CT artifacts
Last revised by Lam Van Le
on 11 Feb 2025
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Cuete D, Le L, Niknejad M, et al. CT artifacts. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 18 Feb 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-25638
Permalink:
rID:
25638
Article created:
1 Nov 2013,
David Cuete
Disclosures:
At the time the article was created David Cuete had no recorded disclosures.
View David Cuete's current disclosures
Last revised:
11 Feb 2025,
Lam Van Le
Disclosures:
At the time the article was last revised Lam Van Le had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Lam Van Le's current disclosures
Revisions:
31 times, by
16 contributors -
see full revision history and disclosures
Sections:
Synonyms:
- CT artifact
- CT artefacts
- CT artefact
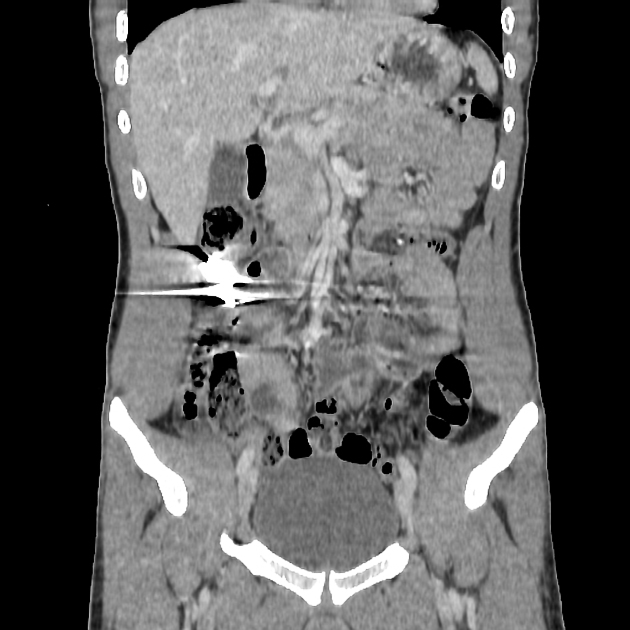
CT artifacts are common and can occur for various reasons. Knowledge of these artifacts is important because they can mimic pathology (e.g. partial volume artifact) or can degrade image quality to non-diagnostic levels.
CT artifacts can be classified according to the underlying cause of the artifact.
Patient-based artifacts
Physics-based artifacts
-
beam hardening
- cupping artifact
- streak and dark bands
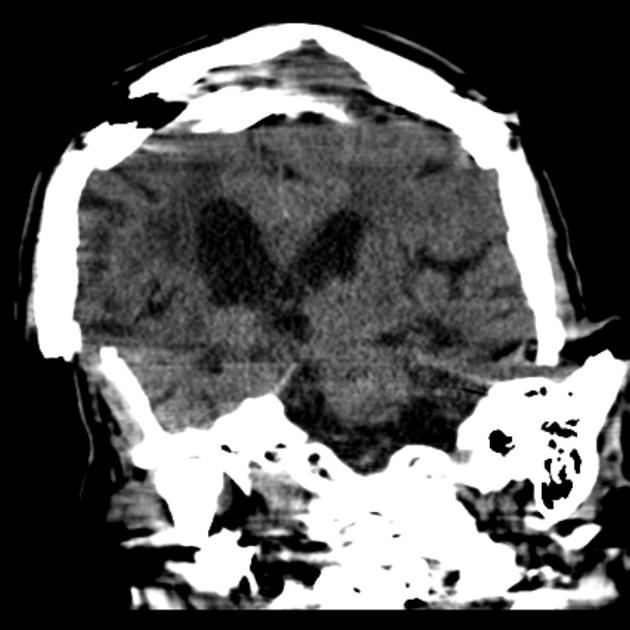
- metal artifact / high-density foreign material artifact
- partial volume averaging
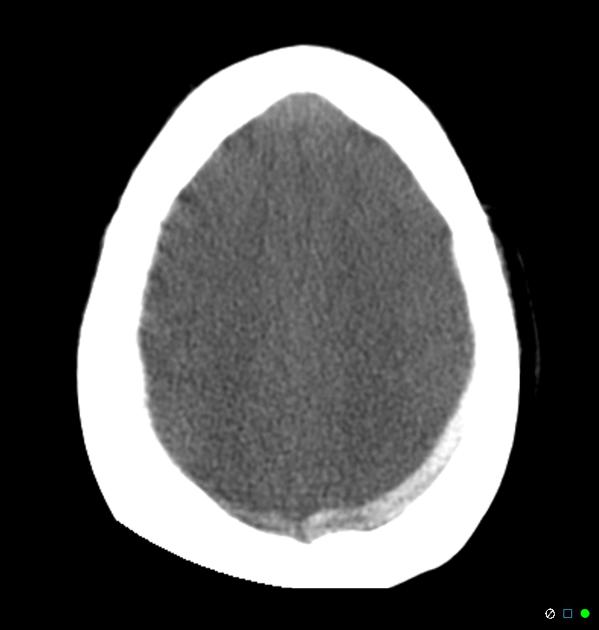
- quantum mottle (noise)
- photon starvation
- aliasing
- truncation artifact
Hardware-based artifacts
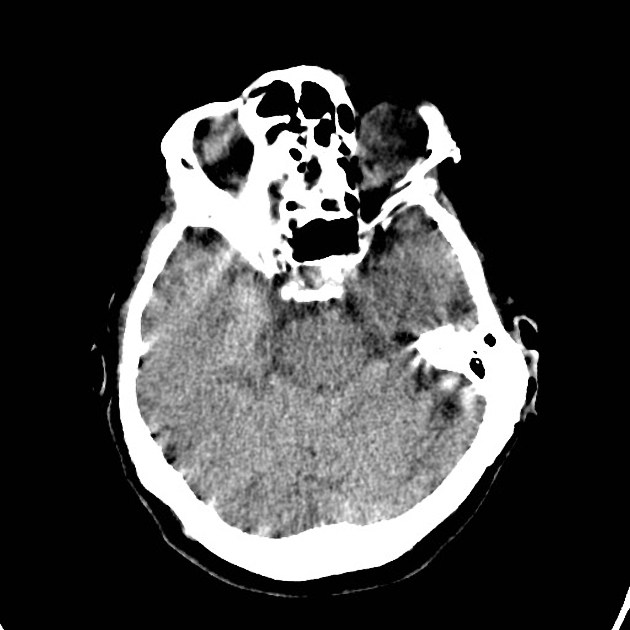
- ring artifact
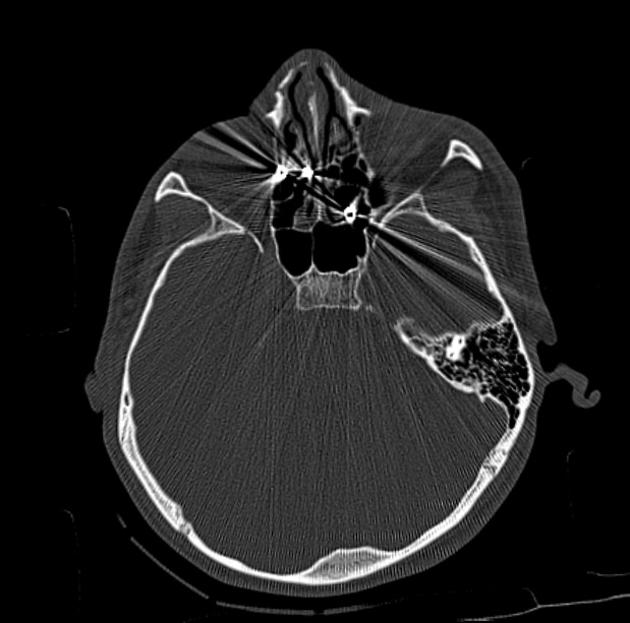
- tube arcing
- out of field artifact
- air bubble artifact
- helical and multichannel artifact
- windmill artifact
- cone beam effect
- multiplanar reconstruction (MPR) artifact
See also
