Toes series
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Gorton S, Murphy A, Knipe H, et al. Toes series. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 09 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-47985
rID:
47985
Article created:
12 Sep 2016,
Sarah Gorton
Disclosures:
At the time the article was created Sarah Gorton had no recorded disclosures.
View Sarah Gorton's current disclosures
Last revised:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was last revised Andrew Murphy had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Andrew Murphy's current disclosures
Revisions:
9 times, by
5 contributors -
see full revision history and disclosures
Systems:
Sections:
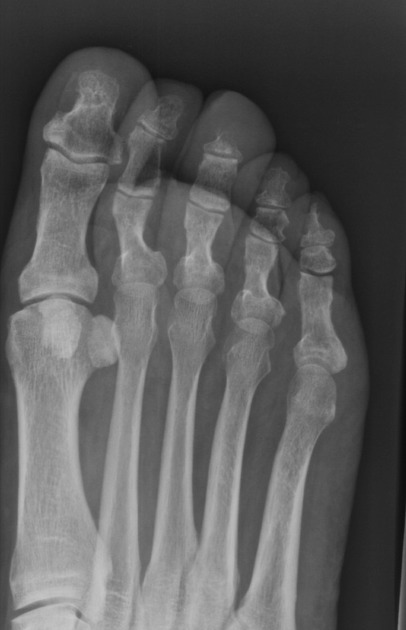
The toes series is comprised of an AP, AP oblique, and a lateral projection. The series is often utilized in trauma situations. It examines the entirety of the proximal middle and distal phalanges of the foot.
Indications
Toe radiographs are performed for a variety of indications including 1:
- fracture
- dislocation
- osteoarthritis
- gout
- osteomyelitis
- general toe pain
Projections
Standard projections
- AP: demonstrates the toe(s) of interest in the dorsal-plantar/AP plane
- AP oblique: toes of interest are projected 30 degrees to the AP projection
- lateral: orthogonal view of the AP projection often used to determine dislocation directed and fracture displacement.
Additional projections
- sesamoid view: tangential projection of the toes can sometimes be performed to demonstrate sesamoid bone
References
- 1. Van Vliet-Koppert ST, Cakir H, Van Lieshout EM et-al. Demographics and functional outcome of toe fractures. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2011;50 (3): 307-10. doi:10.1053/j.jfas.2011.02.003 - Pubmed citation
- 2. RT(R) KLBMA, (CT) JLMR. Textbook of Radiographic Positioning and Related Anatomy, 8e. Mosby. ISBN:0323083889. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
Incoming Links
Related articles: Radiographs (adult)
- general radiography (adult)
- radiographic positioning terminology[+][+]
-
systematic radiographic technical evaluation (mnemonic)
- portable radiography
- chest radiography[+][+]
- abdominal radiography[+][+]
-
upper limb radiography[+][+]
-
shoulder girdle radiography
- scapula series
-
shoulder series
- shoulder (AP view)
- shoulder (internal rotation view)
- shoulder (external rotation view)
- shoulder (superior-inferior axial view)
- shoulder (inferior-superior axial)
- shoulder (West Point view)
- shoulder (Velpeau view)
- shoulder (modified trauma axial view)
- shoulder (supine lateral view)
- shoulder (modified transthoracic supine lateral)
- shoulder (lateral scapula view)
- shoulder (AP glenoid view)
- shoulder (Garth view)
- shoulder (outlet view)
- shoulder (Stryker notch view)
- acromioclavicular joint series
-
clavicle series
- clavicle (AP view)
- clavicle (AP cephalic view)
- clavicle (oblique view)
- sternoclavicular joint series
- arm and forearm radiography
- wrist and hand radiography
- wrist series
- scaphoid series
- hand series
- thumb series
- fingers series
- rheumatology hands series
- bone age (radiograph)
-
shoulder girdle radiography
-
lower limb radiography
- pelvic girdle radiography[+][+]
- thigh and leg radiography[+][+]
- ankle and foot radiography
- ankle series[+][+]
- foot series[+][+]
- hindfoot[+][+]
- calcaneus series[+][+]
- toes series
- skull radiography[+][+]
-
paranasal sinus and facial bone radiography[+][+]
- facial bones
- mandible
- nasal bone
- zygomatic arches
- paranasal sinuses
- temporal bones
- dental radiography[+][+]
- orthopantomography
- temporomandibular joints
- temporomandibular joint (AP axial view)
- temporomandibular joint (axiolateral oblique view)
-
spinal radiography[+][+]
- cervical spine series
-
thoracic spine series
- thoracic spine (AP view)
- thoracic spine (lateral view)
- thoracic spine (oblique view)
- lumbar spine series
- sacrococcygeal radiography






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.