Infarct core
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Frank Gaillard had no recorded disclosures.
View Frank Gaillard's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Andrew Murphy had no recorded disclosures.
View Andrew Murphy's current disclosuresThe infarct core denotes the part of an acute ischemic stroke that has already infarcted or is irrevocably destined to infarct regardless of reperfusion. It is also referred to as established infarct and is in distinction from the penumbra, which remains potentially salvageable.
CT perfusion
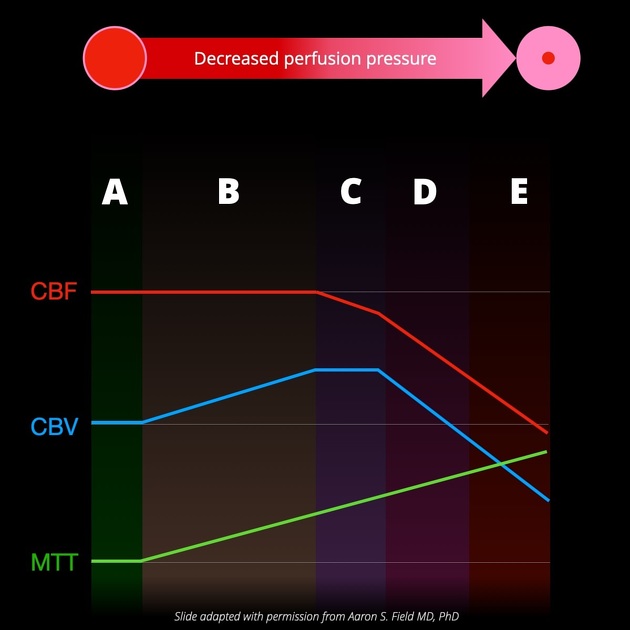
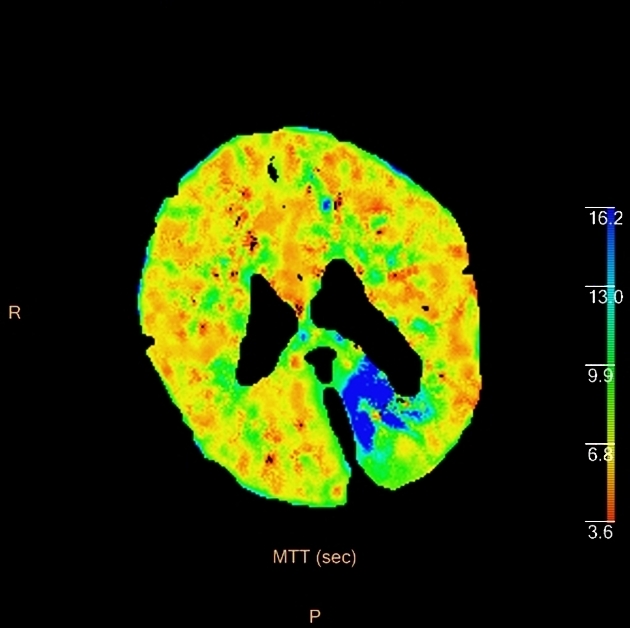
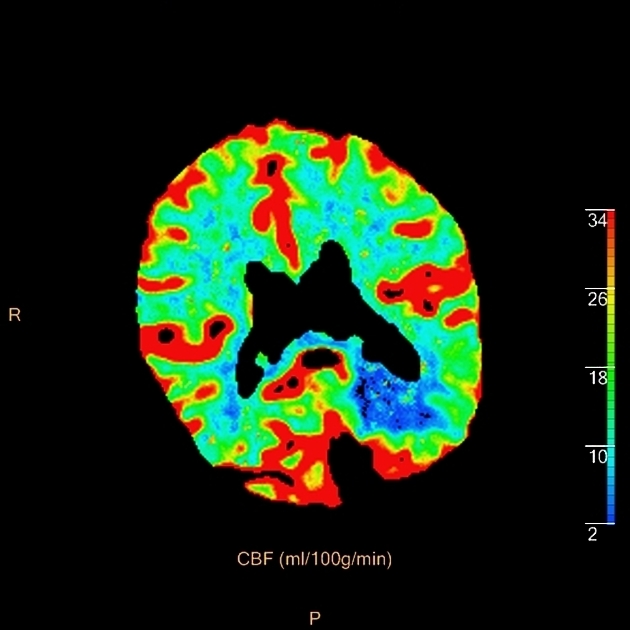
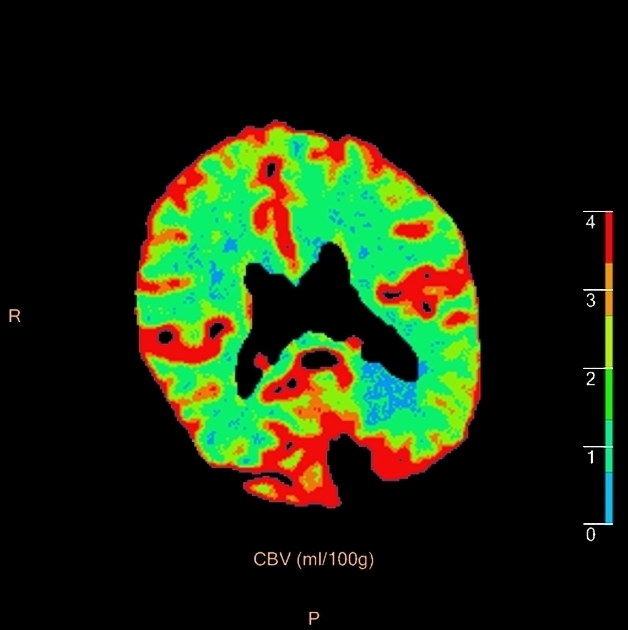
On CT perfusion, the infarct core is defined as the area of the brain with 1,2:
- increased mean transit time (MTT)
- markedly decreased relative cerebral blood flow (CBF): <30% normal
- decreased cerebral blood volume (CBV): <40% normal
By contrast, the ischemic penumbra will have only moderately decreased cerebral blood flow and normal or even increased cerebral blood volume due to autoregulation.
It is of note that CT perfusion may overestimate infarct core on admission, especially in the early time window of a stroke, by predicting lesion in areas that will not show infarct on follow-up imaging, a phenomenon known as a ghost infarct core 3.
MRI
On MRI, the infarct core correlates closely with restricted diffusion on diffusion-weighted imaging 1.
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Srinivasan A, Goyal M, Al Azri F et-al. State-of-the-art imaging of acute stroke. Radiographics. 2006;26 Suppl 1 (suppl 1): S75-95. Radiographics (full text) - doi:10.1148/rg.26si065501 - Pubmed citation
- 2. de Lucas EM, Sánchez E, Gutiérrez A et-al. CT protocol for acute stroke: tips and tricks for general radiologists. Radiographics. 2008;28 (6): 1673-87. Radiographics (full text) - doi:10.1148/rg.286085502 - Pubmed citation
