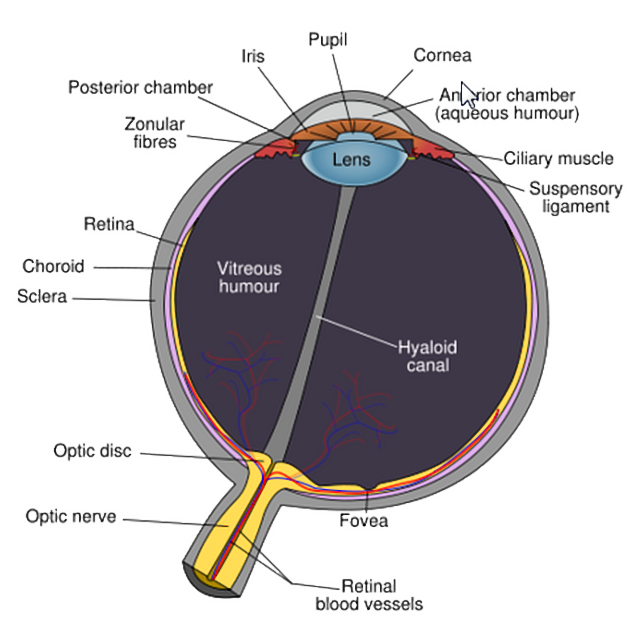
Retinal detachment is a detachment of the neurosensory retina from the underlying pigmented choroid. Apposition of the retinal pigmented epithelium to the overlying retina is essential for normal retinal function.
On this page:
Terminology
There are numerous subtypes of retinal detachment 5:
rhegmatogenous retinal detachment: fluid ingression from the vitreous cavity to the subretinal space causing retinal separation (most common)
retinal break: full-thickness defect in the neurosensory retina, which can be caused by trauma or inflammation
lattice degeneration: circular retinal holes or atrophic holes
tractional retinal detachment: secondary to retinal fibrosis
exudative retinal detachment: due to choroidal tumors causing increased flow through the subretinal space
Epidemiology
Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment is most common in the 6th and 7th decade of life but can occur at any age and has a slight male predilection 5. The annual incidence is variable. Observational studies with sample sizes >300 showed a median annual incidence of 1 in 10,000 6.
Clinical presentation
Retinal detachment is often associated with:
retinal photopsia (flashes)
visual floaters
reduced visual acuity
progressive peripheral visual field loss
Pathology
Etiology
Retinal detachments are classified as rhegmatogenous, meaning caused by a tear (rhegma) in the retina, or non-rhegmatogenous. The interplay between vitreoretinal traction and predisposing retinal lesions is associated with retinal detachment.
Rhegmatogenous retinal detachments are more common, with the primary causes being:
posterior vitreous detachment (most common)
Causes of non-rhegmatogenous retinal detachment include tractional and exudative. Tractional retinal detachment occurs when the vitreous pulls the retina, such as from:
proliferative diabetic retinopathy
sickle cell retinopathy
Exudative retinal detachment occurs with fluid accumulation in the subretinal space, such as from:
central serous chorioretinopathy
choroidal neoplasms such as melanoma
Major risk factors include:
myopia (most common)
surgical aphakia (cataract removal) and pseudophakia (lens implant)
Radiographic features
Imaging is usually not required unless a specific underlying cause, such as metastasis is in the differential.
