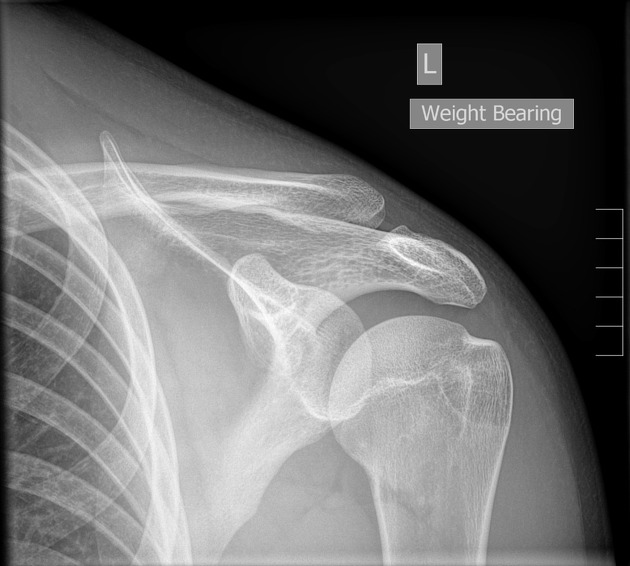
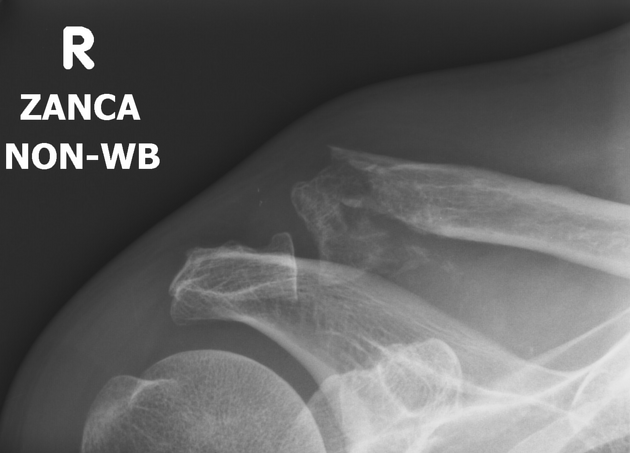
The Zanca view is a specialized projection of the acromioclavicular joint (ACJ), which will better demonstrate the acromioclavicular joint free from superimposition and aid in the assessment of distal osteophytes.
On this page:
Indications
The Zanca view is used in the assessment of acute and chronic acromioclavicular joint injuries. The view optimizes visualization of the acromioclavicular joint, as overlying structures can limit assessment in an AP projection, with distal osteophytes better visualized. It is also useful in preoperative planning of ACJ disruption post-screw fixation.
Patient position
patient is erect
midcoronal plane of the patient is parallel to the image receptor, in other words, the patient's back is against the image receptor
acromioclavicular joint of the affected side is at the center of the image receptor
affected arm is in a neutral position by the patient side
Technical factors
anteroposterior projection
-
centering point
at the acromioclavicular joint with a 10-15° cephalad angle
-
collimation
superior to the skin margins
inferior to the humeral head
lateral to include the skin margin
medial to lateral third of the clavicle
-
orientation
landscape
-
detector size
18 cm x 24 cm
-
exposure
40-50 kVp
10-15 mAs
-
SID
100 cm
-
grid
no
Image technical evaluation
the acromioclavicular joint is free from superimposition
Practical points
The differences between this projection and a standard AP are the cephalic angle and the decrease in kVp.





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.