- 3. 1. Boned S, Padroni M, Rubiera M, Tomasello A, Coscojuela P, Romero N, Muchada M, Rodríguez-Luna D, Flores A, Rodríguez N, Juega J, Pagola J, Alvarez-Sabin J, Molina CA, Ribó M. Admission CT perfusion may overestimate initial infarct core: the ghost infarct core concept. (2017) Journal of neurointerventional surgery. doi:10.1136/neurintsurg-2016-012494 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Stroke protocol (CT)
- Acute basilar artery occlusion
- Terms used in radiology
- Cerebral intraparenchymal hyperattenuation post thrombolysis
- CT perfusion in ischaemic stroke
- Ischaemic penumbra
- Early DWI reversal in ischaemic stroke
- Infarct core
- Ghost infarct core
- Potential recuperation ratio (PRR)
- Endovascular clot retrieval (ECR)
- Ischemic stroke
- Code stroke CT (an approach)
Related articles: Stroke and intracranial haemorrhage
-
stroke and intracranial hemorrhage
- general articles
-
ischemic stroke
- general discussions
- scoring and classification systems
- Alberta stroke program early CT score (ASPECTS)
- ASCOD classification
- Canadian Neurological Scale
- Heidelberg bleeding classification
- NIH Stroke Scale
- Mathew stroke scale
- modified Rankin scale
- Orgogozo Stroke Scale
- Scandinavian Stroke Scale
- thrombolysis in cerebral infarction (TICI) scale
- TOAST classification
- collateral vessel scores
- signs
- by region
- hemispheric infarcts
- frontal lobe infarct
- parietal lobe infarct
- temporal lobe infarct
- occipital lobe infarct
- alexia without agraphia syndrome: PCA
- cortical blindness syndrome (Anton syndrome): top of basilar or bilateral PCA
- Balint syndrome: bilateral PCA
- lacunar infarct
-
thalamic infarct
- artery of Percheron infarct
- Déjerine-Roussy syndrome (thalamic pain syndrome): thalamoperforators of PCA
- top of the basilar syndrome
- striatocapsular infarct
- choroid plexus infarct
- cerebellar infarct
-
brainstem infarct
- midbrain infarct
- Benedikt syndrome: PCA
- Claude syndrome: PCA
- Nothnagel syndrome: PCA
- Weber syndrome: PCA
- Wernekink commissure syndrome
- pontine infarct
- Brissaud-Sicard syndrome
- facial colliculus syndrome
- Gasperini syndrome: basilar artery or AICA
- inferior medial pontine syndrome (Foville syndrome): basilar artery
