Ghost image (orthopantomogram)
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Andrew Murphy had no recorded disclosures.
View Andrew Murphy's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Andrew Murphy had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
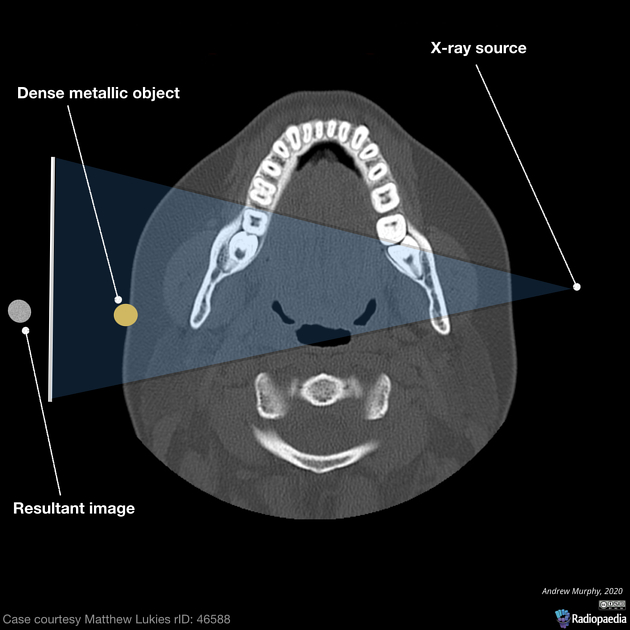
View Andrew Murphy's current disclosuresA ghost image is a commonly observed artifact in an orthopantomogram whereby a dense, often metallic object is located between the source of x-ray and the focal center, resulting in a duplicate 'ghost' image at the contralateral aspect of the image.
Real image vs ghost image
In panoramic image such as the orthopantomogram, structures within the focal trough (a panoramic arch similar to that of the teeth) will be sharp, well defined and overall lacking in distortion. Objects outside of this focal trough that are dense enough to attenuate x-rays will occasionally present twice as the x-ray tube rotates around the patient, this is known as a ghost image. The density will appear at the true location and secondly on the contralateral aspect of the image as a distorted 'ghost' image. The ghost image is distorted and larger than the actual object projected and often not at the same height 1.
Practical points
When positioning for an orthopantomogram take into account any metallic objects on the patient's face and head can impact the image. This includes earrings, cheek piercings and hair clips.
References
- 1. Ramos BC, da Silva Izar BR, Pereira JL, Souza PS, Valerio CS, Tuji FM, Manzi FR. Formation of ghost images due to metal objects on the surface of the patient's face: A pictorial essay. (2016) Imaging science in dentistry. 46 (1): 63-8. doi:10.5624/isd.2016.46.1.63 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Radiographs (adult)
- general radiography (adult)
- radiographic positioning terminology[+][+]
-
systematic radiographic technical evaluation (mnemonic)
- portable radiography
- chest radiography[+][+]
- abdominal radiography[+][+]
-
upper limb radiography[+][+]
-
shoulder girdle radiography
- scapula series
-
shoulder series
- shoulder (AP view)
- shoulder (internal rotation view)
- shoulder (external rotation view)
- shoulder (superior-inferior axial view)
- shoulder (inferior-superior axial)
- shoulder (West Point view)
- shoulder (Velpeau view)
- shoulder (modified trauma axial view)
- shoulder (supine lateral view)
- shoulder (modified transthoracic supine lateral)
- shoulder (lateral scapula view)
- shoulder (AP glenoid view)
- shoulder (Garth view)
- shoulder (outlet view)
- shoulder (Stryker notch view)
- acromioclavicular joint series
-
clavicle series
- clavicle (AP view)
- clavicle (AP cephalic view)
- clavicle (oblique view)
- sternoclavicular joint series
- arm and forearm radiography
- wrist and hand radiography
- wrist series
- scaphoid series
- hand series
- thumb series
- fingers series
- rheumatology hands series
- bone age (radiograph)
-
shoulder girdle radiography
-
lower limb radiography[+][+]
- pelvic girdle radiography
- thigh and leg radiography
- ankle and foot radiography
- skull radiography[+][+]
-
paranasal sinus and facial bone radiography[+][+]
- facial bones
- mandible
- nasal bone
- zygomatic arches
- paranasal sinuses
- temporal bones
- dental radiography
-
orthopantomography
- ghost image (orthopantomogram)
- temporomandibular joints[+][+]
- temporomandibular joint (AP axial view)
- temporomandibular joint (axiolateral oblique view)
-
orthopantomography
-
spinal radiography[+][+]
- cervical spine series
-
thoracic spine series
- thoracic spine (AP view)
- thoracic spine (lateral view)
- thoracic spine (oblique view)
- lumbar spine series
- sacrococcygeal radiography




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.