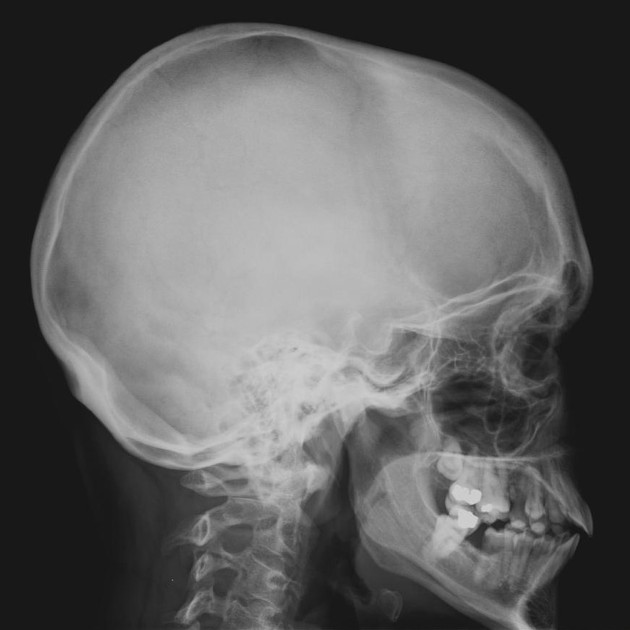
The skull lateral view is a non-angled lateral radiograph of the skull. This view provides an overview of the entire skull rather than attempting to highlight any one region.
On this page:
Indications
This projection is used to evaluate for skull fractures, in addition to neoplastic changes and Paget disease. In the trauma setting, a horizontal beam lateral projection may demonstrate air-fluid levels in the sphenoid sinus 1, an indication of basal skull fracture.
Patient position
the sagittal midline of the patient's head is parallel to the image detector
sella turcica in profile
temporomandibular joints are superimposed
Technical factors
lateral projection
-
centering point
the beam travels laterally, with 0° of angulation, through a point ~4 cm above the external auditory meatus
-
collimation
superiorly to include skin margins
inferiorly to include base of skull
anteriorly to include frontal bone
posteriorly to the skin margins
-
orientation
landscape
-
detector size
24 cm x 30 cm
-
exposure
60-70 kVp
10-20 mAs
-
SID
100 cm
-
grid
no
Image technical evaluation
the sagittal midline of the patient's head is parallel to the image detector
sella turcica in profile
temporomandibular joints are superimposed
Practical points
remove earrings, glasses, hairclips, hearing aids and dentures to avoid artifact obscuring important pathology










 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.