Motion artifact
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Andrew Murphy had no recorded disclosures.
View Andrew Murphy's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Craig Hacking had the following disclosures:
- Philips Australia, Paid speaker at Philips Spectral CT events (ongoing)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosures- Motion artefact
- Movement artifact
- Movement artefact
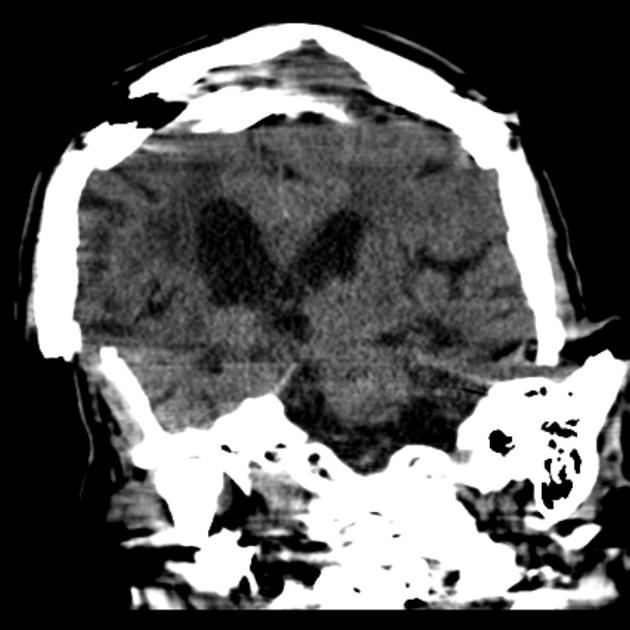
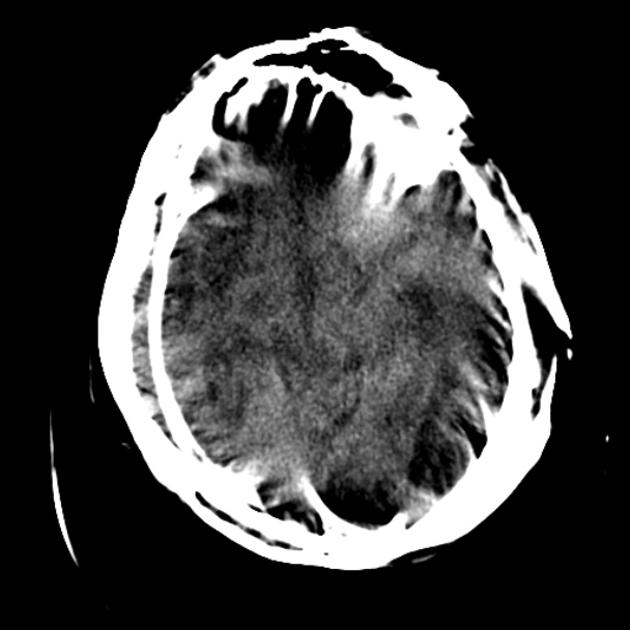
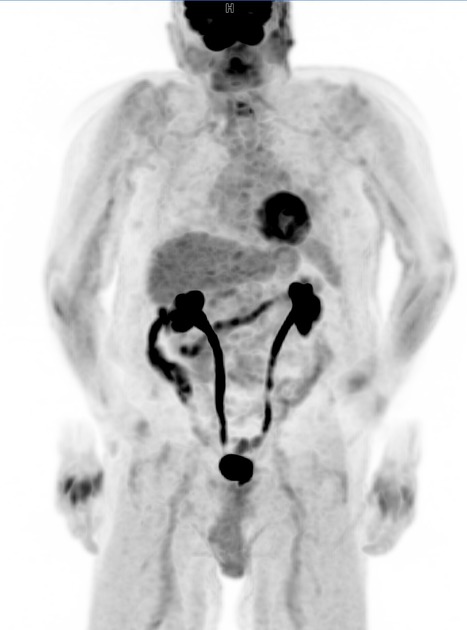
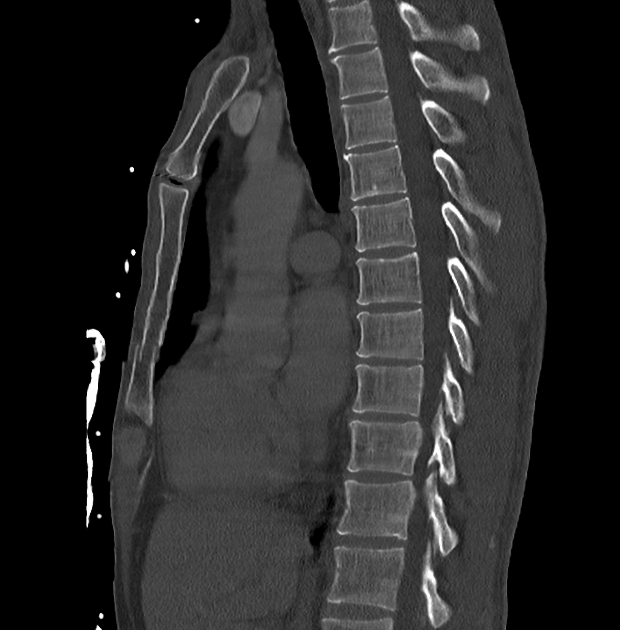
Motion artifact is a patient-based artifact that occurs with voluntary or involuntary patient movement during image acquisition.
Misregistration artifacts, which appear as blurring, streaking, or shading, are caused by patient movement during a CT scan. Blurring also occurs with patient movement during radiographic examinations.
If patient movement is voluntary, patients may require immobilization or sedation to prevent this.
Involuntary motion, such as respiration or cardiac motion, may cause artifacts that mimic pathology in surrounding structures.
This artifact can be reduced by using a fast scanning technique. Techniques, such as cardiac gating, may be used for examinations that concern the mediastinum.
References
- 1. Barrett JF, Keat N. Artifacts in CT: recognition and avoidance. Radiographics. 2004;24 (6): 1679-91. doi:10.1148/rg.246045065 - Pubmed citation
Incoming Links
- Paediatric finger (oblique view)
- MR enteroclysis
- Lower limb radiography (paediatric)
- Paediatric foot (DP view)
- Paediatric tibia fibula (lateral view)
- Superb microvascular imaging (ultrasound)
