Extrapulmonary tuberculosis (TB) refers to the hematogenous spread of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Pathology
Extrapulmonary tuberculosis can occur as a primary form of the disease, i.e. direct infection of an extrapulmonary organ without the presence of primary pulmonary tuberculosis or it can occur as a result of the spread of primary pulmonary tuberculosis.
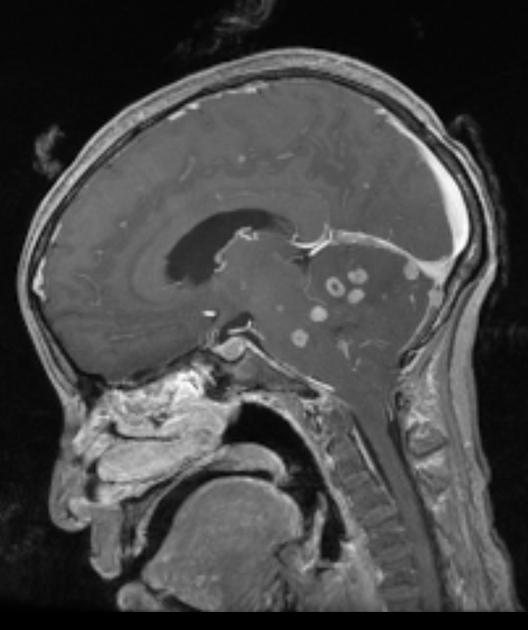
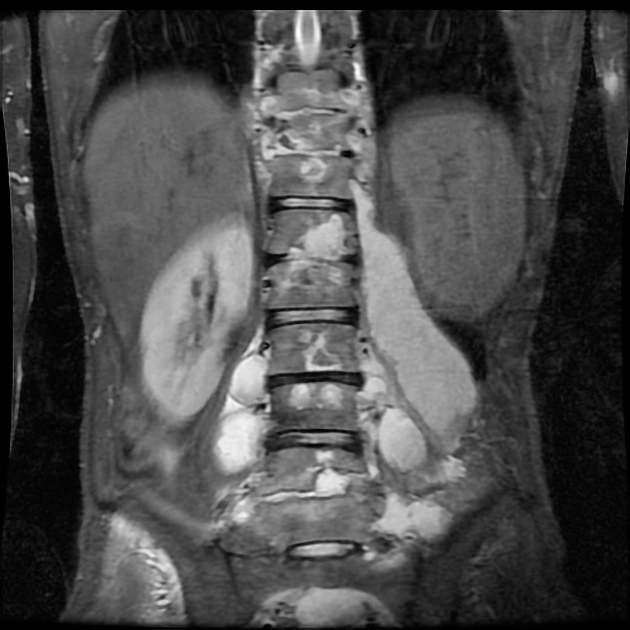
It appears classically as tuberculous granulomata (tuberculomas) within the affected organs. However, certain forms of the disease exist manifesting with specific findings:
-
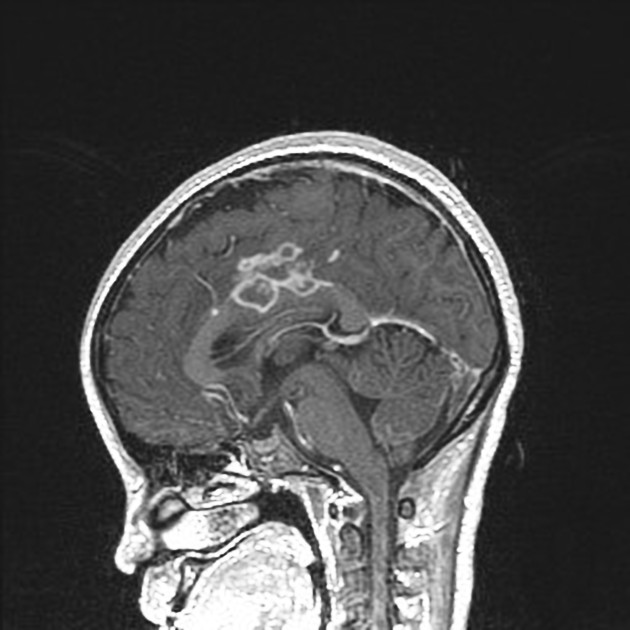