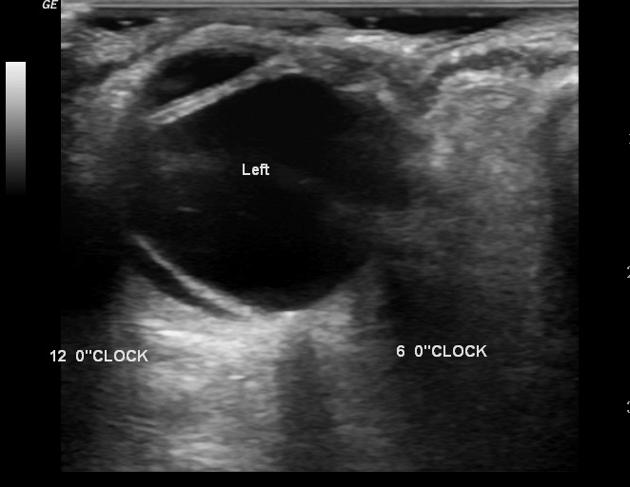
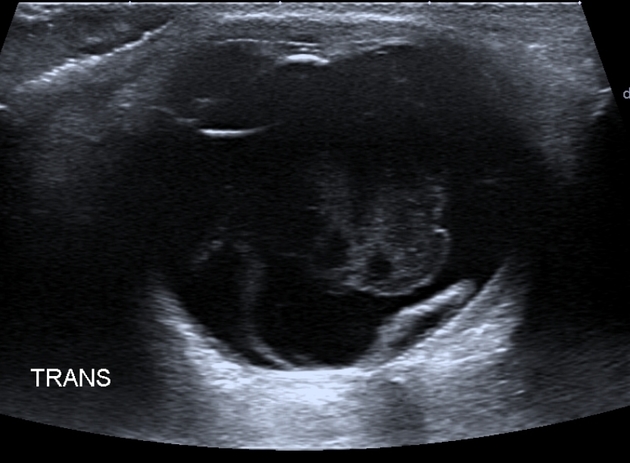
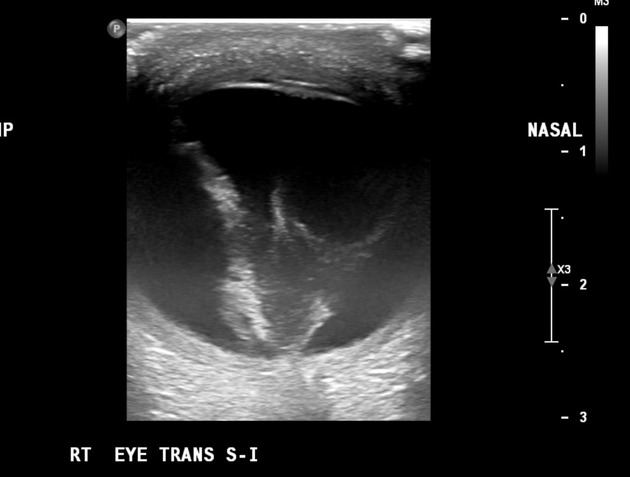
Ultrasound
A high frequency, small footprint probe, performed through the closed eyelid provides good detail:
-
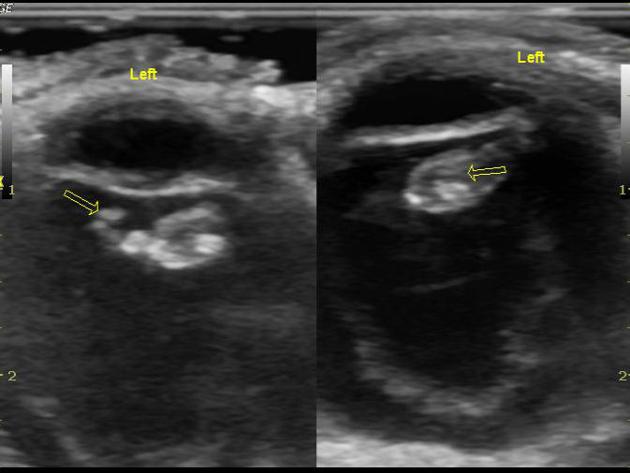
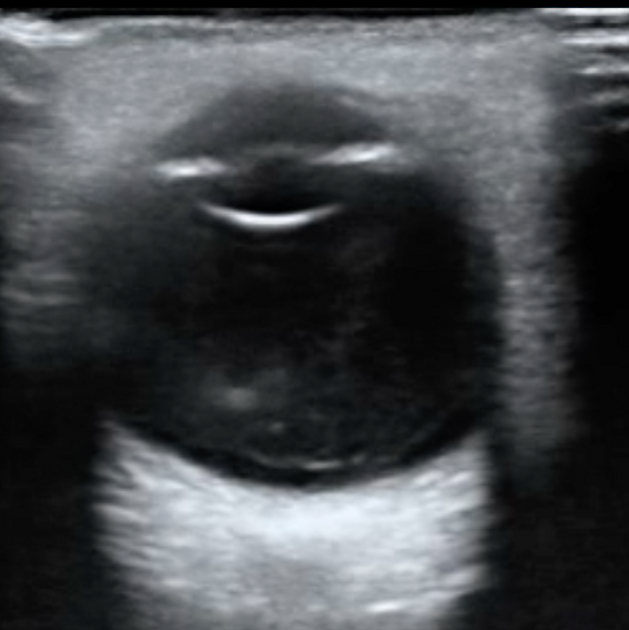
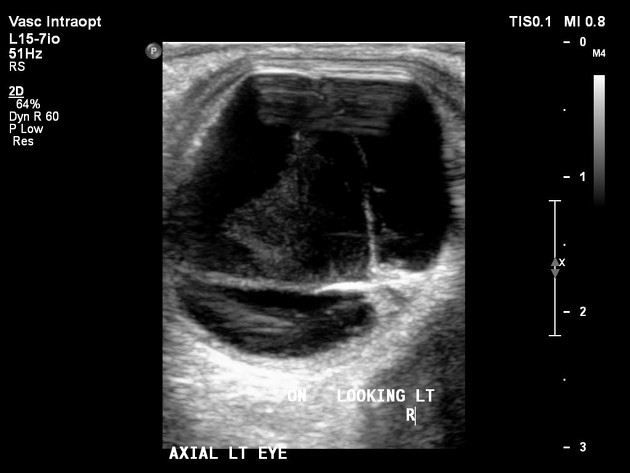
typically appears as a bright, continuous, smooth and somewhat folded membrane within the vitreous, which is reflective and freely moving on real-time imaging
with recruitment of extraocular muscles, the observed independent excursion of this membrane is referred to as an "aftermovement"
acute retinal detachment is mobile, allowing differentiation from choroidal detachment (which does not demonstrate aftermovements) 4
it is, however, less mobile than a posterior vitreous detachment
