Visual pathway deficits
Updates to Article Attributes
Body
was changed:
Visual pathway deficits are determined by the location of the lesion or pathology. Understanding of the visual system is paramount and provided the globe is normal, the field defects can be defined from anterior to posterior as:
-
Unilateralunilateral central scotoma -
Bitemporalbitemporal hemianopsia -
Junctionaljunctional defect (ipsilateral central scotoma and a contralateral superior temporal field cut)-
Anterioranterior chiasm
-
-
Centralcentral temporal scotomas-
Posteriorposterior chiasm
-
-
Incongruousincongruous homonymous hemianopsia, afferent pupillary defect, and bow-tie atrophy -
Homonymoushomonymous sectoranopia -
Incongruousincongruous homonymous hemianopsia-
Laterallateral geniculate nucleus
-
-
Homonymoushomonymous upper quadrant defect "pie in the sky" -
Homonymoushomonymous defect, denser inferiorly -
Gerstmann syndrome and a homonymous defect, denser inferiorly
-
Parietalparietal lobe
-
-
Completecomplete homonymous hemianopsia- Not well-localized
-
Homonymoushomonymous upper quadrantanopsia with macular sparing- occipital lobe (lower bank)
-
Homonymoushomonymous lower quadrantanopsia with macular sparing-
Occipitaloccipital lobe (upper bank)
-
-
Isolatedisolated homonymous defect (macular sparing) without other neurologic findings-
Occipitaloccipital lobe
-
- Anton syndrome (cortical blindness)
-
Bilateralbilateral occipital lobe lesions
-
-
Balint syndrome
-
Bilateralbilateral occipitoparietal lesions
-
-
Alexiaalexia without agraphia-
Leftleft occipital lobe and angular gyrus
-
-
Centralcentral achromatopsia-
Bilateralbilateral occipito-temporal lesions
-
-<p><strong>Visual pathway deficits</strong> are determined by the location of the lesion or pathology. Understanding of the <a title="Visual system" href="/articles/visual-system-1">visual system</a> is paramount and provided the <a title="globe" href="/articles/globe">globe</a> is normal, the field defects can be defined from anterior to posterior as:</p><ul>-<li>Unilateral central scotoma<ul><li><a title="Optic nerve" href="/articles/optic-nerve">Optic nerve</a></li></ul>- +<p><strong>Visual pathway deficits</strong> are determined by the location of the lesion or pathology. Understanding of the <a href="/articles/visual-system-1">visual system</a> is paramount and provided the <a href="/articles/globe">globe</a> is normal, the field defects can be defined from anterior to posterior as:</p><ul>
- +<li>unilateral central scotoma<ul><li><a href="/articles/optic-nerve">optic nerve</a></li></ul>
-<li>Bitemporal hemianopsia<ul><li><a title="Optic chiasm" href="/articles/optic-chiasm">Optic chiasm</a></li></ul>- +<li>bitemporal hemianopsia<ul><li><a href="/articles/optic-chiasm">optic chiasm</a></li></ul>
-<li>Junctional defect (ipsilateral central scotoma and a contralateral superior temporal field cut)<ul><li>Anterior chiasm</li></ul>- +<li>junctional defect (ipsilateral central scotoma and a contralateral superior temporal field cut)<ul><li>anterior chiasm</li></ul>
-<li>Central temporal scotomas<ul><li>Posterior chiasm</li></ul>- +<li>central temporal scotomas<ul><li>posterior chiasm</li></ul>
-<li>Incongruous homonymous hemianopsia, afferent pupillary defect, and bow-tie atrophy<ul><li><a title="Optic tract" href="/articles/optic-tract">Optic tract</a></li></ul>- +<li>incongruous homonymous hemianopsia, afferent pupillary defect, and bow-tie atrophy<ul><li><a href="/articles/optic-tract">optic tract</a></li></ul>
