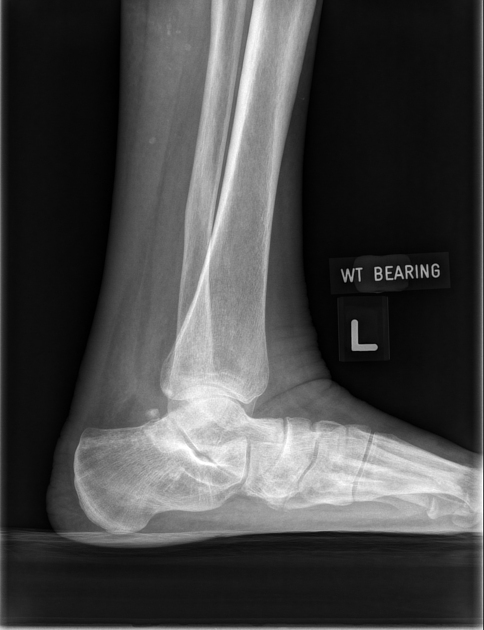
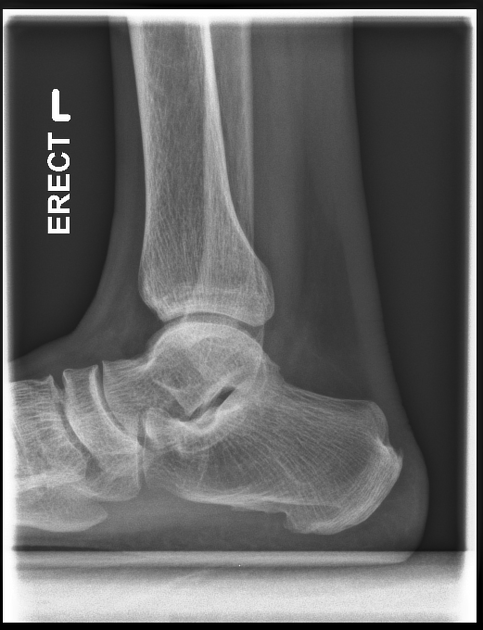
The weight-bearing lateral view of the ankle is a specialized projection that places the joint under normal weight-bearing conditions. The projection is utilized to assess the joint under stress and better demonstrate structural and functional deformities.
On this page:
Indications
This projection is utilized to assess the structural integrity of the ankle joint. If the patient is able, weight-bearing views should be performed in acute and follow-up settings 1.
Ultimately the radiographer will determine if the projection is safe to perform.
Patient position
the patient is standing on an upright stand with the ankle in question parallel to the detector
-
patient is distributing weight evenly
have something for the patient to hold onto, especially if they are unsteady on their feet
Technical factors
mediolateral projection
-
centering point
the bony prominence of the medial malleolus of the distal tibia
-
collimation
-
orientation
portrait
-
detector size
18 cm x 24 cm
-
exposure
50-60 kVp
3-5 mAs
-
SID
100 cm
-
grid
no
Image technical evaluation
distal fibula should be superimposed by the posterior portion of the distal tibia
talar domes should be superimposed, allowing for adequate inspection of the superior articular surface of the talus
joint space between the distal tibia and the talus is open and uniform.
Useful measurements
Practical points
Superior-inferior malalignment of the superior aspect of the talus is the resultant of the tibia not lying parallel to the image receptor.
Anterior-posterior malalignment of the talar domes is due to over or under rotation of the foot.
Although this projection is helpful to assess lower limb injuries better, it must be performed safely. Explain and demonstrate to the patient how it is performed. Give them something to hold on to. If the exam does not feel safe, explore alternative methods such as a standard, supine lateral projection.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.