CT angiography of the cerebral arteries (protocol)
Updates to Article Attributes
Noninvasive technique allows visualization of the carotid and vertebrobasilar arteries at extra and intra cranial levels.
By using Multi-Detector CT and after IVintravenous contrast administration, the vessels become enhanced with contrast allow them to be differentiated from adjacent tissues.
Following image acquisition, post processing techniques are applied for better 3D visualization of the vessels and their abnormalities.
Anatomical consideration
The brain is supplied by two sets of vessels. The anterior circulation roughly supplies the anterior 2/3 while the posterior circulation supplies the posterior 1/3 of the brain.
The anterior circulation consists of the carotid arteries. The right common carotid artery arises from the brachiocephalic trunk while the left common carotid artery arises directly from the aortaAorta. They ascend behind the sternoclavicular joints, lateral to the thyroid gland and at the level of upper border of thyroid cartilage, each one divides into external and internal carotid arteries. The internal carotid artery ascends to enter the skull through the carotid canal and bifurcates into the anterior and middle cerebral arteries.
The posterior circulation consists of the vertebrobasilar system. Each vertebral artery arises from the 1st part of the corresponding subclavian artery. At the neck it ascends inside the transverse foramina from C6 to C2 where it emerges and enter the cranium through foramen magnum. Both vertebral arteries unite to form the basilar artery which passes in front of the pons and ends by bifurcation to posterior cerebral arteries on both sides.
Indications
·
·Patients withtransient ischemic attack TIA to detect carotid artery stenosis and plaques.
·Patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage for detection of aneurysms.
·Patients with cerebral parenchymal hemorrhage for AVM.
Contraindications
·
Advantages
·
·Non-flow dependent technique which allows accurate estimation of degree and length of stenosis.
·Less expensive and lower risk to the patient.
Disadvantages
·
·Beam hardening artifacts from dense calcification.
·Require the use of iodinated contrast media.
Technique
To obtain high quality images of vessels, iodinated contrast media should be administered. The contrast material could be injected using fixed scan delay technique, test bolus injection technique or automated bolus tracking technique. The amount of contrast agent differs according to the patient's weight, technique of injection and the number of detector in CT machine.
MDCT is essential for acquiring volume that can be used in post processing formation. 4 slices MDCT scanners or more are ideal, yet more slices give better images.
2D set of images is obtained which contains the axial source images. These images are transferred to workstation for more processing. Post processing techniques include:
Maximum intensity projection MIP. Displays pixels with higher CT value. Easy to obtain but less sensitive.
Multiplanar curved reformat MPR. Delineates the entire course of the vessel and can be used when the vessel is tortuous.
Surface shaded display SSD. Only the pixels above a user defined threshold value are displayed. It is used mainly for pre-operative planning.
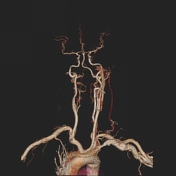
Volume rendering VR. Again a threshold value is determined by the user as SSD however it includes surface and non-surface pixels and displayed processed data on 3D.