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Barrett JF, Keat N. Artifacts in CT: recognition and avoidance. Radiographics. 2004;24 (6): 1679-91. doi:10.1148/rg.246045065 - Pubmed citation
- 2. Mori I, Machida Y, Osanai M et-al. Photon starvation artifacts of X-ray CT: their true cause and a solution. Radiol Phys Technol. 2013;6 (1): 130-41. doi:10.1007/s12194-012-0179-9 - Pubmed citation
- 3. Kalender WA. Computed Tomography. Publicis. (2011) ISBN:389578317X. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
Incoming Links
Articles:
Cases:
Multiple choice questions:
Related articles: Computed tomography
- computed tomography in practice
-
computed tomography overview
- iodinated contrast media[+][+]
- CT IV contrast media administration[+][+]
-
CT artifacts
- patient-based artifacts
- physics-based artifacts
- hardware-based artifacts
- ring artifact
- tube arcing
- out of field artifact
- air bubble artifact
- helical and multichannel artifacts[+][+]
- CT technology[+][+]
-
generations of CT scanners
- helical CT scanning
- step and shoot scanning
- ultra-high-resolution CT (UHRCT)
- CT x-ray tube
- CT fluoroscopy
- cone-beam CT
-
generations of CT scanners
- dual-energy CT[+][+]
- CT image reconstruction[+][+]
- CT image quality[+][+]
- CT dose[+][+]
-
CT protocols[+][+]
- composite
- head & neck
- chest
- abdomen and pelvis
- CT abdomen-pelvis (protocol)
- CT abdominal aorta
- CT adrenals (protocol)
- CT cholangiography (protocol)
- CT colonography (protocol)
- CT enteroclysis (protocol)
- CT enterography (protocol)
- CT gastrography (protocol)
- CT kidneys, ureters and bladder (protocol)
- CT urography (protocol)
- CT Renal mass (protocol)
- CT angiography of the splanchnic vessels (protocol)
- CT renal split bolus
- CT pancreas (protocol)
- liver









 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.