102 results found
Article
CT pelvis (protocol)
The CT pelvis protocol serves as an outline for the acquisition of a pelvic CT. As a separate examination, it might be performed as a non-contrast or contrast study or might be combined with a CT hip or rarely with a CT cystogram. A pelvic CT might be also conducted as a part of other scans such...
Article
Tuberculous pelvic inflammatory disease
Tuberculous pelvic inflammatory disease refers to pelvic inflammatory disease due to Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Epidemiology
Genital tract involvement may be present in ~1.5% of cases of those affected with tuberculosis 4.
Pathology
Infection almost always results from spread from an extrag...
Article
Obstetrics and gynecology imaging for students (curriculum)
This is a basic article for medical students and other non-radiologists
Obstetrics and Gynecology imaging for students curriculum represents a core set of common pathologies seen on the wards, in theater and in the emergency O&G patient.
Fundamental to most imaging of the O&G patient is an und...
Article
Ovarian transposition
Ovarian transposition is a surgical procedure in which the ovaries are displaced from the pelvis before pelvic radiation therapy in order to protect them from radiation injury.
It is performed in premenopausal women with a variety of pelvic malignancies (e.g cervical cancer, rectal cancer, and ...
Article
Lymphoma of the uterine cervix
Lymphoma of the uterine cervix is generally uncommon and when it does occur tends to present as cervical involvement with added background multi-organ disease rather than isolated primary cervical lymphoma 1. It is often considered part of the spectrum of uterine lymphoma.
Epidemiology
In the ...
Article
Pelvis
The term pelvis (plural: pelvises or pelves) can refer to either the bony pelvis or the pelvic cavity.
Bony pelvis
The bony pelvis is formed by the sacrum and coccyx and a pair of hip bones ("ossa coxae"), which are part of the appendicular skeleton. Its primary function is the transmission of...
Article
Cervical carcinoma
Cervical carcinoma is a malignancy arising from the cervix. It is the third most common gynecologic malignancy (after endometrial and ovarian).
Epidemiology
It typically presents in younger women with an average age of onset at around 45 years.
Risk factors
human papillomavirus (HPV) 16 and...
Article
Pelvic congestion syndrome
Pelvic congestion syndrome (some prefer pelvic venous insufficiency 9 ) is a condition that results from retrograde flow through incompetent valves in ovarian veins resulting in pelvic varices and pelvic pain. It is a commonly missed and potentially treatable cause of chronic abdominopelvic pain...
Article
Perineum
The perineum is a diamond-shaped region below the pelvic diaphragm and is divided by an imaginary line drawn between the ischial tuberosities into anteriorly the urogenital triangle and posteriorly the anal triangle.
Gross anatomy
The perineum is bounded by the pubis anteriorly, the ischial tu...
Case
Bilateral ovarian dermoid cyst
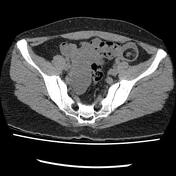
Published
16 Mar 2022
83% complete
CT
Article
Endometrioma
Endometriomas, also known as chocolate cysts or endometriotic cysts, are a localized form of endometriosis and are usually within the ovary. They are readily diagnosed on ultrasound, with most demonstrating classical radiographic features.
Epidemiology
These occur in up to 10% of women of rep...
Article
Kissing ovaries sign
The kissing ovaries sign refers to the appearance seen when both ovaries are located in close proximity or are touching each other in the pouch of Douglas, usually due to pelvic adhesions, and may be seen on ultrasound, CT or MRI.
This sign is most frequently associated with the severe form of ...
Article
Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome
Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome (FHCS), or perihepatitis, is the inflammation of the liver capsule and overlying peritoneum associated with adhesion formation, without the involvement of the hepatic parenchyma. It is a chronic complication of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
Epidemiology
The preva...
Article
Pelvic lipomatosis
Pelvic lipomatosis or pelvic fibrolipomatosis represents excessive deposition of fat in the pelvis due to overgrowth of adipose cells leading to compression of pelvic organs.
Epidemiology
The condition usually presents in patients 20-50 years of age. The condition is predominantly (~66% of cas...
Article
Mullerianosis
Mullerianosis is a rare type of choristoma, in which normal Mullerian-derived structures (endometrium, endosalpinx, and endocervix) are ectopically located in another organ (e.g. the bladder) through a developmental anomaly. Mullerianosis differs from endometriosis in that at least two types of ...
Article
Endometrial carcinoma
Endometrial carcinoma is generally considered the most common gynecological malignancy. It frequently presents with vaginal bleeding. Both ultrasound and pelvic MRI are useful modalities for evaluation.
Epidemiology
Endometrial carcinoma is the most common gynecological malignancy, with peak i...
Article
Intrapelvic cup migration
Intrapelvic cup migration is a serious complication after total hip arthroplasty, in which the prosthetic acetabular cup migrates or drifts into the pelvic inlet.
Epidemiology
Fortunately, this complication is very rare. There seems to be a female predisposition 1-3.
Risk factors
Factors inc...
Article
Endosalpingiosis
Endosalpingiosis refers to the presence of ciliated, glandular epithelium resembling the inner lining of the fallopian tube located in an ectopic location. The condition may present as cystic structures usually implanted on the peritoneal serosa 1.
Epidemiology
Endosalpingiosis is considered a...
Article
CT abdomen-pelvis (protocol)
The CT abdomen-pelvis protocol serves as an outline for an examination of the whole abdomen including the pelvis. It is one of the most common CT protocols for any clinical questions related to the abdomen and/or in routine and emergencies. It forms also an integral part of trauma and oncologic ...
Article
Uterus
The uterus is an extraperitoneal hollow, thick-walled, muscular organ of the female reproductive tract that lies in the lesser pelvis.
Gross anatomy
The uterus has an inverted pear shape. It measures about 7.5 cm in length, 5 cm wide at its upper part, and nearly 2.5 cm in thickness in adults....









 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.