Glioblastoma NOS (multicentric)
Updates to Case Attributes
This patient went on to have a craniotomy andwhich confirmed the diagnosis of glioblastoma (grade IV). In this case, as areas of enhancement do not appear bridged by highabnormal T2/FLAIR signal the, the term multicentric glioblastoma is justified.
Note: IDH mutation status is not provided in this case and according to the current (2016) WHO classification of CNS tumours, this tumour would, therefore, be designated as a glioblastoma NOS.
-<p>This patient went on to have a craniotomy and confirmed the diagnosis of <a title="GBM" href="/articles/glioblastoma">glioblastoma</a> (grade IV). In this case, as areas of enhancement do not appear bridged by high T2 signal the term <a title="Multicentric glioblastoma" href="/articles/multicentric-glioblastoma">multicentric glioblastoma</a> is justified. </p>- +<p>This patient went on to have a craniotomy which confirmed the diagnosis of <a href="/articles/glioblastoma">glioblastoma</a> (grade IV). In this case, as areas of enhancement do not appear bridged by abnormal T2/FLAIR signal, the term <a href="/articles/multicentric-glioblastoma">multicentric glioblastoma</a> is justified.</p><p><strong>Note:</strong> IDH mutation status is not provided in this case and according to the current (2016) <a title="WHO classification of CNS tumours" href="/articles/who-classification-of-cns-tumours-1">WHO classification of CNS tumours</a>, this tumour would, therefore, be designated as a <a title="Glioblastoma NOS" href="/articles/glioblastoma-nos">glioblastoma NOS</a>. </p>
Systems changed:
- Oncology
Updates to Study Attributes
Multiple irregularirregularly shaped lesions with hypodense centres can identified acrossin both hemispheres. Most of the lesions have an irregular hyperdense marginsrim.
There is no significant midline line shift. Incidental note is madeSmall calcified nodule (or rather, cluster of a cavum septum pellucidum.
A small hyperdense lesion can be identified just to the rightnodules) immediately left of the superior sagittal sinus near the torcula, probably meningioma(s).
Incidental cavum veli interpositi.
Image CT (non-contrast) ( update )
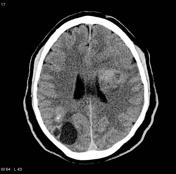
Image CT (bone window) ( update )
Updates to Study Attributes
Multiple lesions with hypointensea T1-hypointense/T2-hyperinense centre on T1 signal and hyperinense on T2 in keeping of, likely representing necrosis or cystic degeneration or more likely necrosis. Extensive high T2 signal surrounds the lesions, suggestive of oedema.
Following contrast administration of contrast, most of the lesions demonstrated a well defined enhancing edge with heterogeneous centredemonstrate intense rim enhancement.
Image MRI (T1 C+) ( update )
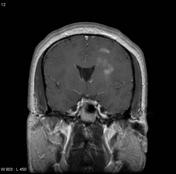
Image MRI (T1) ( update )
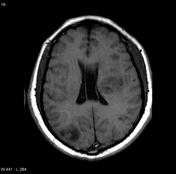
Image MRI (T2) ( update )
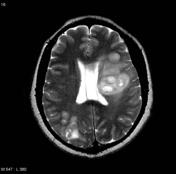
Image MRI (FLAIR) ( update )
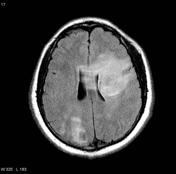
Image MRI (T1 C+) ( update )
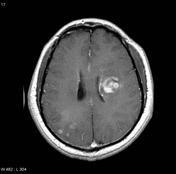
Image MRI (Gradient Echo) ( update )
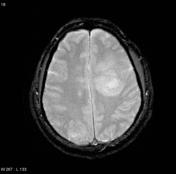
Updates to Study Attributes
There is hugesubstantial disease progression comparecompared to the last investigation. The lesions nearin the left cerebral white matter have grown and are exerting mass effect manifesting as subfalcine herniation and partial 3rd ventricle have large progress in sizeeffacement. WithFollowing contrast administration of contrast, these lesionlesions demonstrate a enhancing irregular thick edge with hetergenous centreintense rim enhancement.
The distortion of 3rd ventricle has been progressively worsen with definitive evidence of mid-line shift
Updates to Study Attributes
With comparisonIn addition to the last MRI imagefindings on the contrast-enhanced CT, the lesion has greatly progressed in size with increasing mass effect. The lesions and perilesional oedema on the left are expandingcan clearly be seen (particularly on the T2 and FLAIR sequences) extending across the corupus collosumcorpus callosum to the right, best seen on T2 signal and FLAIR.
Image MRI (T1) ( update )
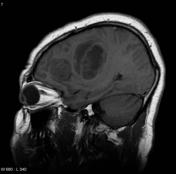
Image MRI (T1) ( update )
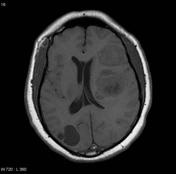
Image MRI (T2) ( update )
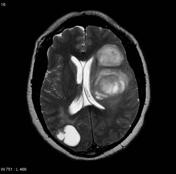
Image MRI (T1 C+) ( update )
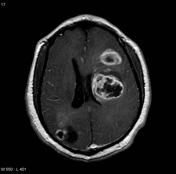
Image 1 MRI (T1) ( update )







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.