Metal artifact reduction algorithm
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Knipe H, Murphy A, Metal artifact reduction algorithm. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 18 Feb 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-67664
Permalink:
rID:
67664
Article created:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was created Henry Knipe had no recorded disclosures.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosures
Last revised:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was last revised Andrew Murphy had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Andrew Murphy's current disclosures
Revisions:
3 times, by
2 contributors -
see full revision history and disclosures
Sections:
Tags:
Synonyms:
- Metal artifact reduction (MAR) algorithm
- MAR algorithm
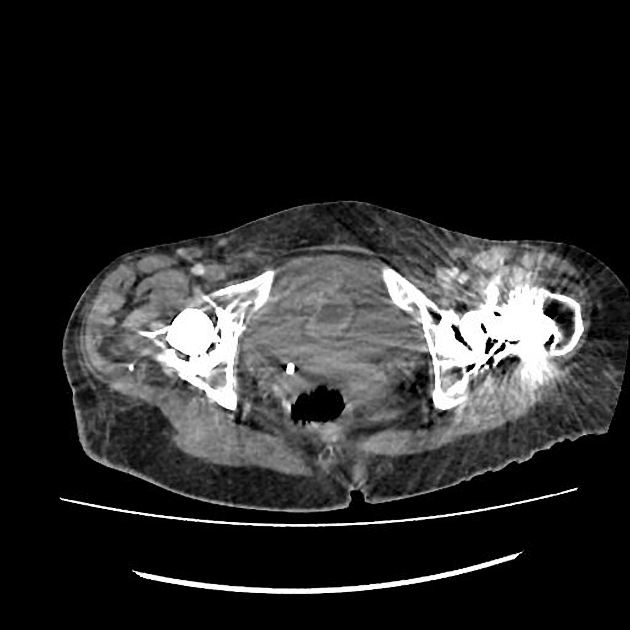
Metal artifact reduction (MAR) algorithms are used to improve CT image quality in patients with metalware, however, can be affected by novel artifacts 1-3. There are a number of commercially-available algorithms (in 2019) 1,3:
- iterative MAR (iMAR) - Siemens
- MAR for orthopedic implants (O-MAR) - Philips
- single-energy MAR (SEMAR) - Toshiba/Canon
- SmartMAR - GE
Practical points
- images obtained with and without MAR should be reviewed together with multiplanar reformats to avoid misinterpreting newly created artifacts 3
References
- 1. Bolstad K, Flatabø S, Aadnevik D, Dalehaug I, Vetti N. Metal artifact reduction in CT, a phantom study: subjective and objective evaluation of four commercial metal artifact reduction algorithms when used on three different orthopedic metal implants. (2018) Acta radiologica (Stockholm, Sweden : 1987). 59 (9): 1110-1118. doi:10.1177/0284185117751278 - Pubmed
- 2. Wellenberg RHH, Hakvoort ET, Slump CH, Boomsma MF, Maas M, Streekstra GJ. Metal artifact reduction techniques in musculoskeletal CT-imaging. (2018) European journal of radiology. 107: 60-69. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2018.08.010 - Pubmed
- 3. Masaki Katsura, Jiro Sato, Masaaki Akahane, Akira Kunimatsu, Osamu Abe. Current and Novel Techniques for Metal Artifact Reduction at CT Practical Guide for Radiologists. (2018) RadioGraphics. 38 (2): 450-461. doi:10.1148/rg.2018170102 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Articles:
- CT neck (protocol)
- CT knee (protocol)
- CT shoulder (protocol)
- CT thoracic spine (protocol)
- CT hip (protocol)
- CT chest non-contrast (protocol)
- CT elbow (protocol)
- CT hand and wrist (protocol)
- CT lumbar spine (protocol)
- CT cervical spine (protocol)
- Beam hardening
- CT pelvis (protocol)
- Prostate MRI protocol
Related articles: Computed tomography
- computed tomography in practice
-
computed tomography overview
- iodinated contrast media
- CT IV contrast media administration
-
CT artifacts
- patient-based artifacts
- physics-based artifacts
- hardware-based artifacts
- ring artifact
- tube arcing
- out of field artifact
- air bubble artifact
- helical and multichannel artifacts
- CT technology
-
generations of CT scanners
- helical CT scanning
- step and shoot scanning
- ultra-high-resolution CT (UHRCT)
- CT x-ray tube
- CT fluoroscopy
- cone-beam CT
-
generations of CT scanners
- dual-energy CT
- CT image reconstruction
- CT image quality
- CT dose
-
CT protocols
- composite
- head & neck
- chest
- abdomen and pelvis
- CT abdomen-pelvis (protocol)
- CT abdominal aorta
- CT adrenals (protocol)
- CT cholangiography (protocol)
- CT colonography (protocol)
- CT enteroclysis (protocol)
- CT enterography (protocol)
- CT gastrography (protocol)
- CT kidneys, ureters and bladder (protocol)
- CT urography (protocol)
- CT Renal mass (protocol)
- CT angiography of the splanchnic vessels (protocol)
- CT renal split bolus
- CT pancreas (protocol)
- liver





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.