Unlike the sagittal plane, which is intrinsically defined by our inherent left-right plane of symmetry, axial and coronal planes need to be agreed upon and over the ye...
Article
Mitral annular plane systolic excursion
Mitral annular plane systolic excursion (MAPSE) refers to the displacement of the mitral valvular plane in the z-direction and reflects left ventricular longitudinal contraction or shortening, which has been attributed to account for about 60% of the stroke volume 1.
Terminology
Mitral annular...
Article
Tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion
Tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE) also known as tricuspid annular motion refers to the displacement of the tricuspid valvular plane in the z-direction, reflects right ventricular longitudinal contraction or shortening.
Usage
Tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion can be me...
Article
Subcallosal line
The subcallosal line connects the inferior surface of the genu of the corpus callosum to the inferior surface of the splenium and is used to define an axial plane for imaging of the brain 1.
The alternative AC-PC line is most commonly used, however, the subcallosal plane remains recommended fo...
Article
Properitoneal fat
The properitoneal fat, also known as the preperitoneal space, is a fat-containing space in the abdomen.
Posteriorly it lies deep to the transversalis fascia and fills the posterior pararenal space. Laterally it thickens and forms the properitoneal fat pad, which is the anterior extension of pos...
Article
Pronator quadratus sign
The pronator quadratus sign, also known as MacEwan sign, can be an indirect sign of distal forearm trauma. It relies on displacement of the fat pad that lies superficial to the pronator quadratus muscle as seen on a lateral wrist radiograph.
Pathology
Displacement, anterior bowing, or oblitera...
Case
Temporal bone CT planes
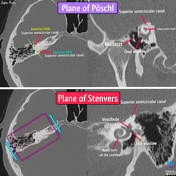
Published
31 Aug 2022
42% complete
Annotated image
CT
Article
Scapula method
The scapula method is used to assess posterior humeral head subluxation in patients with glenohumeral osteoarthritis as part of the work-up for shoulder arthroplasty.
Method
First, the scapular axis (medial border of the scapular body to centre of the glenoid) is drawn on an axial image that ...
Article
Saddle joint
Saddle joints are a type of synovial joint that allow articulation by reciprocal reception. Both bones have concave-convex articular surfaces which interlock like two saddles opposed to one another.
Movements
Saddle joints allow movement with two degrees of freedom much like condyloid joints...
Case
Avascular plane of Brodel (diagram)

Published
19 May 2012
35% complete
Diagram
Case
Transcerebellar plane and nuchal fold measurement
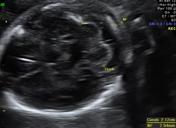
Published
25 Jul 2014
32% complete
Ultrasound
Case
Anatomical planes (creative commons illustration)
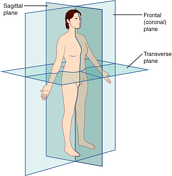
Published
20 Mar 2018
32% complete
Diagram
Case
Cardiac MRI - standard imaging planes

Published
08 Jul 2011
24% complete
MRI
Question
Question 935
Which of the following does NOT occur at the transthoracic plane?









 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.