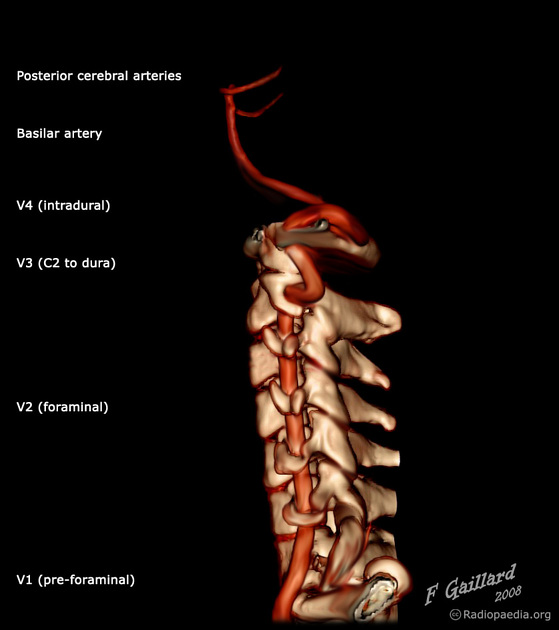
Basilar artery
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Yahya Baba had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
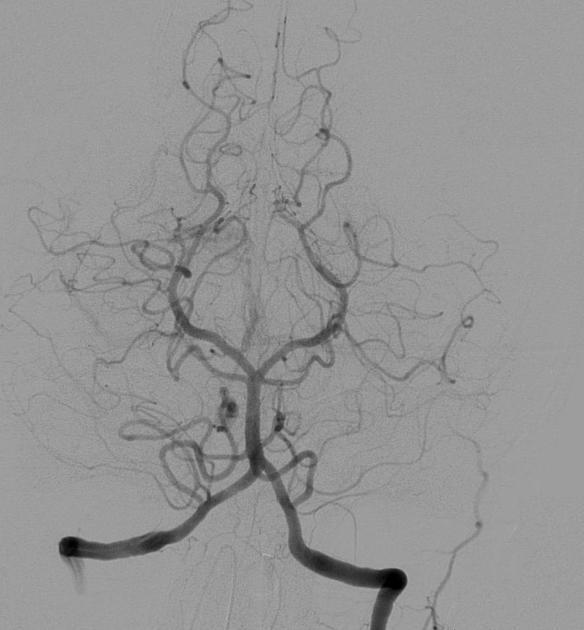
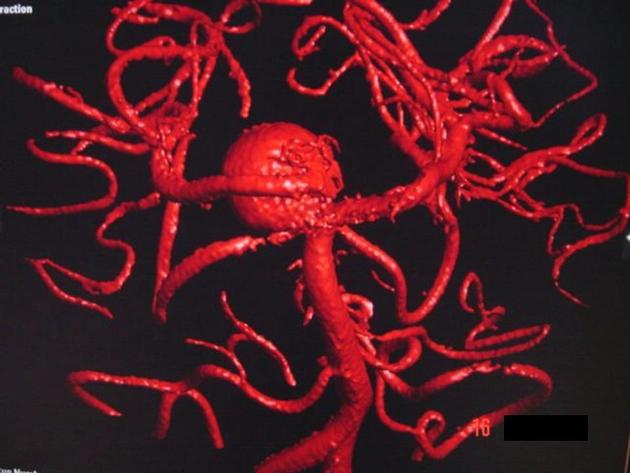
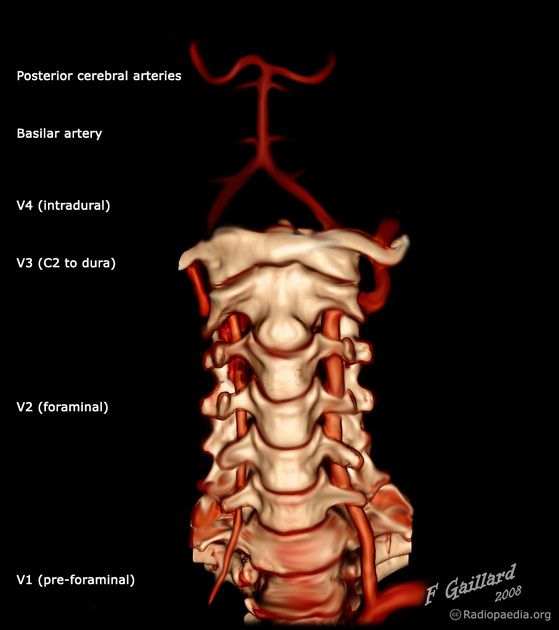
View Yahya Baba's current disclosuresThe basilar artery is part of the posterior cerebral circulation. It arises from the confluence of the left and right vertebral arteries at the base of the pons as they rise towards the base of the brain.
