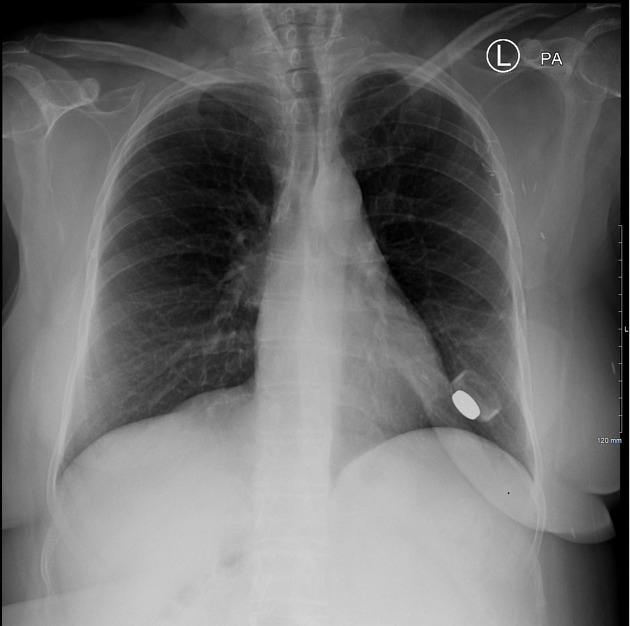
Breast implants are increasingly common in general breast radiology practice.
On this page:
Classification
Location
Breast implants may be placed behind the glandular tissue but in front of the pectoral muscle:
subglandular
submammary
retroglandular
retromammary
The second position of breast implants is behind the pectoral muscle; this has been termed subpectoral or retropectoral.
In women who have implants placed after mastectomy, the implant may be placed behind the pectoralis muscle. Augmentation can also be done by using an implant and rotated latissimus dorsi muscle (so-called LADO-FLAP).
Surgical access
There are multiple options regarding the surgical access for placing the breast implant. Selection of access is primarily based