The CT chest-abdomen-pelvis protocol serves as an outline for an examination of the trunk covering the chest, abdomen and pelvis. It is one of the most common CT examinations conducted in routine and emergencies. It can be combined with a CT angiogram.
Note: This article aims to frame a genera...
CT polytrauma/multitrauma, also called trauma CT, whole body CT (WBCT) or panscan, is an increasingly used investigation in patients with multiple injuries sustained after significant trauma.
The majority of the evidence regarding whole-body CT is, understandably, retrospective. There is some e...
This article lists a series of labeled imaging anatomy cases by body region and modality.
Brain
CT head: non-contrast axial
CT head: non-contrast coronal
CT head: non-contrast sagittal
CT head: non-contrast axial with clinical questions
CT head: angiogram axial
CT head: angiogram coronal
...
Urinothorax (plural: urinothoraces), also known as urothorax, is a rare cause of pleural effusion due to the accumulation of urine within the pleural space.
Clinical presentation
Patients present with varying degrees of respiratory distress depending on the amount of fluid that has accumulated...
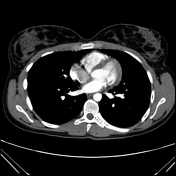
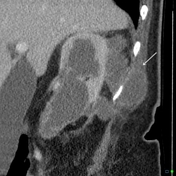
Brachytherapy seed migration to the lung is a known complication of radioactive seed therapy. These seeds are used for localized treatment of malignancies, most commonly prostate cancer.
Regarding staging, nearly 79% of the cases are localized, 12% are regional and 5% present with distant disea...
The term milk of calcium (MOC) is given to dependent, sedimented calcification within a cystic structure or hollow organ. This sort of colloidal calcium suspension layering can occur in various regions:
renal: milk of calcium in renal cyst (most common)
ureter: milk of calcium in the ureter 7
...
Body imaging is the term assigned to cross-sectional imaging of the body, which radiologically refers to the chest, abdomen and pelvis. It is often used by radiologists who report this region (sometimes known as body imagers/radiologists) to differentiate their primary area of interest from othe...
The viscera (singular: viscus) refers to all the internal organs within the major cavities of the thorax, abdomen and pelvis. Therefore it does not include organs of the CNS, head and neck or musculoskeletal compartments nor does it encompass non-internal organs (e.g. the skin) 1.
Splanchnology...
Sickle cell disease (SCD) (historically also known as drepanocytosis) is a hereditary (autosomal recessive) condition resulting in the formation of abnormal hemoglobin (a hemoglobinopathy), which manifests as multisystem ischemia and infarction, as well as hemolytic anemia.
Hemoglobin SC (HbSC...
This article lists examples of normal imaging divided by body region and system.
brain
head and neck
spine
chest
breast
gastrointestinal
genitourinary
hepatobiliary
upper limb
lower limb
pediatrics













 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.