- Paediatric knee (lateral view)
- Paediatric thumb (lateral view)
- Knee series (paediatric)
- Shoulder series (paediatric)
- Radiological image artifact
- Humerus series (paediatric)
- Spine radiography (paediatric)
- Blur
- Thoracic spine series (paediatric)
- Central vein sign
- Paediatric knee (AP view)
- Paediatric knee (horizontal beam lateral view)
- Paediatric lumbar spine (AP/PA view)
- Paediatric shoulder (lateral view)
Related articles: Computed tomography
- computed tomography in practice
-
computed tomography overview
- iodinated contrast media
- CT IV contrast media administration
-
CT artifacts
- patient-based artifacts
- physics-based artifacts
- hardware-based artifacts
- ring artifact
- tube arcing
- out of field artifact
- air bubble artifact
- helical and multichannel artifacts
- CT technology
-
generations of CT scanners
- helical CT scanning
- step and shoot scanning
- ultra-high-resolution CT (UHRCT)
- CT x-ray tube
- CT fluoroscopy
- cone-beam CT
-
generations of CT scanners
- dual-energy CT
- CT image reconstruction
- CT image quality
- CT dose
-
CT protocols
- composite
- head & neck
- chest
- abdomen and pelvis
- CT abdomen-pelvis (protocol)
- CT abdominal aorta
- CT adrenals (protocol)
- CT cholangiography (protocol)
- CT colonography (protocol)
- CT enteroclysis (protocol)
- CT enterography (protocol)
- CT gastrography (protocol)
- CT kidneys, ureters and bladder (protocol)
- CT urography (protocol)
- CT Renal mass (protocol)
- CT angiography of the splanchnic vessels (protocol)
- CT renal split bolus
- CT pancreas (protocol)
- liver




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.