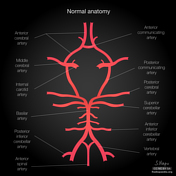
Internal carotid artery
Updates to Article Attributes
The internal carotid artery is a terminal branch of the common carotid artery.
Gross anatomy
Origin
It arises most frequently between C3and C5 vertebral level, where the common carotid bifurcates to form the internal carotid and the external carotid artery (ECA).
Variations in origin
Although the majority arise between C3 and C5 vertebral level, a wide variation exists.
- C1/2: 0.3%
- C2/3: 3.7%
- C3/4: 34.2%
- C4/5: 48.1%
- C5/6: 13%
- C6/7: 0.15%
Asymmetry
There may be significant asymmetry between left and right ICA origins:
- level of bifurcation
- left higher 50%
- right higher 22%
- same height 28%
- orientation of origin
- dorsolateral or dorsal aspect of CCA: right 82% and left 94%
Segments
There are several classification systems, the most recent of which was described by Bouthillier et al in 1996 1 (see below). Their classification system is used clinically by neurosurgeons, neuroradiologists and neurologists and relies on the angiographic appearance of the vessel and histological comparison rather than on the embryonic development.
There are seven segments in the Bouthillier classification:
- cervical segment
- petrous (horizontal) segment
- lacerum segment
- cavernous segment
- clinoid segment
- ophthalmic (supraclinoid) segment
- communicating (terminal) segment
Branches
Except for the terminal segment (C7) the odd numbered segments usually have no branches, whereas the even numbered segments (C2, C4, C6) each have two branches.
- C1: cervical segment, none
- C2: petrous (horizontal) segment
- C3: lacerum segment, none
- C4: cavernous segment
- C5: clinoid segment, none
- C6: ophthalmic (supraclinoid) segment
- C7: communicating segment
A useful mnemonic to remember the branches of the internal carotid artery is:
Variant anatomy
- aberrant ICA
- congenital absence of the ICA
- retropharyngeal ICA (rare) 4
- kissing carotids
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar anastomoses
- lateralised internal carotid artery
Related pathology
-<p>The <strong>internal carotid artery</strong> is a terminal branch of the <a href="/articles/common-carotid-artery-2">common carotid artery</a>. </p><h4>Gross anatomy</h4><h5>Origin</h5><p>It arises most frequently between C3 and C5 vertebral level, where the common carotid<a href="/articles/carotid-bifurcation"> bifurcates</a> to form the internal carotid and the <a href="/articles/external-carotid-artery-1">external carotid artery (ECA)</a>.</p><h6>Variations in origin</h6><p>Although the majority arise between C3 and C5 vertebral level, a wide variation exists.</p><ul>- +<p>The <strong>internal carotid artery</strong> is a terminal branch of the <a href="/articles/common-carotid-artery-2">common carotid artery</a>. </p><h4>Gross anatomy</h4><h5>Origin</h5><p>It arises most frequently between C3 and C5 vertebral level, where the common carotid<a href="/articles/carotid-bifurcation"> bifurcates</a> to form the internal carotid and the <a href="/articles/external-carotid-artery-1">external carotid artery (ECA)</a>.</p><h6>Variations in origin</h6><p>Although the majority arise between C3 and C5 vertebral level, a wide variation exists.</p><ul>
-</ul><h5>Segments</h5><p>There are several classification systems, the most recent of which was described by Bouthillier et al in 1996 <sup>1</sup> (see below). Their classification system is used clinically by neurosurgeons, neuroradiologists and neurologists and relies on the angiographic appearance of the vessel and histological comparison rather than on the embryonic development.</p><p>There are seven segments in the <a href="/articles/bouthillier-classification-of-ica-segments">Bouthillier classification</a>:</p><ol>- +</ul><h5>Segments</h5><p>There are several classification systems, the most recent of which was described by Bouthillier et al in 1996 <sup>1</sup> (see below). Their classification system is used clinically by neurosurgeons, neuroradiologists and neurologists and relies on the angiographic appearance of the vessel and histological comparison rather than on the embryonic development.</p><p>There are seven segments in the <a href="/articles/bouthillier-classification-of-internal-carotid-artery-segments">Bouthillier classification</a>:</p><ol>
-</ul><p>A useful<strong> mnemonic</strong> to remember the branches of the internal carotid artery is:</p><ul><li><a title="Branches of internal carotid artery (mnemonic)" href="/articles/branches-of-internal-carotid-artery-mnemonic">A VIP'S COMMA</a></li></ul><h4>Variant anatomy</h4><ul>- +</ul><p>A useful<strong> mnemonic</strong> to remember the branches of the internal carotid artery is:</p><ul><li><a href="/articles/branches-of-internal-carotid-artery-mnemonic">A VIP'S COMMA</a></li></ul><h4>Variant anatomy</h4><ul>
Image 4 Diagram ( create )







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.