- lateral pontine syndrome (Marie-Foix syndrome): basilar artery or AICA
- locked-in syndrome: basilar artery
- Millard-Gubler syndrome: basilar artery
- Raymond syndrome: basilar artery
- medullary infarct
- Babinski-Nageotte syndrome
- Cestan-Chenais syndrome
- hemimedullary syndrome (Reinhold syndrome)
- lateral medullary stroke syndrome (Wallenberg syndrome)
- medial medullary syndrome (Déjerine syndrome)
- Opalski syndrome
- midbrain infarct
- acute spinal cord ischemia syndrome
- hemispheric infarcts
- by vascular territory
- by vessel size
- treatment options
- complications
-
intracranial hemorrhage
-
intra-axial hemorrhage
- signs and formulas
- ABC/2 (volume estimation)
- black hole sign
- blend sign
- cashew nut sign
- CTA spot sign
- island sign
- satellite sign
- swirl sign
- zebra sign
- by type
- by location
- signs and formulas
- extra-axial hemorrhage
- extradural hemorrhage (EDH)
- intralaminar dural hemorrhage
- subdural hemorrhage (SDH)
-
subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH)
- types
- complications
- grading systems
- subpial hemorrhage
-
intra-axial hemorrhage
Related articles: Terms used in radiology
- general
- ancillary
- Cinderella
- diagnosis of exclusion
- dilation vs dilatation
- epiphenomenon
- florid
- forme fruste
- gold standard
- heterogeneous vs heterogenous
- Hickam's dictum
- iatrogenic disease
- idiopathic
- in extremis
- natural history
- non-specific
- Occam's razor
- prodrome
- Saint's triad
- self-limiting
- sequela
- sine qua non
- status post
- subclinical disease
- syndrome
- radiology-specific
- pathology
- agenesis
- anlage
- aplasia
- apoptosis
- atresia
- atrophy
- cyst
- dehiscence
- diathesis
- diverticulum
- dyscrasia
- dysplasia
- exophytic
- fistula
- fluid collection
- granulation tissue
- hernia
- hyperplasia
- hypertrophy
- hypoplasia
- lamellated
- laminated
- malignancy
- metaplasia
- necrosis
- neoplasm
- phlegmon
- septum
- synechia
- trabecula
- CNS
- chest
- epidemiology
- gastrointestinal
- genetics
- musculoskeletal
- oncology




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.