Asplenia
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Shetty A, Bell D, Elfeky M, et al. Asplenia. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 09 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-28740
Permalink:
rID:
28740
Article created:
10 Apr 2014,
Aditya Shetty
Disclosures:
At the time the article was created Aditya Shetty had no recorded disclosures.
View Aditya Shetty's current disclosures
Last revised:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was last revised Daniel J Bell had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Daniel J Bell's current disclosures
Revisions:
5 times, by
5 contributors -
see full revision history and disclosures
Systems:
Sections:
Synonyms:
- Asplenic state
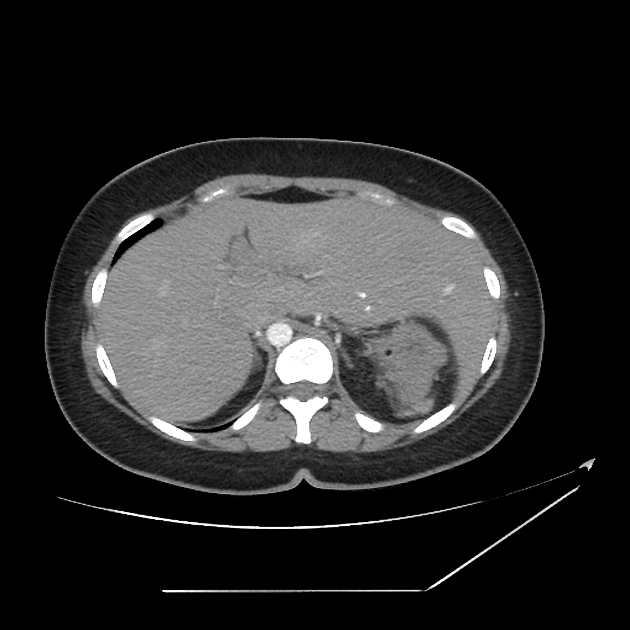
Asplenia refers to absence of the spleen thereby leading to deficient splenic function.
On this page:
Article:
Images:
Images:
Epidemiology
Seen in 3% of neonates with structural heart disease and in 30% of patients who die from cardiac malposition. The male-to-female ratio is 2:1.
Associations
Pathology
Asplenia can be classified into two types:
- anatomical asplenia: absence of splenic tissue (can be congenital, acquired or iatrogenic)
- functional asplenia: splenic tissue present, however it is non-functioning
Related pathology
References
- 1. Fulcher AS, Turner MA. Abdominal manifestations of situs anomalies in adults. Radiographics. 2002;22 (6): 1439-56. Radiographics (full text) - doi:10.1148/rg.226025016 - Pubmed citation
- 2. Jiang H, Wang H, Wang Z et-al. Surgical correction of common atrium without noncardiac congenital anomalies. J Card Surg. 2013;28 (5): 580-6. doi:10.1111/jocs.12202 - Pubmed citation
Incoming Links
Articles:
Related articles: Splenic pathology
- normal appearance of the spleen
- pseudolesion of the spleen: inhomogeneous splenic enhancement
-
splenic lesions and anomalies
- congenital anomalies
- mass lesions
- benign
- indeterminate
- malignant
- infiltrative processes
- miscellaneous
- incidental splenic lesion (approach)
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- celiac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.