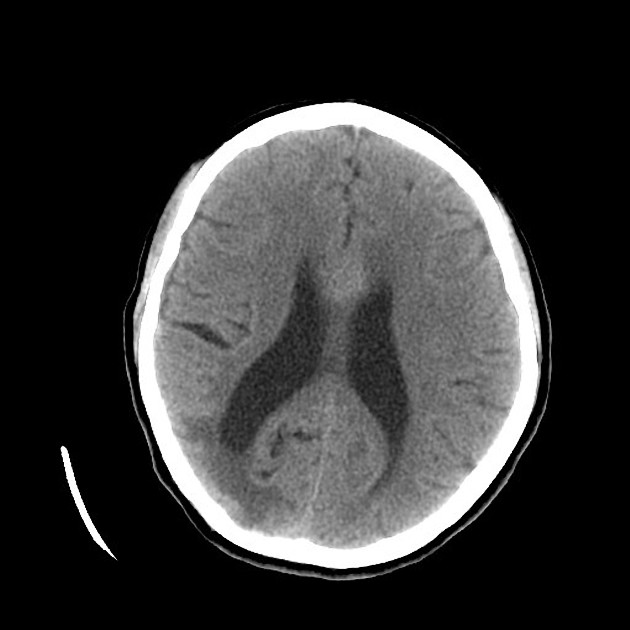
CNS
-
head and neck
-
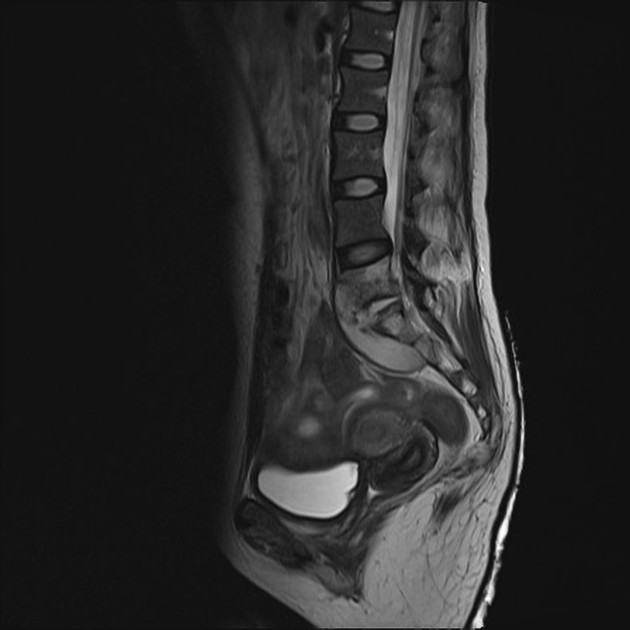
musculoskeletal
-
-
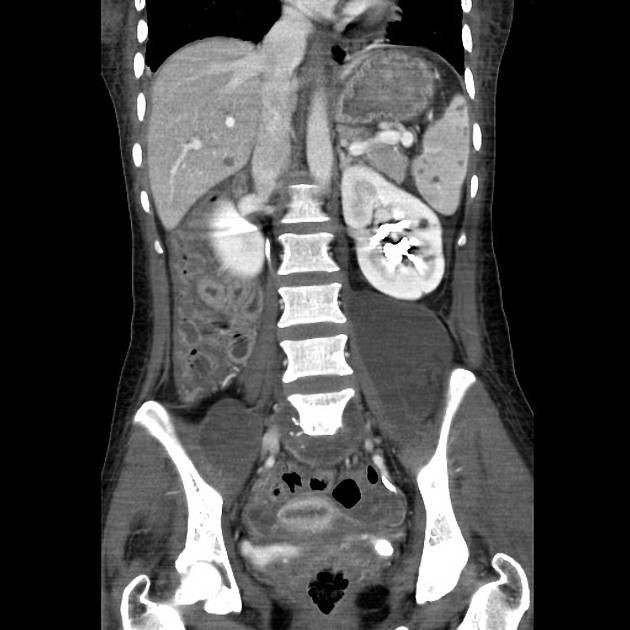
visceral tuberculosis
-
scrotal tuberculosis (testes, epididymis, seminal vesicles, ductus (vas) deferens)
Radiographic features
Widely variable dependent on the site of involvement. It is best to refer to site-specific articles.
As tuberculous organ infection can mimic malignant disease, studies have reported the usefulness of 18 FDG PET-CT in evaluating and following up patients in whom the diagnosis is in doubt 4.





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.