-<p style="text-align:justify"><span style="font-size:14.0pt">Noninvasive technique allows visualization of the carotid and vertebrobasilar arteries at extra and intra cranial levels.</span></p><p style="text-align:justify"><span style="font-size:14.0pt">By using Multi-Detector CT and after IV contrast administration, the vessels become enhanced with contrast allow them to be differentiated from adjacent tissues. </span></p><p style="text-align:justify"><span style="font-size:14.0pt">Following image acquisition, post processing techniques are applied for better 3D visualization of the vessels and their abnormalities. </span></p><p style="text-align:justify"><span style="font-size:14.0pt"> </span></p><h4 style="text-align: justify;"><strong><span style="font-size:14.0pt">Anatomical consideration</span></strong></h4><p style="text-align:justify"><span style="font-size:14.0pt">The brain is supplied by two sets of vessels. The anterior circulation roughly supplies the anterior 2/3 while the posterior circulation supplies the posterior 1/3 of the brain. </span></p><p style="text-align:justify"><span style="font-size:14.0pt">The anterior circulation consists of the carotid arteries. The right common carotid artery arises from the brachiocephalic trunk while the left common carotid artery arises directly from the aorta. They ascend behind the sternoclavicular joints, lateral to the thyroid gland and at the level of upper border of thyroid cartilage, each one divides into external and internal carotid arteries. The internal carotid artery ascends to enter the skull through the carotid canal and bifurcates into the anterior and middle cerebral arteries. </span></p><p style="text-align:justify"><span style="font-size:14.0pt">The posterior circulation consists of the vertebrobasilar system. Each vertebral artery arises from the 1<sup>st</sup> part of the corresponding subclavian artery. At the neck it ascends inside the transverse foramina from C6 to C2 where it emerges and enter the cranium through foramen magnum. Both vertebral arteries unite to form the basilar artery which passes in front of the pons and ends by bifurcation to posterior cerebral arteries on both sides. </span></p><p style="text-align:justify"> </p><p style="text-align:justify"><strong><span style="font-size:14.0pt">Indications</span></strong></p><p style="text-align:justify"><!--[if !supportLists]--><span style="font-family:symbol; font-size:14.0pt">·<span style="font-family:times new roman; font-size:7pt"> </span></span><!--[endif]--><span style="font-size:14.0pt">Patients with acute stroke to detect occlusion and thrombosis.</span></p><p style="text-align:justify"><!--[if !supportLists]--><span style="font-family:symbol; font-size:14.0pt">·<span style="font-family:times new roman; font-size:7pt"> </span></span><!--[endif]--><span style="font-size:14.0pt">Patients with TIA to detect carotid artery stenosis and plaques.</span></p><p style="text-align:justify"><!--[if !supportLists]--><span style="font-family:symbol; font-size:14.0pt">·<span style="font-family:times new roman; font-size:7pt"> </span></span><!--[endif]--><span style="font-size:14.0pt">Patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage for detection of aneurysms.</span></p><p style="text-align:justify"><!--[if !supportLists]--><span style="font-family:symbol; font-size:14.0pt">·<span style="font-family:times new roman; font-size:7pt"> </span></span><!--[endif]--><span style="font-size:14.0pt">Patients with cerebral parenchymal hemorrhage for AVM.</span></p><h4 style="text-align: justify;"> </h4><h4 style="text-align: justify;"> </h4><h4 style="text-align: justify;"><strong><span style="font-size:14.0pt">Contraindications</span></strong></h4><p style="text-align: justify;"><!--[if !supportLists]--><span style="font-family:symbol; font-size:14.0pt">·<span style="font-family:times new roman; font-size:7pt"> </span></span><!--[endif]--><span style="font-size:14.0pt">Known hypersensitivity to iodinated contrast media.</span></p><p style="text-align: justify;"> </p><p style="text-align: justify;"><strong><span style="font-size:14.0pt">Advantages </span></strong></p><p style="text-align:justify"><!--[if !supportLists]--><span style="font-family:symbol; font-size:14.0pt">·<span style="font-family:times new roman; font-size:7pt"> </span></span><!--[endif]--><span style="font-size:14.0pt">Multi-detector CT can cover the vessels from their origin at the aortic arch to the intra cranial portion. It is not only useful for assessment of the blood vessel, but also can evaluate neck structures and brain parenchyma.</span></p><p style="text-align:justify"><!--[if !supportLists]--><span style="font-family:symbol; font-size:14.0pt">·<span style="font-family:times new roman; font-size:7pt"> </span></span><!--[endif]--><span style="font-size:14.0pt">Non-flow dependent technique which allows accurate estimation of degree and length of stenosis.