Wilhelm C Roentgen (1845-1923) was a German physicist who is celebrated globally for his discovery of x-rays on 8 November 1895.
On this page:
Images:
Early life
Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen (Röntgen in German) was born on 27 March 1845 in Lennep, Germany. He attended the primary and secondary school run by Martinus Herman van Doorn in the town of Apeldoorn, Netherlands 1. Although born in Germany to a German father, his mother was Dutch, and he grew up in the Netherlands.
At the age of 17, he moved to Utrecht, also in the Netherlands, and enrolled in the Utrecht Technical School. A few years later, he was expelled because of a caricature of one of their teachers on the blackboard. In reality, he was innocent of this but refused to say who had been responsible 1.
In 1865, aged 20, Wilhelm enrolled at the Mechanical Technical Division of the Zurich Polytechnicab School in Switzerland. Three years later, he received the degree of mechanical engineer 1.
In 1869 he received his PhD in "Studies on Gases" from Zurich Polytechnicab School, where he remained until 1870.
In 1870 he followed his mentor, Professor Kundt, to the Julius Maximilians University of Würzburg in Germany. This proved to be short-lived, with the appointment proving a disappointment to both Roentgen and Kundt 1.
Two years later, in 1872, both moved to Kaiser Wilhelms University of Strasbourg 1.
At the age of 30, in 1875, he became Professor of Physics at the Academy of Stuttgart-Hohenheim in Württemberg, which granted him German citizenship 1. This appointment was also short-lived, and Wilhelm moved back to Strasbourg in 1876 as Professor of Theoretical Physics at the Kaiser Wilhelms University.
Following significant publications, he moved in 1879 to the Justus von Liebig University of Giessen, where he was given the opportunity to design a new department.
In 1888 he moved to the Physical Institute at the University of Würzburg, a city in the region of Franconia, Northern Bavaria, Germany. It was in Würzburg that he was to make the discovery he is most famous for.
In 1900 he moved from Würzburg to take up the Chair of Physics in Munich.
Discovery of x-rays
Towards the end of 1895, Wilhelm became interested in the physical properties of cathode ray tubes, and began amassing relevant experimental equipment.
On Friday, 8 November 1895, Wilhelm was reproducing earlier work using low-output Lenard tubes, whereby fluorescence was visible on a screen coated with barium platinocyanide. He moved on to a higher output Hittorf-Crookes tube and reproduced the same phenomenon on a screen located near the tube. While in the darkened room, he noticed similar fluorescence arising from another barium platinocyanide-coated screen over a meter away, far further than cathode ray tubes were known to work. Despite moving the screen even further, fluorescence was still visible 1.
Enraptured in the thrill of discovery, he worked through the night and soon noticed that these new rays seemed to effortlessly pass through many objects opaque to visible light (e.g. books), but were blocked by metal objects, their outline visible on the screen. While holding such an object he noted the outline of the bones of his hand 1. As the nature of the rays were unknown he called them x-rays.
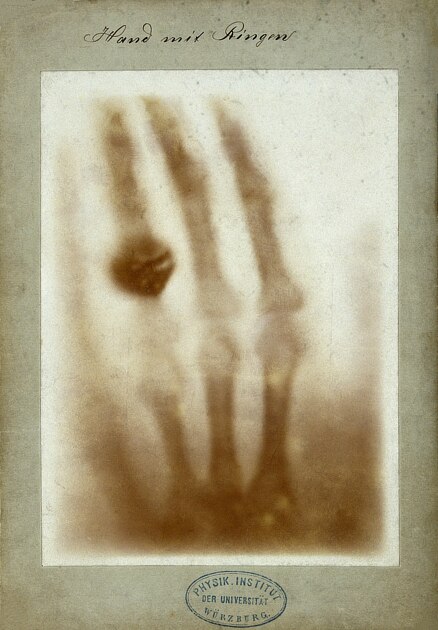
Arguably the most famous x-ray ever taken, that of the hand of his wife Bertha, was dated 27 December 1895. This was not the first x-ray ever taken as is erroneously believed by most. The next day, he delivered a paper titled “On a New Kind of Rays” to the Würzburg Physical-Medical Society 1. Only the first page of his original manuscript is extant; the other pages were destroyed after his death as he stipulated in his will 2.
Later life
Roentgen was awarded the inaugural Nobel Prize for Physics in 1901, the citation read "The Academy has awarded Professor Röntgen of Munich the Nobel Prize for Physics on the grounds of discovery, the name of which will always be linked with him as Röntgen rays or as he calls them himself X-rays. From the properties associated with Röntgen rays, only those are considered that contribute to the far reaching applications these rays have found in medical practice" 2.
Accolades
Rumford Medal (1896)
Matteucci Medal (1896)
Elliott Cresson Medal (1897)
Barnard Medal for Meritorious Service to Science (1900)
Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen developed colon cancer, eventually dying on 10 February 1923, at the age of 78 1.
Legacy
discovery of x-rays, and arguably, the whole of radiology as we know it
roentgenology, a synonym for radiology, popular in North America
roentgen rays, a synonym for x-rays, e.g. ARRS
rem (roentgen equivalent man), a legacy unit of measurement of effective dose
roentgen, a legacy unit of measurement of radiation exposure
element number 111 was named roentgenium (Rg) in his honor 3
International Day of Radiology is celebrated annually on the anniversary of the discovery of x-rays, i.e. 8 November
Deutsche Roentgen-Museum in Remscheid (a city in the state of North Rhine-Westphalia in Germany) houses items related to Roentgen and his life. The house where Roentgen was born is nearby and can be visited.
Roentgen Memorial Site in Würzburg, includes the laboratory where Roentgen made his epoch-making discovery and an exhibition.
Roentgen Peak, a mountain in Antarctica
Roentgen, a crater on the moon 5





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.