The forearm AP view is one of two standard projections in the forearm series to assess the radius and ulna.
On this page:
Indications
This view demonstrates the elbow joint in its natural anatomical position allowing for assessment of suspected dislocations or fractures and localizing foreign bodies within the forearm.
Patient position
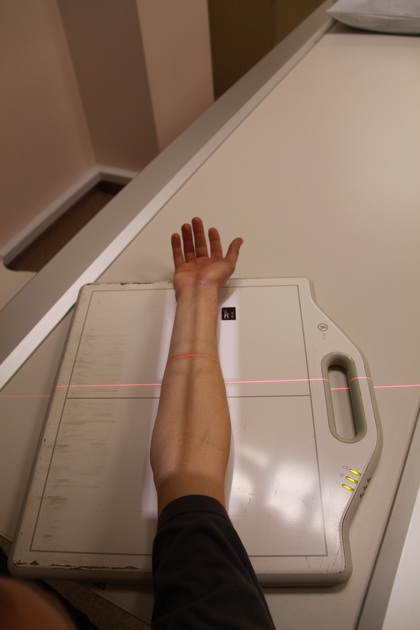
patient is seated alongside the table
forearm is supinated, and its dorsal surface is kept in contact with the cassette with extension at the elbow joint
both elbow joint and wrist joints are also kept in contact with the cassette
Technical factors
anteroposterior projection
-
centering point
mid-forearm region
-
collimation
distal to the wrist joint
proximal to elbow joint
-
orientation
portrait
-
detector size
24 cm x 30 cm
-
exposure
50-60 kVp
3-5 mAs
-
SID
100 cm
-
grid
no
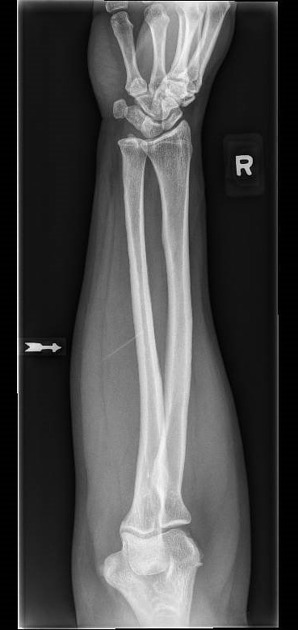
Image technical evaluation
trochlea and capitulum being seen in profile
the wrist is in AP position, with minimal superimposition of the distal radius and ulna
the arm should be extended appropriately, as evidenced by the radial head being seen in profile
Practical points
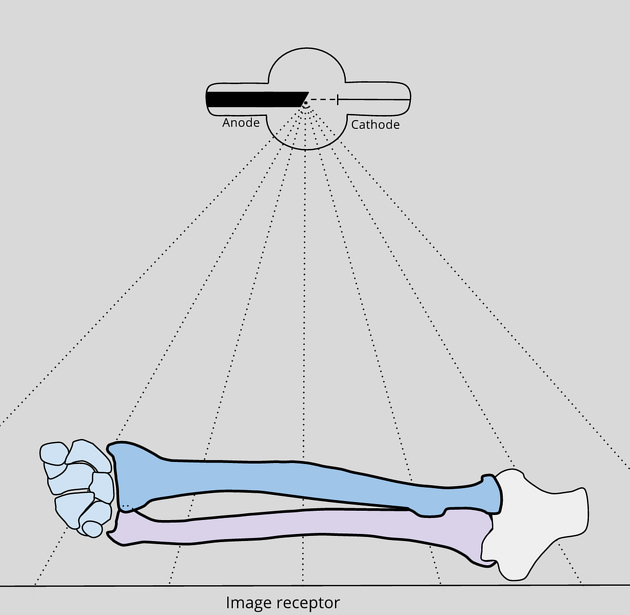
Contrary to popular belief, the AP forearm view should not be considered when evaluating any occult injuries of the wrist joint and or elbow due to beam divergence (see Figure 1). Beam divergence at the edges of the image should be acknowledged when assessing anatomy 2.





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.