</span></p><p style="text-align:justify"><!--[if !supportLists]--><span style="font-family:symbol; font-size:14.0pt">·<span style="font-family:times new roman; font-size:7pt"> </span></span><!--[endif]--><span style="font-size:14.0pt">Less expensive and lower risk to the patient. </span></p><h4 style="text-align: justify;"> </h4><h4 style="text-align: justify;"><strong><span style="font-size:14.0pt">Disadvantages</span></strong></h4><p style="text-align:justify"><!--[if !supportLists]--><span style="font-family:symbol; font-size:14.0pt">·<span style="font-family:times new roman; font-size:7pt"> </span></span><!--[endif]--><span style="font-size:14.0pt">Long processing time.</span></p><p style="text-align:justify"><!--[if !supportLists]--><span style="font-family:symbol; font-size:14.0pt">·<span style="font-family:times new roman; font-size:7pt"> </span></span><!--[endif]--><span style="font-size:14.0pt">Beam hardening artifacts from dense calcification. </span></p><p style="text-align:justify"><!--[if !supportLists]--><span style="font-family:symbol; font-size:14.0pt">·<span style="font-family:times new roman; font-size:7pt"> </span></span><!--[endif]--><span style="font-size:14.0pt">Require the use of iodinated contrast media. </span></p><p style="text-align:justify"><span style="font-size:14.0pt"> </span></p><p style="text-align:justify"><strong><span style="font-size:14.0pt">Technique</span></strong></p><p style="text-align:justify"><span style="font-size:14.0pt">To obtain high quality images of vessels, iodinated contrast media should be administered. The contrast material could be injected using fixed scan delay technique, test bolus injection technique or automated bolus tracking technique. The amount of contrast agent differs according to the patient's weight, technique of injection and the number of detector in CT machine. </span></p><p style="text-align:justify"><span style="font-size:14.0pt">MDCT is essential for acquiring volume that can be used in post processing formation. 4 slices MDCT scanners or more are ideal, yet more slices give better images. </span></p><p style="text-align:justify"><span style="font-size:14.0pt">2D set of images is obtained which contains the axial source images. These images are transferred to workstation for more processing. Post processing techniques include:</span></p><p style="text-align:justify"><!--[if !supportLists]--><span style="font-family:symbol; font-size:14.0pt">·<span style="font-family:times new roman; font-size:7pt"> </span></span><!--[endif]--><span style="font-size:14.0pt"><strong>Maximum intensity projection MIP</strong>. Displays pixels with higher CT value. Easy to obtain but less sensitive. </span></p><p style="text-align:justify"><!--[if !supportLists]--><span style="font-family:symbol; font-size:14.0pt">·<span style="font-family:times new roman; font-size:7pt"> </span></span><!--[endif]--><span style="font-size:14.0pt"><strong>Multiplanar curved reformat MPR</strong>. Delineates the entire course of the vessel and can be used when the vessel is tortuous. </span></p><p style="text-align:justify"><!--[if !supportLists]--><span style="font-family:symbol; font-size:14.0pt">·<span style="font-family:times new roman; font-size:7pt"> </span></span><span style="font-size:14.0pt"><strong>Surface shaded display SSD</strong>. Only the pixels above a user defined threshold value are displayed. It is used mainly for pre-operative planning. </span></p><p style="text-align:justify"><!--[if !supportLists]--><span style="font-family:symbol; font-size:14.0pt">·<span style="font-family:times new roman; font-size:7pt"> </span></span><!--[endif]--><span style="font-size:14.0pt"><strong>Volume rendering VR</strong>. Again a threshold value is determined by the user as SSD however it includes surface and non-surface pixels and displayed processed data on 3D. </span></p><p style="text-align:justify"><span style="font-size:14.0pt"> </span></p>- +<p>Noninvasive technique allows visualization of the carotid and vertebrobasilar arteries at extra and intra cranial levels.</p><p>By using Multi-Detector CT and after intravenous contrast administration, the vessels become enhanced with contrast allow them to be differentiated from adjacent tissues.</p><p>Following image acquisition, post processing techniques are applied for better 3D visualization of the vessels and their abnormalities.</p><h4><strong>Anatomical consideration</strong></h4><p>The brain is supplied by two sets of vessels. The anterior circulation roughly supplies the anterior 2/3 while the posterior circulation supplies the posterior 1/3 of the brain.