on the implant size, type and location. Furthermore, skin quality, residual breast tissue and body habitus also influence the decision for the used surgical access. Prior breast surgery or breast deformities (e.g. Poland syndrome) limit the possible options. The typical access ways are:
inframammary (most common)
periareolar
transaxillary
transumbilical
Types
The implants may be composed of saline, silicone or a combination of both.
They come in a variety of types including:
-
single-lumen gel:
silicone gel-filled
-
single-lumen adjustable:
silicone gel-filled, to which can be added a variable amount of saline at the time of placement
-
saline-filled, dextran-filled, PVP-filled:
dextran-filled (some early implants), PVP-filled (Bioplasty), and the rest saline-filled
-
standard double-lumen:
silicone gel inner lumen, saline outer lumen
-
reverse double-lumen:
saline inner lumen, silicone gel outer lumen
-
reverse-adjustable double-lumen:
silicone gel inner and outer lumens, variable amount of saline added to inner lumen at the time of placement
-
gel-gel double-lumen:
silicone gel inner and outer lumens
-
triple-lumen:
silicone gel inner and middle lumens, saline outer lumen
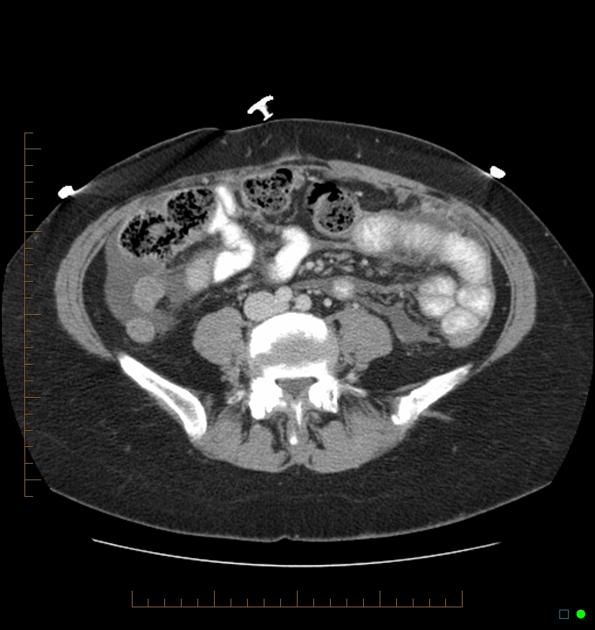
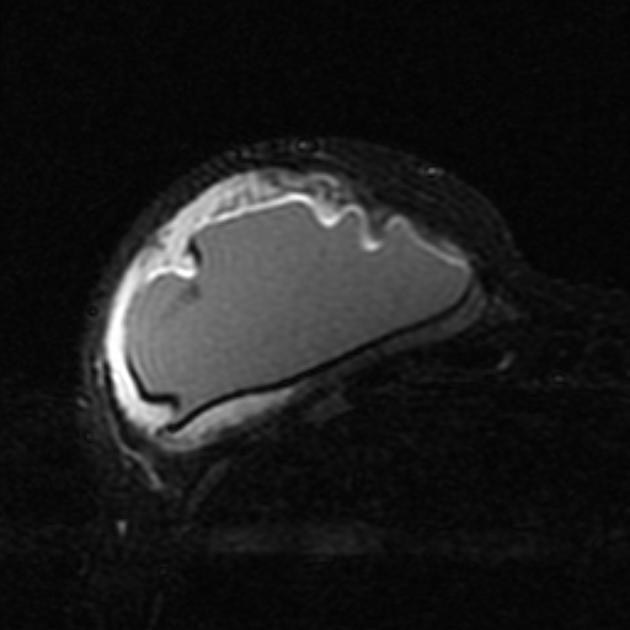
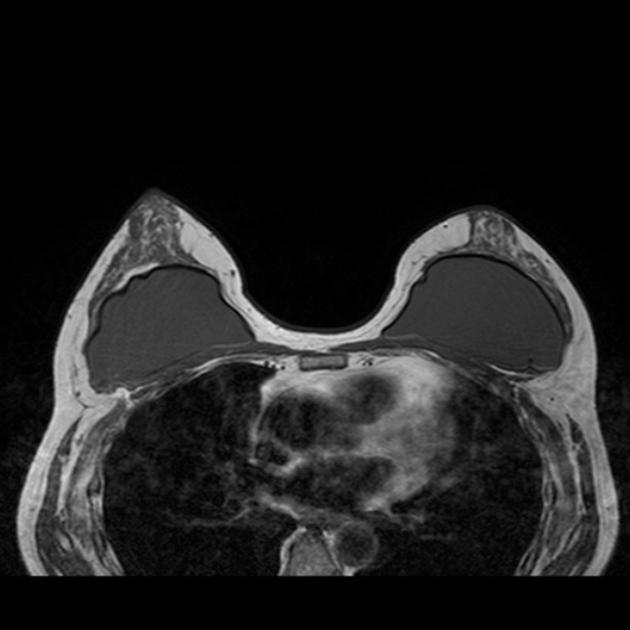
Complications
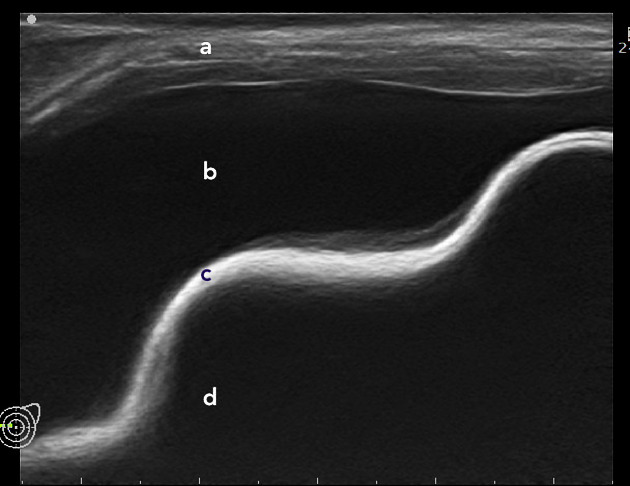
breast implant collapse: typically occurs with saline implants and is also sometimes considered a type of rupture
-
the capsule contracts making the implant hard to palpate and may cause pain
