Aspergillus fumigatus
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Daniel J Bell had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Daniel J Bell's current disclosures- A. fumigatus
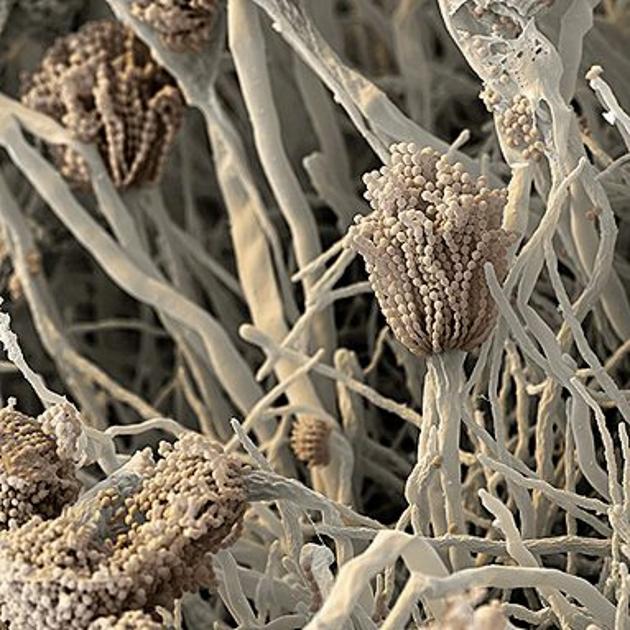
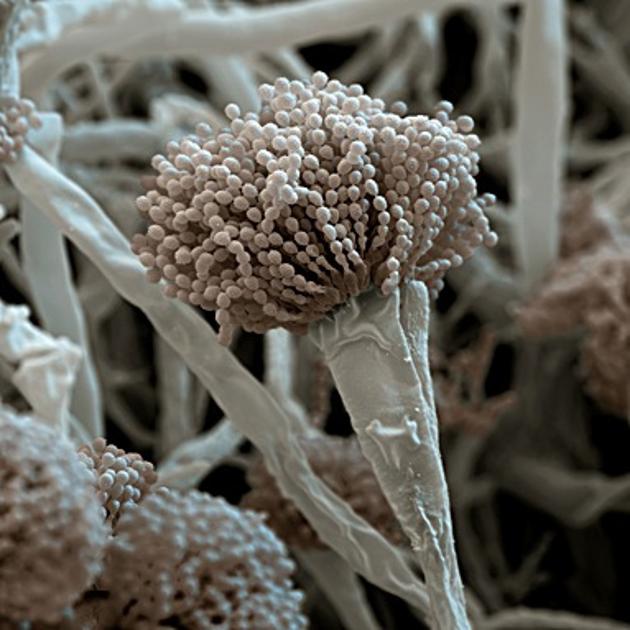
Aspergillus fumigatus is a fungus of the genus Aspergillus, and is one of the most common Aspergillus species to cause disease in immunocompromised individuals.
A. fumigatus is a saprotroph (an organism that gets its energy from non-living organic matter) that is widespread in nature, typically found in soil and decaying organic matter. Colonies produce thousands of minute grey-green conidia (2–3 μm) that readily become airborne.
Its spores are ubiquitous in the atmosphere and it is estimated that everybody inhales several hundred spores each day; typically, these are quickly eliminated by the immune system in healthy individuals.
In immunocompromised individuals the fungus is not eliminated appropriately, causing disease, commonly pulmonary aspergillosis.
Related pathology
References
- 1. O'gorman CM, Fuller HT, Dyer PS. Discovery of a sexual cycle in the opportunistic fungal pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. Nature. 2009;457 (7228): 471-4. doi:10.1038/nature07528 - Pubmed citation
Incoming Links
Related articles: Infections
- bacterial
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Streptococcus anginosus group
- Staphylococcus aureus
- group A Streptococcus
- Klebsiella pneumonia
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Moraxella catarrhalis
- atypical
-
tuberculosis
- causative agent
- tuberculoma (tuberculous granuloma)
- tuberculous abscess
- miliary tuberculosis
- pulmonary tuberculosis
-
extrapulmonary tuberculosis
- intracranial tuberculosis
- tuberculous otomastoiditis
- tuberculous lymphadenopathy
- cardiac tuberculosis
- tuberculous mastitis
-
abdominal tuberculosis
- gastrointestinal tuberculosis
- tuberculous peritonitis
- visceral tuberculosis
- hepatic tuberculosis
- gallbladder tuberculosis
- pancreatic tuberculosis
- splenic tuberculosis
-
genitourinary tuberculosis
- renal tuberculosis
- bladder and ureteric tuberculosis
- prostatic tuberculosis
- scrotal tuberculosis (testes, epididymis, seminal vesicles, vas deferens)
- tuberculous pelvic inflammatory disease (female)
- skeletal tuberculosis
-
tuberculosis
- viral
- fungal
- Aspergillus
-
aspergillosis
- CNS aspergillosis
-
fungal sinusitis
- non-invasive: hyphae do not invade mucosa
- invasive: hyphae seen invading mucosa +/- beyond
- pulmonary aspergillosis





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.