</p><p>The anterior circulation consists of the carotid arteries. The right <a href="/articles/common-carotid-artery-2">common carotid artery</a> arises from the <a href="/articles/brachiocephalic-trunk">brachiocephalic trunk </a>while the left <a href="/articles/common-carotid-artery-2">common carotid artery</a> arises directly from the <a href="/articles/aorta">Aorta</a>. They ascend behind the sternoclavicular joints, lateral to the thyroid gland and at the level of upper border of thyroid cartilage, each one divides into <a href="/articles/external-carotid-artery-1">external</a> and <a href="/articles/internal-carotid-artery-1">internal carotid arteries</a>. The <a href="/articles/internal-carotid-artery-1">internal carotid artery</a> ascends to enter the skull through the carotid canal and bifurcates into the anterior and middle cerebral arteries.</p><p>The posterior circulation consists of the vertebrobasilar system. Each <a href="/articles/vertebral-artery">vertebral artery</a> arises from the 1<sup>st</sup> part of the corresponding <a href="/articles/subclavian-artery">subclavian artery</a>. At the neck it ascends inside the transverse foramina from C6 to C2 where it emerges and enter the cranium through foramen magnum. Both <a href="/articles/vertebral-artery">vertebral arteries</a> unite to form the <a href="/articles/basilar-artery">basilar artery</a> which passes in front of the pons and ends by bifurcation to <a href="/articles/posterior-cerebral-artery">posterior cerebral arteries</a> on both sides.</p><h4><strong>Indications</strong></h4><ul>
- +<li>Patients with acute stroke to detect occlusion and thrombosis.</li>
- +<li>Patients with <a href="/articles/transient-ischaemic-attack">transient ischemic attack</a> TIA to detect <a href="/articles/carotid-artery-stenosis">carotid artery stenosis</a> and plaques.</li>
- +<li>Patients with <a href="/articles/subarachnoid-haemorrhage">subarachnoid hemorrhage</a> for detection of aneurysms.</li>
- +<li>Patients with cerebral parenchymal hemorrhage for <a href="/articles/cerebral-arteriovenous-malformation">AVM</a>.</li>
- +</ul><h4><strong>Contraindications</strong></h4><ul><li>Known hypersensitivity to iodinated contrast media.</li></ul><h4><strong>Advantages </strong></h4><ul>
- +<li>Multi-detector CT can cover the vessels from their origin at the aortic arch to the intra cranial portion. It is not only useful for assessment of the blood vessel, but also can evaluate neck structures and brain parenchyma.</li>
- +<li>Non-flow dependent technique which allows accurate estimation of degree and length of stenosis.</li>
- +<li>Less expensive and lower risk to the patient.</li>
- +</ul><h4><strong>Disadvantages</strong></h4><ul>
- +<li>Long processing time.</li>
- +<li>Beam hardening artifacts from dense calcification.</li>
- +<li>Require the use of iodinated contrast media.</li>
- +</ul><h4><strong>Technique</strong></h4><p>To obtain high quality images of vessels, iodinated contrast media should be administered. The contrast material could be injected using fixed scan delay technique, test bolus injection technique or automated bolus tracking technique. The amount of contrast agent differs according to the patient's weight, technique of injection and the number of detector in CT machine.</p><p>MDCT is essential for acquiring volume that can be used in post processing formation. 4 slices MDCT scanners or more are ideal, yet more slices give better images.</p><p>2D set of images is obtained which contains the axial source images. These images are transferred to workstation for more processing. Post processing techniques include:</p><p><strong><a href="/articles/maximum-intensity-projection-mip">Maximum intensity projection</a></strong><a href="/articles/maximum-intensity-projection-mip"><strong> MIP</strong></a>. Displays pixels with higher CT value. Easy to obtain but less sensitive.</p><p><strong>Multiplanar curved reformat MPR</strong>. Delineates the entire course of the vessel and can be used when the vessel is tortuous.</p><p><strong>Surface shaded display SSD</strong>. Only the pixels above a user defined threshold value are displayed. It is used mainly for pre-operative planning.</p><p><strong>Volume rendering VR</strong>. Again a threshold value is determined by the user as SSD however it includes surface and non-surface pixels and displayed processed data on 3D.</p><p> </p>
References changed:
- 2. Roberto Passariello. Multidetector-Row CT Angiography. <a href="https://books.google.co.uk/books?vid=ISBN9783540269847">ISBN: 9783540269847</a><span class="ref_v4"></span>
- 1. R. Gilberto González, Joshua A. Hirsch, Michael H. Lev, et al. Acute Ischemic Stroke. <a href="https://books.google.co.uk/books?vid=ISBN9783642127519">ISBN: 9783642127519</a><span class="ref_v4"></span>
Tags changed:
- brain
- ct-angiogram
Sections changed:
- Approach
Systems changed:
- Central Nervous System
Image 1 CT (MIP) ( create )
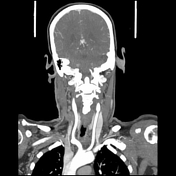
Image 2 CT (3D VR) ( create )







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.