Epiphrenic diverticulum
Updates to Article Attributes
Epiphrenic diverticula are pulsion diverticula of the distal oesophagus arising just above the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), more frequently on the right side.
They are less frequent than traction mid oesophageal diverticula, but may have more clinical relevance.
Clinical presentation
Epiphrenic diverticula may present with symptoms of dysphagia, and regurgitation. When large they can cause distal oesophageal compression.
Associations
They are associated with:
-
achalasiaand other forms of neuromuscular dysfunction of the oesophagus hiatus hernias
PathophysiologyPathology
These are considered to be pulsion type diverticula, thought to arise due to increased intraluminal pressure - and hence the strong association with oesophageal dysmotility.
The diverticulum forms as the submucosa and mucosa herniate focally through the muscularis propria. Since the diverticular wall thus lacks the muscular layer, it is classified as a false diverticulum.
Associations
They are associated with:
- achalasia and other forms of neuromuscular dysfunction of the oesophagus
- hiatus hernias
Radiographic features
Fluoroscopy - Barium swallow
Best imaging method is a contrast oesophagogram, including prone oblique views of the distal oesophagus. One should look for evidence of oesophageal motility disorders and hiatus hernia.
Plain film
On chest x ray, they may appear as a retrocardiac soft tissue mass with or without an air fluid level, mimicing a hiatus hernia.
Treatment and prognosis
Epiphrenic diverticula can be treated surgically with myomectomy or diverticulectomy.
-<p><strong>Epiphrenic diverticula</strong> are pulsion diverticula of the distal oesophagus arising just above the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), more frequently on the right side.</p><p>They are less frequent than traction mid oesophageal diverticula, but may have more clinical relevance. </p><h4>Clinical presentation</h4><p>Epiphrenic diverticula may present with symptoms of dysphagia, and regurgitation. When large they can cause distal oesophageal compression.</p><h5>Associations</h5><p>They are associated with:</p><ul>- +<p><strong>Epiphrenic diverticula</strong> are pulsion diverticula of the distal oesophagus arising just above the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), more frequently on the right side.</p><p>They are less frequent than traction mid oesophageal diverticula, but may have more clinical relevance. </p><h4>Clinical presentation</h4><p>Epiphrenic diverticula may present with symptoms of dysphagia, and regurgitation. When large they can cause distal oesophageal compression.</p><h4>Pathology</h4><p>These are considered to be pulsion type diverticula, thought to arise due to increased intraluminal pressure - and hence the strong association with oesophageal dysmotility.</p><p>The diverticulum forms as the submucosa and mucosa herniate focally through the muscularis propria. Since the diverticular wall thus lacks the muscular layer, it is classified as a false diverticulum.</p><h5>Associations</h5><p>They are associated with:</p><ul>
-<a href="/articles/achalasia">achalasia</a> and other forms of neuromuscular dysfunction of the oesophagus</li>- +<a href="/articles/achalasia">achalasia</a> and other forms of neuromuscular dysfunction of the oesophagus</li>
-</ul><h4>Pathophysiology</h4><p>These are considered to be pulsion type diverticula, thought to arise due to increased intraluminal pressure - and hence the strong association with oesophageal dysmotility.</p><p>The diverticulum forms as the submucosa and mucosa herniate focally through the muscularis propria. Since the diverticular wall thus lacks the muscular layer, it is classified as a false diverticulum.</p><h4>Radiographic features</h4><h5>Fluoroscopy - Barium swallow</h5><p>Best imaging method is a contrast oesophagogram, including prone oblique views of the distal oesophagus. One should look for evidence of oesophageal motility disorders and hiatus hernia. </p><h5>Plain film</h5><p>On chest x ray, they may appear as a retrocardiac soft tissue mass with or without an air fluid level, mimicing a hiatus hernia.</p>- +</ul><h4>Radiographic features</h4><h5>Fluoroscopy - Barium swallow</h5><p>Best imaging method is a contrast oesophagogram, including prone oblique views of the distal oesophagus. One should look for evidence of oesophageal motility disorders and hiatus hernia. </p><h5>Plain film</h5><p>On chest x ray, they may appear as a retrocardiac soft tissue mass with or without an air fluid level, mimicing a hiatus hernia.</p><h4>Treatment and prognosis</h4><p>Epiphrenic diverticula can be treated surgically with myomectomy or diverticulectomy.</p>
References changed:
- 3. Aravinthan A, Nikolic M, Ouyang X et-al. The hidden cause of dysphagia-epiphrenic diverticulum and esophageal motility disorders. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 2012;26 (2): 68-9. <a href="http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3275406">Free text at pubmed</a> - <a href="http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22312603">Pubmed citation</a><span class="auto"></span>
Image 1 Fluoroscopy ( update )
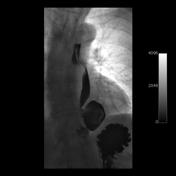
Image 5 Photo ( create )







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.