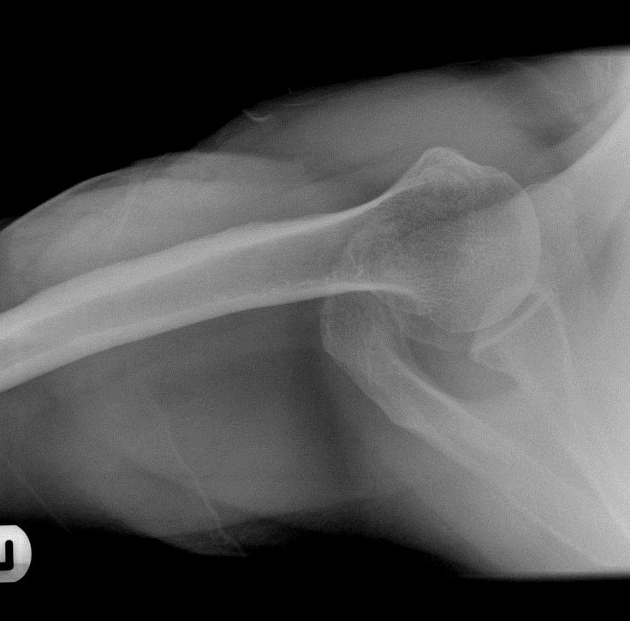
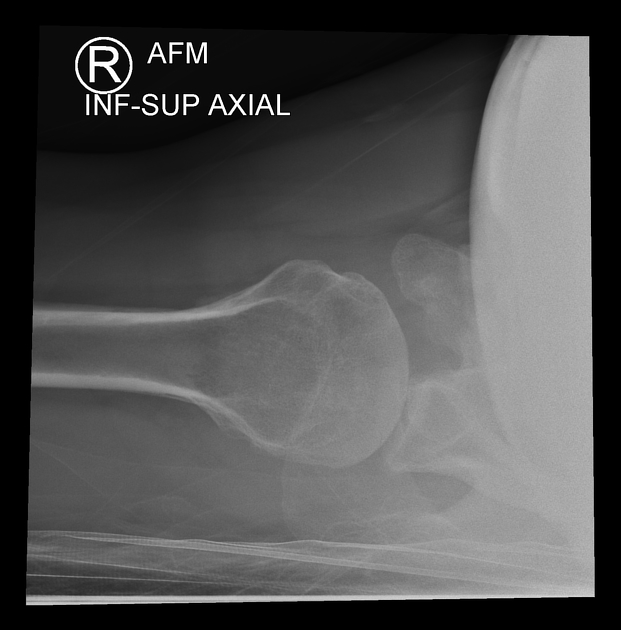
The inferosuperior axial view also known as a Lawrence view of the shoulder is a modified axial projection best utilized with supine patients. It is an orthogonal projection to the AP view and replaces the lateral shoulder projection.
On this page:
Indications
It is an appropriate projection to assess suspected dislocations, proximal humerus pathology and effective in demonstrating the articular surfaces of the humeral head and glenoid 1-3. Hill-Sachs lesions are well demonstrated on this projection along with the lesser tubercle of the humerus.
This view is performed when the patient can only lie supine; thus making the superior-inferior axial view difficult to achieve. This view provides additional information for assessing dislocations and glenohumeral instability; particularly if these are not seen well on a standard AP view 4.
Patient position
the patient is supine
image receptor is rested upon the superior part of the affected shoulder
the affected arm is abducted as much as achievable
the arm is externally rotated
the patient's head is to be tilted away towards the unaffected side
Technical factors
axial projection (inferosuperior)
-
centering point
the x-ray tube is in the same plane as the glenohumeral joint shooting inferosuperior
there is a 20-30° medial angle aimed at the glenohumeral joint
-
collimation
anterior-posterior to the skin margins
lateral to proximal third of the humerus
medial to include glenohumeral joint
-
orientation
landscape
-
detector size
18 cm x 24 cm
-
exposure
50-60kVp
8-15 mAs
-
SID
100-150 cm
-
grid
no
Image technical evaluation
Clear visualization of the humeral head (with no superimposition) and its relationship with the glenoid of the scapula. In addition to the acromion and the coracoid process. The lesser tubercle should be seen projected anteriorly in profile. The coracoid process is pointing anteriorly
Practical points
This is an ideal projection when patients are unable to move from the supine position. It can cause patient pain when abducting but nowhere near as much as the standard axial projection.
Be wary of your surroundings when moving the x-ray tube in position, there is a high potential of hitting the patients feet.
Other projections suitable for supine patients that require an orthogonal view of the AP view include:
modified transthoracic supine lateral (spinal patients)




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.