Toes (sesamoid view)
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Murphy A, Yap J, Er A, et al. Toes (sesamoid view). Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 09 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-58723
rID:
58723
Article created:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was created Andrew Murphy had no recorded disclosures.
View Andrew Murphy's current disclosures
Last revised:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was last revised Joshua Yap had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Joshua Yap's current disclosures
Revisions:
5 times, by
4 contributors -
see full revision history and disclosures
Systems:
Sections:
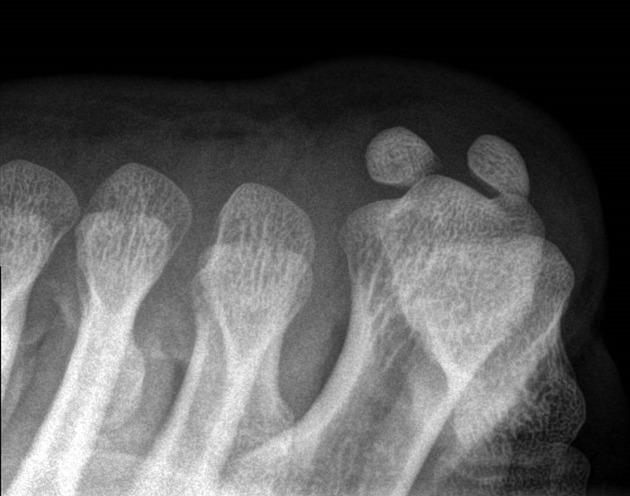
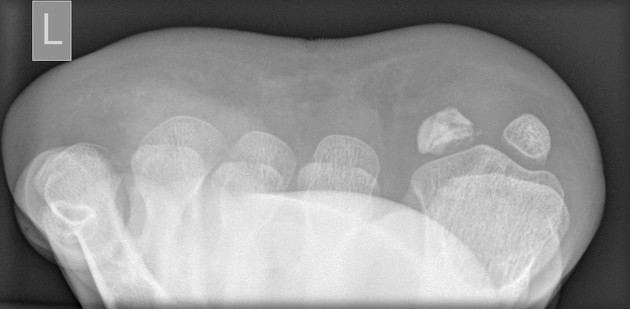
The sesamoid view of the toes is a specialized view examining the sesamoid bones of the first metatarsal.
On this page:
Indications
This view provides a better profile of any fractures or dislocation of the sesamoid bones with their articulation at the first metatarsophalangeal joint 1.
Patient position
- the patient may be supine or sitting upright with their leg straighten on the table
- the foot is in dorsiflexion
- the toes pulled back toward the patient
Technical factors
- axial projection
-
centering point
- the base of the first metatarsal
-
collimation
- laterally to the extent of the base of the first metatarsal
- anteriorly mid distal first metatarsal
- posterior to the skin margin
-
orientation
- portrait
-
detector size
- 24 cm x 30 cm
-
exposure
- 50-60 kVp
- 3-5 mAs
-
SID
- 100 cm
-
grid
- no
Image technical evaluation
- both the sesamoid bones are free from any superimposition
Practical points
Seldom requested, however technically simple to perform, offer the patient tape/string to help pull the toes back.
References
- 1. Painful sesamoid of the great toe. (2014) World Journal of Orthopedics. 5 (2): 146. doi:10.5312/wjo.v5.i2.146 - Pubmed
- 2. John Lampignano, Leslie E. Kendrick. Bontrager's Textbook of Radiographic Positioning and Related Anatomy. (2017) ISBN: 9780323399661
Incoming Links
Related articles: Radiographs (adult)
- general radiography (adult)
- radiographic positioning terminology[+][+]
-
systematic radiographic technical evaluation (mnemonic)
- portable radiography
- chest radiography[+][+]
- abdominal radiography[+][+]
-
upper limb radiography[+][+]
-
shoulder girdle radiography
- scapula series
-
shoulder series
- shoulder (AP view)
- shoulder (internal rotation view)
- shoulder (external rotation view)
- shoulder (superior-inferior axial view)
- shoulder (inferior-superior axial)
- shoulder (West Point view)
- shoulder (Velpeau view)
- shoulder (modified trauma axial view)
- shoulder (supine lateral view)
- shoulder (modified transthoracic supine lateral)
- shoulder (lateral scapula view)
- shoulder (AP glenoid view)
- shoulder (Garth view)
- shoulder (outlet view)
- shoulder (Stryker notch view)
- acromioclavicular joint series
-
clavicle series
- clavicle (AP view)
- clavicle (AP cephalic view)
- clavicle (oblique view)
- sternoclavicular joint series
- arm and forearm radiography
- wrist and hand radiography
- wrist series
- scaphoid series
- hand series
- thumb series
- fingers series
- rheumatology hands series
- bone age (radiograph)
-
shoulder girdle radiography
-
lower limb radiography
- pelvic girdle radiography[+][+]
- thigh and leg radiography[+][+]
- ankle and foot radiography
- ankle series[+][+]
- foot series[+][+]
- hindfoot[+][+]
- calcaneus series[+][+]
-
toes series
- toes (AP view)
- toes (oblique view)
- toes (lateral view)
- toes (sesamoid view)
- skull radiography[+][+]
-
paranasal sinus and facial bone radiography[+][+]
- facial bones
- mandible
- nasal bone
- zygomatic arches
- paranasal sinuses
- temporal bones
- dental radiography[+][+]
- orthopantomography
- temporomandibular joints
- temporomandibular joint (AP axial view)
- temporomandibular joint (axiolateral oblique view)
-
spinal radiography[+][+]
- cervical spine series
-
thoracic spine series
- thoracic spine (AP view)
- thoracic spine (lateral view)
- thoracic spine (oblique view)
- lumbar spine series
- sacrococcygeal radiography




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.