Medial rectus muscle
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Craig Hacking had no recorded disclosures.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosures- Medial rectus
The medial rectus muscle is one of the six extraocular muscles that control eye movements.
On this page:
Summary
- innervation: inferior branch of the oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- origin: annulus of Zinn (tendinous ring)
- insertion: globe (anterior, medial surface)
- primary function: one of three ocular adductors
Gross anatomy
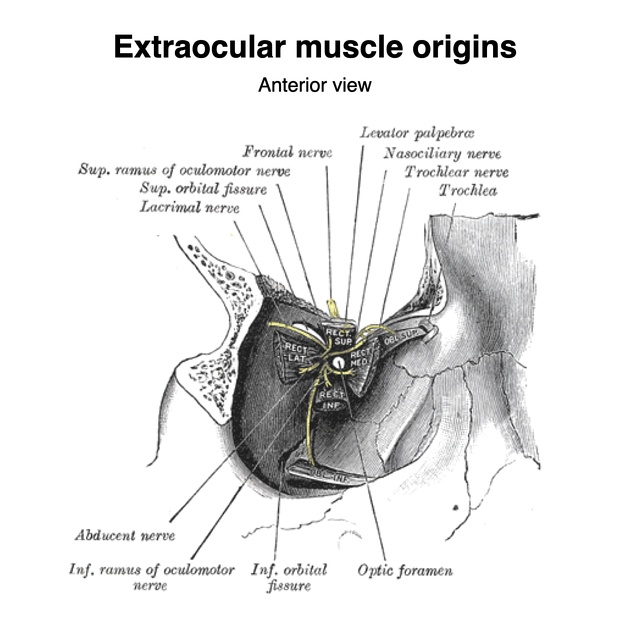
Origin
Medial rectus, along with the other rectus muscles, arises from the annulus of Zinn, the common tendinous ring at the apex of the orbit that surrounds the optic canal 1.
Insertion
Medial rectus runs anteriorly on the medial surface of the eye and inserts into the medial surface of the sclera just posterior to the junction of cornea and sclera 2.
Arterial supply
Branches of the ophthalmic artery, itself a branch of the internal carotid artery.
Innervation
Innervated by the oculomotor nerve, which also supplies superior rectus, inferior rectus and inferior oblique muscles.
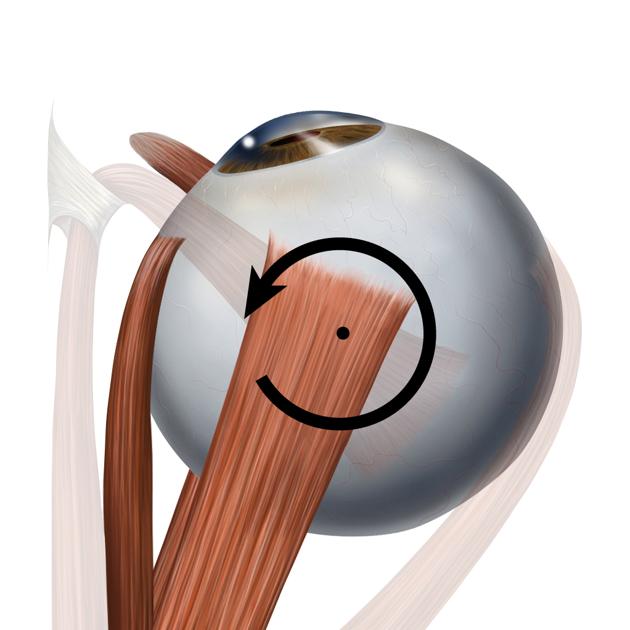
Action
The action of the medial rectus is to adduct the eye (see figure 1) 1. Unlike most of the other extraocular muscles, it has no significant contribution to movement in the other ocular axes.
Simultaneous action of the medial rectus muscles of both eyes causes ocular convergence, which is necessary to allow near-field focus, such as when reading.
Etymology
Rectus comes from the Latin rectos, meaning straight 1.