-<li>Homonymous sectoranopia<ul><li><a title="Lateral geniculate nucleus" href="/articles/lateral-geniculate-nucleus">Lateral geniculate nucleus</a></li></ul>- +<li>homonymous sectoranopia<ul><li><a href="/articles/lateral-geniculate-nucleus">lateral geniculate nucleus</a></li></ul>
-<li>Incongruous homonymous hemianopsia<ul><li>Lateral geniculate nucleus</li></ul>- +<li>incongruous homonymous hemianopsia<ul><li>lateral geniculate nucleus</li></ul>
-<li>Homonymous upper quadrant defect "pie in the sky"<ul><li><a title="Temporal lobe" href="/articles/temporal-lobe">Temporal lobe</a></li></ul>- +<li>homonymous upper quadrant defect "pie in the sky"<ul><li><a href="/articles/temporal-lobe">temporal lobe</a></li></ul>
-<li>Homonymous defect, denser inferiorly<ul><li><a title="Parietal lobe" href="/articles/parietal-lobe">Parietal lobe</a></li></ul>- +<li>homonymous defect, denser inferiorly<ul><li><a href="/articles/parietal-lobe">parietal lobe</a></li></ul>
-<a title="Gerstmann syndrome" href="/articles/gerstmann-syndrome">Gerstmann syndrome</a> and a homonymous defect, denser inferiorly<ul><li>Parietal lobe</li></ul>- +<a href="/articles/gerstmann-syndrome">Gerstmann syndrome</a> and a homonymous defect, denser inferiorly<ul><li>parietal lobe</li></ul>
-<li>Complete homonymous hemianopsia<ul><li>Not well-localized</li></ul>- +<li>complete homonymous hemianopsia<ul><li>Not well-localized</li></ul>
-<li>Homonymous upper quadrantanopsia with macular sparing<ul><li>-<a title="Occipital lobe" href="/articles/occipital-lobe">Occipital lobe</a> (lower bank)</li></ul>- +<li>homonymous upper quadrantanopsia with macular sparing<ul><li>
- +<a href="/articles/occipital-lobe">occipital lobe</a> (lower bank)</li></ul>
-<li>Homonymous lower quadrantanopsia with macular sparing<ul><li>Occipital lobe (upper bank)</li></ul>- +<li>homonymous lower quadrantanopsia with macular sparing<ul><li>occipital lobe (upper bank)</li></ul>
-<li>Isolated homonymous defect (macular sparing) without other neurologic findings<ul><li>Occipital lobe</li></ul>- +<li>isolated homonymous defect (macular sparing) without other neurologic findings<ul><li>occipital lobe</li></ul>
-<li>Anton syndrome (cortical blindness)<ul><li>Bilateral occipital lobe lesions</li></ul>- +<li>Anton syndrome (cortical blindness)<ul><li>bilateral occipital lobe lesions</li></ul>
-<a title="Balint syndrome" href="/articles/balint-syndrome">Balint syndrome</a><ul><li>Bilateral occipitoparietal lesions</li></ul>- +<a href="/articles/balint-syndrome">Balint syndrome</a><ul><li>bilateral occipitoparietal lesions</li></ul>
-<li>Alexia without agraphia<ul><li>Left occipital lobe and <a title="Angular gyrus" href="/articles/angular-gyrus">angular gyrus</a>- +<li>alexia without agraphia<ul><li>left occipital lobe and <a href="/articles/angular-gyrus">angular gyrus</a>
-<li>Central achromatopsia<ul><li>Bilateral occipito-temporal lesions</li></ul>- +<li>central achromatopsia<ul><li>bilateral occipito-temporal lesions</li></ul>
Images Changes:
Image 1 Diagram ( update )

Caption
was added:
Fig 1: optic pathways
Image 2 Diagram ( update )

Caption
was added:
Fig 2 : anatomy of eye and extraocular muscles
Image 3 Diagram ( update )
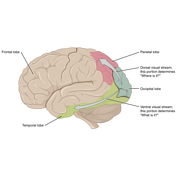
Caption
was added:
Figure 3: visual pathway







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.