Leukoencephalopathy with calcification and cysts, also known as Labrune syndrome, is a rare condition that consists of a triad of leukoencephalopathy, cerebral calcification and edematous cysts.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Leukoencephalopathy with calcification and cysts is an extremely rare condition, with only a small number of cases reported in the literature 2,5. Clinical onset occurs from early infancy to late adulthood, with most cases being diagnosed in children to young adults. A modest predilection for females appears to be present (F:M 3:2) 5.
Clinical presentation
Leukoencephalopathy with calcification and cysts can present with a variety of symptoms depending on cyst location and degree of intracranial hypertension. Symptoms include headaches, slowing of cognitive performance, seizures, visual disturbance and a combination of extra-pyramidal, cerebellar, and pyramidal features 1,5.
Pathology
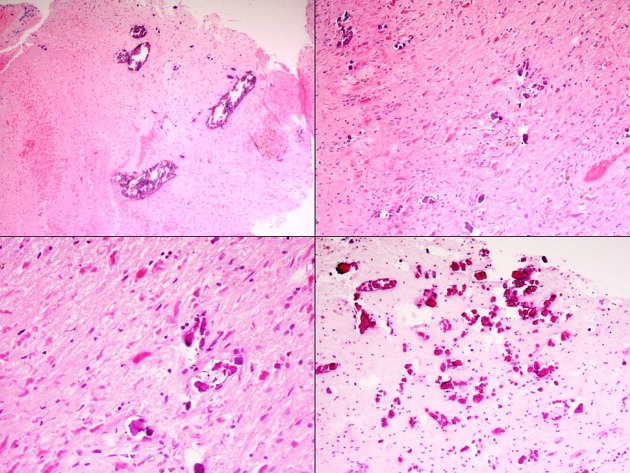
The underlying pathophysiology is thought to be a diffuse cerebral microangiopathy resulting in initially micro cystic, followed by macro cystic, parenchymal degeneration 1.
Histological features include tumor-like vascular hyperplasia, calcification, Renshaw cell proliferation, Rosenthal fibers and glial proliferation 5. A variety of other histological features are also encountered including demyelination, necrosis, iron deposition and hemorrhage 5,6.
Genetics
Leukoencephalopathy with calcification and cysts is caused by mutations in the SNORD118 gene 4,7. This is inherited in an autosomal recessive fashion 7.
Radiographic features
CT
CT is the modality of choice for demonstrating calcification, where progressive calcification in the basal ganglia and cerebellar nuclei, as well as the sub cortical white matter, are invariably seen 5.
MRI
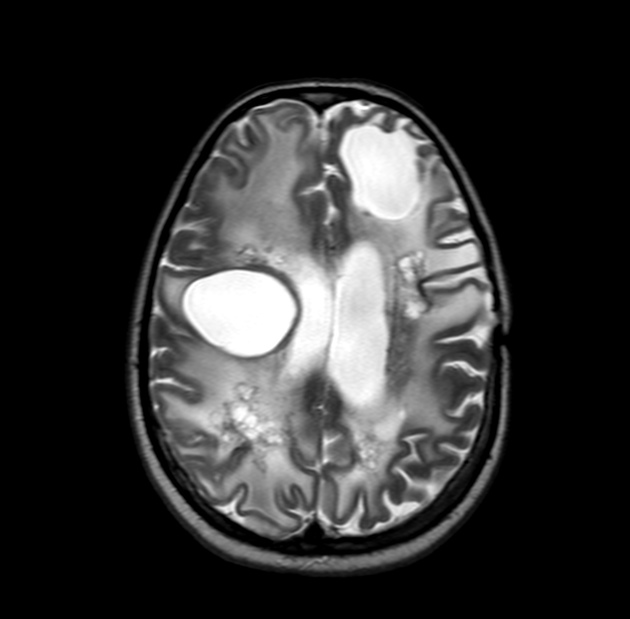
MRI is the modality of choice for demonstrating the leukoencephalopathy and cysts 3,5.
-
cysts
-
location:
supratentorial white matter: centrum semiovale most common
cerebellum
brainstem
basal ganglia
T1: hypointense, but brighter than CSF 3
T2: hyperintense, but brighter than CSF, with FLAIR suppression evident - hyperintensity if presumably due to the absence of flow-induced signal loss 3
DWI: may show increased diffusion signal
-
T1 C+ (Gd)
ring enhancement of the cyst wall may be evident
probably reflecting disruption of the blood-brain barrier 1,3,5
-
-
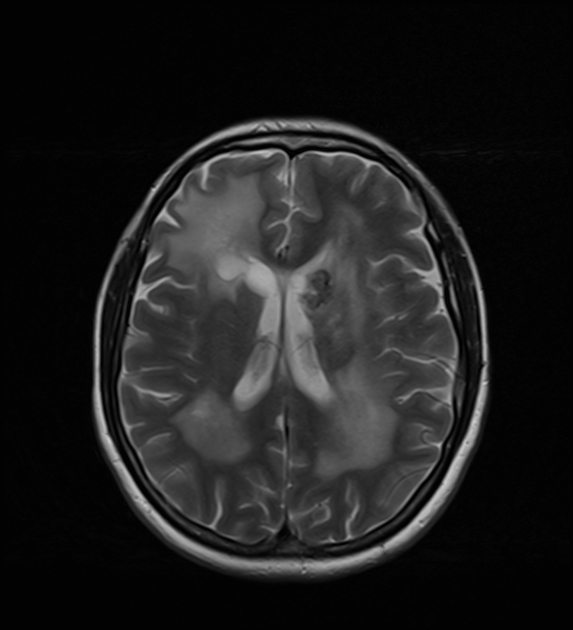
leukoencephalopathy
T2/FLAIR: diffuse hyperintensity in the white matter, especially prominent around cysts (due to vasogenic edema), with relative sparing of the subcortical U-fibers and corpus callosum 3
-
calcification
T1: often hypointense, but can be variable 3
T2/FLAIR: hypointense 3
SWI: hypointense with blooming artifact 3
MR spectroscopy of the cysts may demonstrate a lactate peak and no evidence of the normal metabolites of the brain 3.
Treatment and prognosis
Disease progression is variable in the cases reported in the literature. To date, no specific treatment is available although medical management of epilepsy, edema and raised intracranial pressure is often required 5. Surgical pressure management is also sometimes needed 5.
History and etymology
It was first described by Philippe Labrune (fl. 2017), a French pediatric neurologist, and his colleagues in 1996 1.
Differential diagnosis
On imaging consider:






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.