Related pathology
See also
References
- 1. Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. (2013) ISBN: 9781451119459
- 2. Netter FH. Atlas of Human Anatomy. (2018) ISBN: 9780323393225
- 3. Imaging of the Head and Neck. Thieme. (2012) ISBN:3131505311. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 4. Gray's basic anatomy. Churchill Livingstone. ISBN:1455710784. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
Incoming Links
- Superior rectus muscle
- Inferior rectus muscle
- Orbit
- Ocular adductors
- Stability of the eye
- Facial colliculus syndrome
- Nasociliary nerve
- Extraocular muscle nerve supply (mnemonic)
- Myofascial cone
- Orbital apex
- Orbital blow-out fracture
- Ocular globe
- Senile calcific scleral plaques
- Internuclear ophthalmoplegia
- Orbital nerve supply
- Oculomotor nucleus
- Extraocular muscles
- Barrett's index
- Oculomotor nerve palsy
- Eye movements
- Medial orbital wall blowout fracture with medial rectus muscle displacement
- Frontoethmoidal sinus osteoma
- Orbital medial wall blow-out fracture and retrobulbar emphysema
- Orbital medial wall blow-out fracture
- Orbital medial wall blow-out fracture
- Idiopathic orbital inflammation
- Orbital medial wall blow-out fracture
- Dermoid cyst in the medial canthus
- Blow-out fracture of the orbit and retrobulbar hemorrhage
- Blow-out fracture of the orbital medial wall
- Dermoid cyst in orbital cavity
- Subperiosteal abscess of the orbit
- Orbital medial wall blow-out fracture
- Orbital blow-out fracture and medial rectus muscle transection
- Idiopathic orbital inflammation
- Orbital blow-out fracture, ocular lens dislocation, and retrobulbar hemorrhage
- Graves ophthalmopathy
- Granular cell tumor
- Frontoethmoidal mucocele
- Subperiosteal abscess of the orbit
Related articles: Anatomy: Head and neck
- skeleton of the head and neck
-
cranial vault
- scalp (mnemonic)
- fontanelle
-
sutures
- calvarial
- facial
- frontozygomatic suture
- frontomaxillary suture
- frontolacrimal suture
- frontonasal suture
- temporozygomatic suture
- zygomaticomaxillary suture
- parietotemporal suture (parietomastoid suture)
- occipitotemporal suture (occipitomastoid suture)
- sphenofrontal suture
- sphenozygomatic suture
- spheno-occipital suture (not a true suture)
- lacrimomaxillary suture
- nasomaxillary suture
- internasal suture
- basal/internal
- skull landmarks
- frontal bone
- temporal bone
- parietal bone
- occipital bone
- skull base (foramina)
-
facial bones
- midline single bones
- paired bilateral bones
- cervical spine
- hyoid bone
- laryngeal cartilages
-
cranial vault
- muscles of the head and neck
- muscles of the tongue (mnemonic)
- muscles of mastication
-
facial muscles
- epicranius muscle
- circumorbital and palpebral muscles
- nasal muscles
-
buccolabial muscles
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- levator labii superioris alaeque nasalis muscle
- levator labii superioris muscle
- zygomaticus major muscle
- zygomaticus minor muscle
- levator anguli oris muscle
- malaris muscle
- risorius muscle
- depressors, retractors and evertors of the lower lip
- depressor labii inferioris muscle
- depressor anguli oris muscle
- mentalis muscle
- compound sphincter
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- incisivus labii superioris muscle
- incisivus labii inferioris muscle
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- muscle of mastication
- modiolus
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- muscles of the middle ear
- orbital muscles
- muscles of the soft palate
- pharyngeal muscles
- suprahyoid muscles
- infrahyoid muscles
- intrinsic muscles of the larynx
- muscles of the neck
- platysma muscle
- longus colli muscle
- longus capitis muscle
- scalenus anterior muscle
- scalenus medius muscle
- scalenus posterior muscle
- scalenus pleuralis muscle
- sternocleidomastoid muscle
-
suboccipital muscles
- rectus capitis posterior major muscle
- rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
- obliquus capitis superior muscle
- obliquus capitis inferior muscle
- accessory muscles of the neck
- deep cervical fascia
-
deep spaces of the neck
- anterior cervical space
- buccal space
- carotid space
- danger space
- deep cervical fascia
- infratemporal fossa
- masticator space
- parapharyngeal space
- stylomandibular tunnel
- parotid space
- pharyngeal (superficial) mucosal space
- perivertebral space
- posterior cervical space
- pterygopalatine fossa
- retropharyngeal space
- suprasternal space (of Burns)
- visceral space
- surgical triangles of the neck
- orbit
- ear
- paranasal sinuses
- upper respiratory tract
- viscera of the neck
- blood supply of the head and neck
-
arterial supply
-
common carotid artery
- carotid body
- carotid bifurcation
- subclavian artery
- variants
-
common carotid artery
- venous drainage
-
arterial supply
- innervation of the head and neck
-
cranial nerves
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
-
trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- trigeminal ganglion
- ophthalmic division
- maxillary division
- mandibular division
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- (spinal) accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck
- cervical sympathetic ganglia
- greater occipital nerve
- third occipital nerve
-
cervical plexus
- muscular branches
- longus capitis
- longus colli
- scalenes
- geniohyoid
- thyrohyoid
-
ansa cervicalis
- omohyoid (superior and inferior bellies separately)
- sternothyroid
- sternohyoid
- phrenic nerve
- contribution to the accessory nerve (CN XI)
- cutaneous branches
- muscular branches
- brachial plexus
- pharyngeal plexus
-
cranial nerves
- lymphatic drainage of the head and neck
- embryological development of the head and neck










 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.