movements become less pronounced in long-standing detachments
when total or extensive, the detached retina has a typical triangular or "V" shape with insertion into the optic disc and the anterior extent limited by the ora serrata
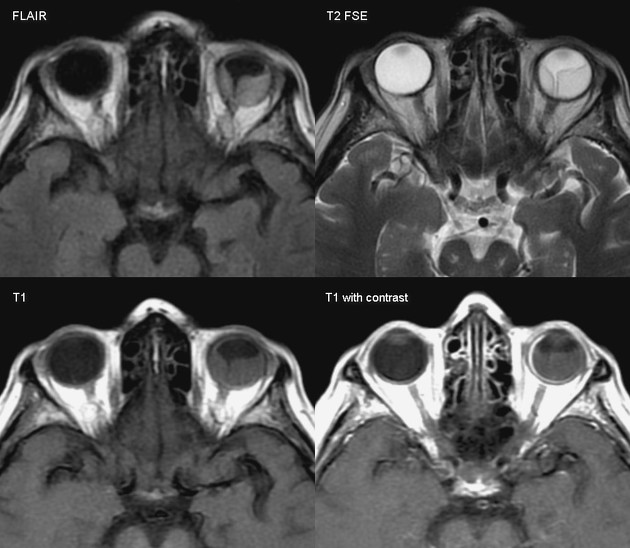
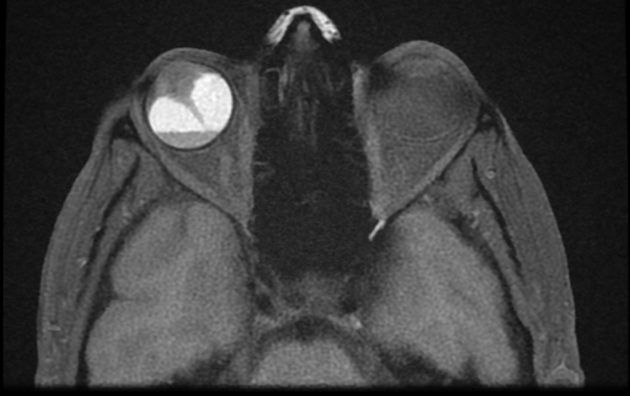
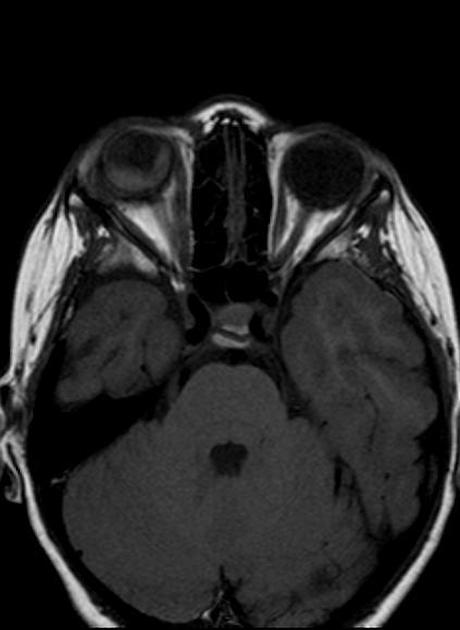
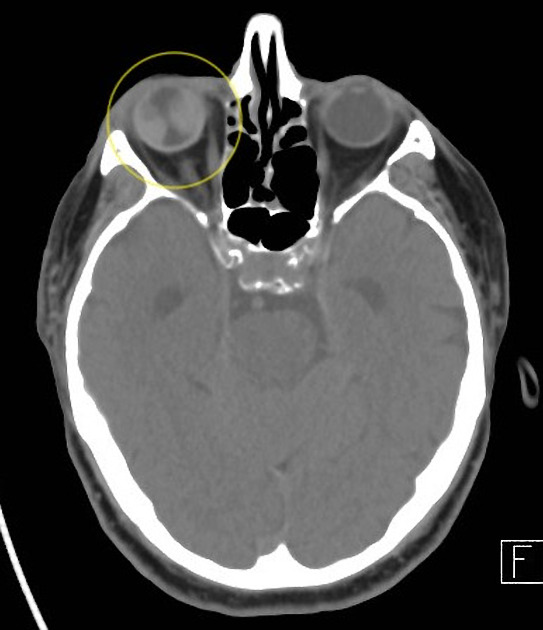
CT/MRI
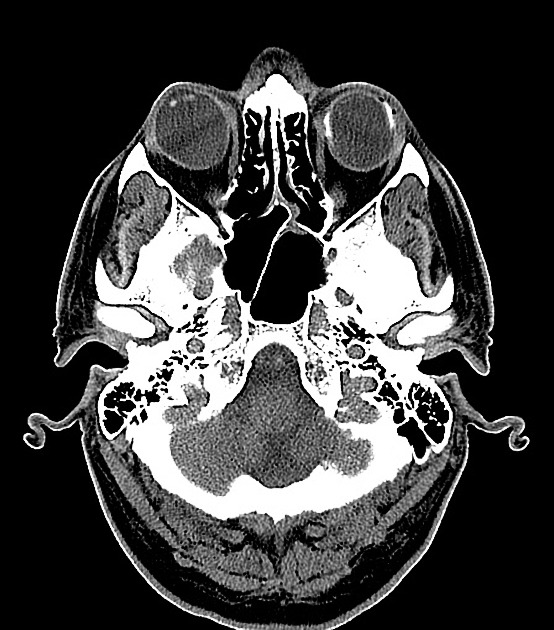
Cross sectional imaging has the advantage of imaging the remainder of the orbit as well as the ability to use contrast. The images may show:
folded membranes with subretinal space fluid (usually hyperdense on CT)
the detachment is limited anteriorly by the ora serrata (compared to a choroidal detachment that extends beyond it)
posteriorly the detachment converges on the optic disc (compared to the choroidal detachment that diverges at the disc)
Treatment and prognosis
Treatment is varied and beyond the scope of this article, but in general terms requires reattachment of the retina using intraocular gas, laser, cryotherapy or surgery. Intra-ocular silicone oil is also sometimes used.
Post-treatment CT may show a scleral band that is can be used to relieve vitreous traction and allow defects to close and reduce the likelihood of recurrence (scleral buckle surgery) 1.
Improved prognosis and surgical outcomes are seen with macula-on retinal detachments where the fovea is still attached 5. Macula-off, or central retinal detachments have worse initial visual acuity and prognosis. Overall prognosis is good with approximately 95% of patients having an anatomically successful repair 5.










 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.