On this page:
Summary
origin: vertebral artery confluence
course: ventral to pons in the pontine cistern
branches: numerous to cerebellum and pons
termination: division into the two posterior cerebral arteries
variants: basilar artery fenestration; persistent carotid-basilar artery anastomoses
Gross anatomy
Course
The basilar artery runs cranially in the central groove of the pons towards the midbrain within the pontine cistern. It travels within this groove from the lower pontine border adjacent to the exit of the abducens nerve to the upper pontine border and the appearance of the oculomotor nerve. It bifurcates at the upper pontine border.
Branches
Before terminating at the upper pontine border where it divides into the two posterior cerebral arteries, it provides several paired branches:
labyrinthine artery (variable origin; more commonly a branch of AICA)
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Variant anatomy
Related pathology
References
- 1. J. Randy Jinkins. Atlas of Neuroradiologic Embryology, Anatomy, and Variants. (2000) ISBN: 9780781716529 - Google Books
- 2. Uchino A, Kato A, Takase Y, Kudo S. Basilar Artery Fenestrations Detected by MR Angiography. Radiat Med. 2001;19(2):71-4. - Pubmed
- 3. Standring S (editor). Gray's Anatomy (39th edition). Churchill Livingstone. (2011) ISBN:0443066841. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 4. Schünke M, Schulte E, Ph.D. LM et-al. Atlas of anatomy, Head and neuroanatomy. George Thieme Verlag. (2007) ISBN:3131421215. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 5. Snell RS. Clinical Neuroanatomy. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. (2010) ISBN:0781794277. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
Incoming Links
- Intracranial atherosclerotic disease
- Pontine arteries
- Trident sign (persistent primitive trigeminal artery)
- Wernekinck commissure syndrome
- Lateral pontine syndrome
- Alobar holoprosencephaly
- Pituitary fossa
- Inferior medial pontine syndrome
- Inferior cervical ganglion
- Gasperini syndrome
- Large vessel occlusion
- Cerebellum
- Central herniation
- Posterior cerebral circulation
- Intracranial epidermoid cyst
- Superior cerebellar artery infarct
- Acute basilar artery occlusion
- Anterior inferior cerebellar artery
- Cerebral arteries
- Peduncular vein
- Tension pneumocephalus
- Anterior inferior cerebellar artery loop (Type III)
- Persistent hypoglossal artery
- Vertebrobasilar artery occlusion - diagnosis and treatment
- Persistent trigeminal artery
- Acute basilar artery occlusion
- Penetrating knife injury to the face and skull
- Intracranial neurenteric cyst
- Bilateral cerebellar infarction
- Diffuse brainstem glioma
- Brainstem arterial territories (diagrams)
- Basilar artery fenestration
- Neurovascular compression syndrome - trigeminal nerve
- Vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia
- Japanese encephalitis
- Epidermoid cyst compressing the trigeminal nerve
- Persistent hypoglossal artery
- Diffuse pontine glioma
- Epidermoid cyst - intracranial
- Intracranial epidermoid cyst
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
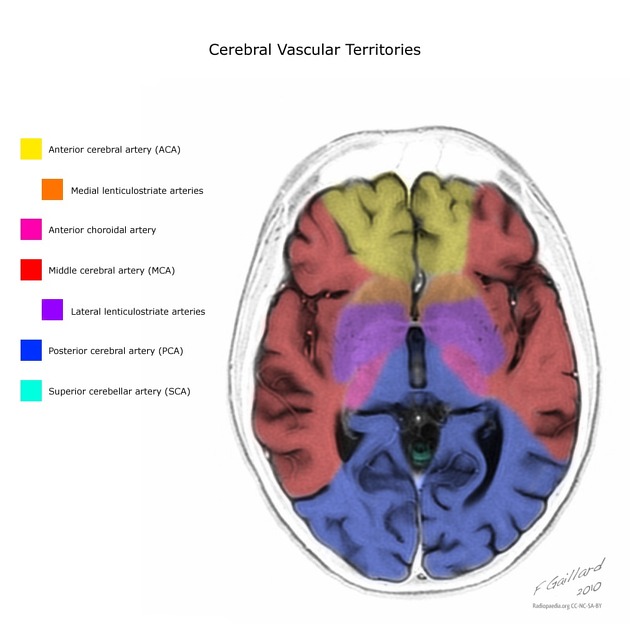
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.