considered one of the commonest complications
infection
breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma (rare) 6
axillary lymph nodes siliconoma
late periprosthetic seroma
gel bleed phenomenon: not considered a true complication
Differential diagnosis
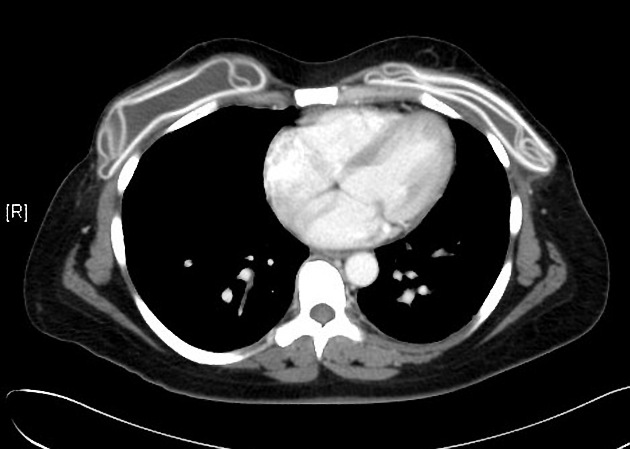
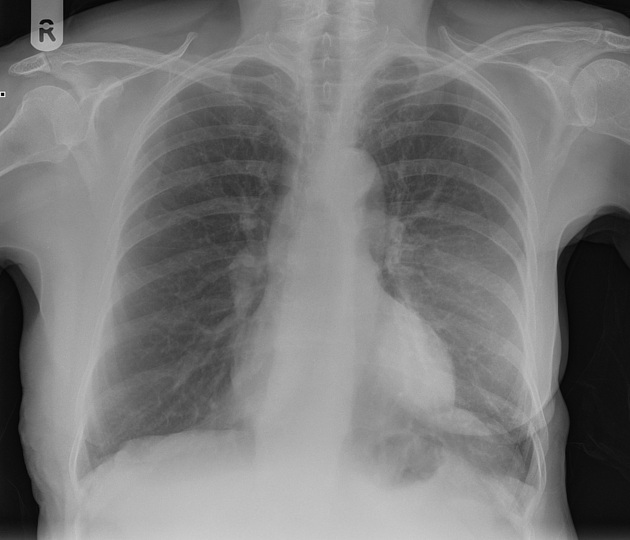
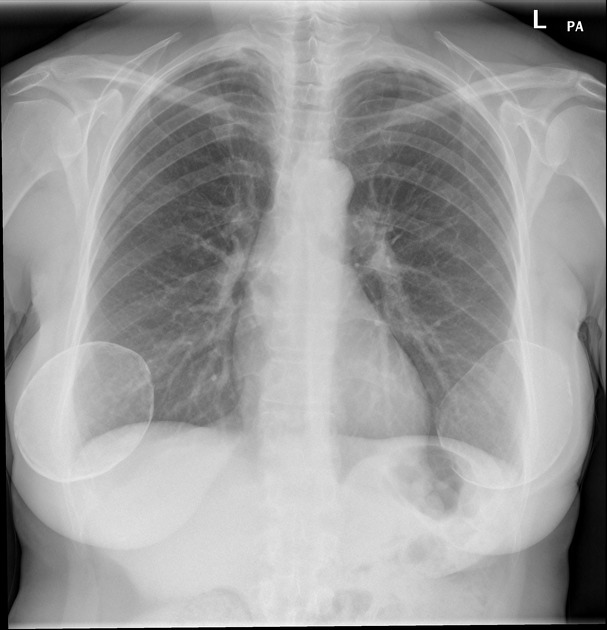
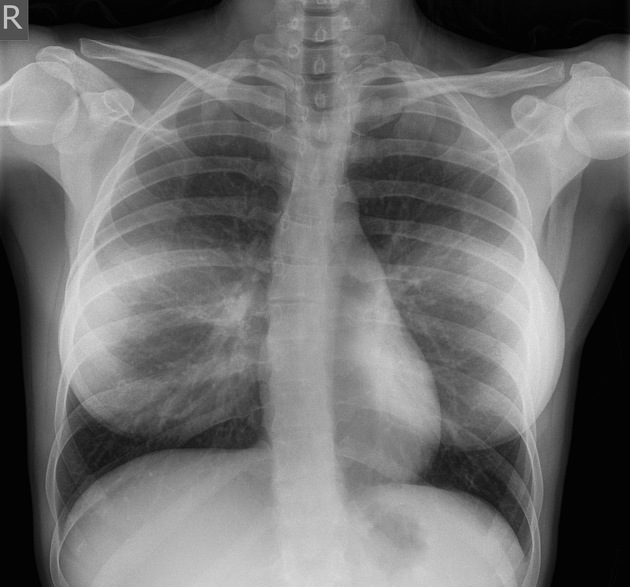
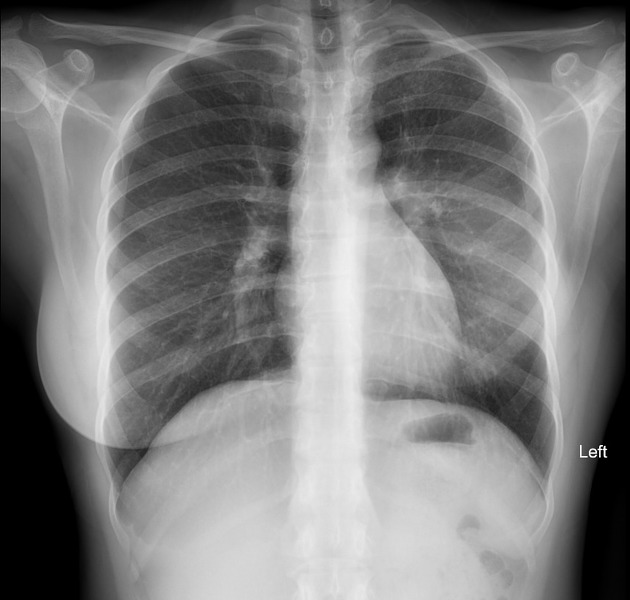
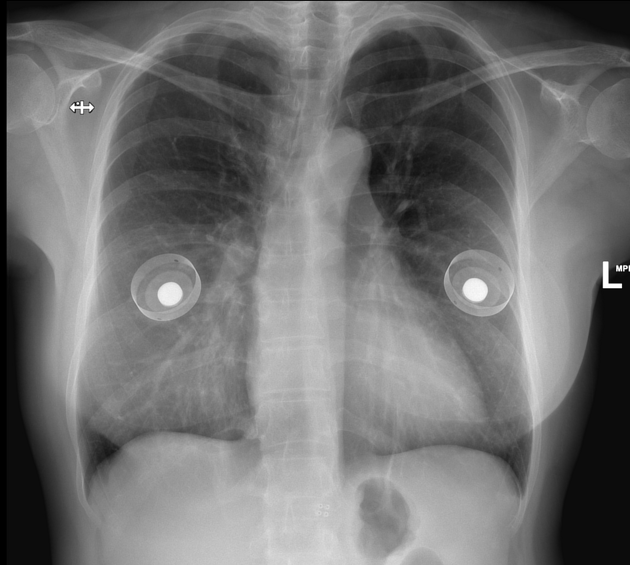
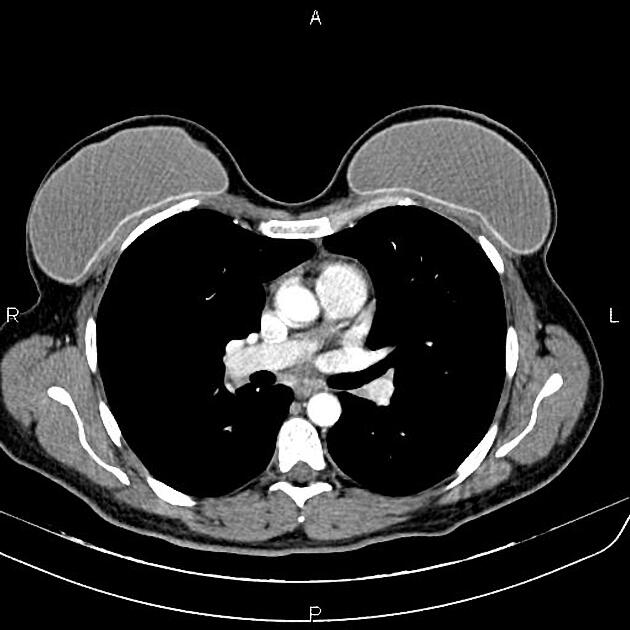
Occasionally on plain chest radiographs, other pathologies may mimic the breast implant appearance:
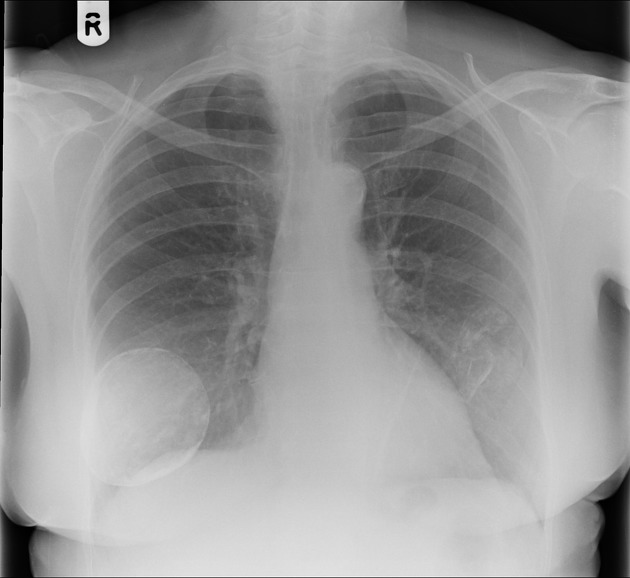
lung cancer - see differential case












 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.