Goiter (rarely thyromegaly) refers to enlargement of the thyroid gland. It can occur from multiple conditions, including iodine deficiency, hormonal dyscrasias, and infectious/inflammatory conditions. The absence of thyroid enlargement does not preclude significant thyroid pathology.
The definition of goiter depends on age and sex. The upper limit of normal thyroid gland volume:
adult males: 12-18 mL 9
adult females: 10-15 mL 9
13-14 years: 8-10 mL 1
3-4 years: 3 mL 1
neonate: 0.8-1.5 mL 1
On this page:
Epidemiology
The prevalence of goiter varies widely depending on the level of iodine deficiency. In severely iodine-deficient areas the prevalence may be as high as 80%. Goiter is more common in women, and incidence declines with age 5.
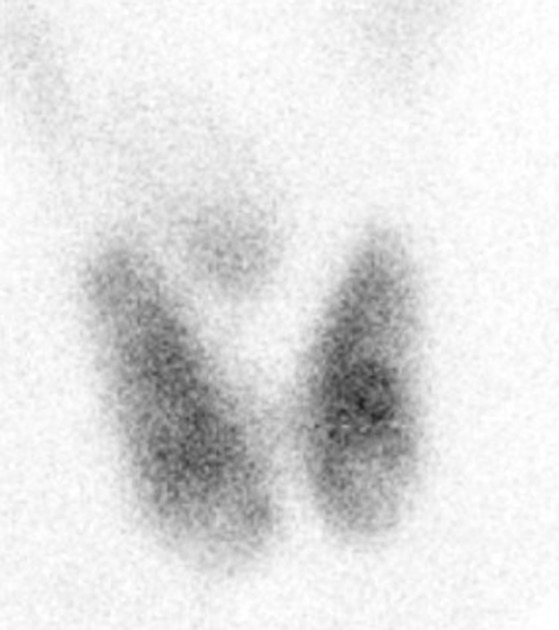
Pathology
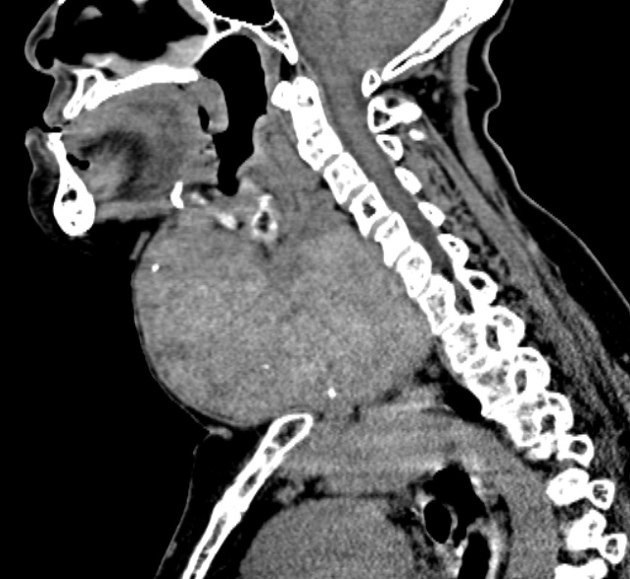
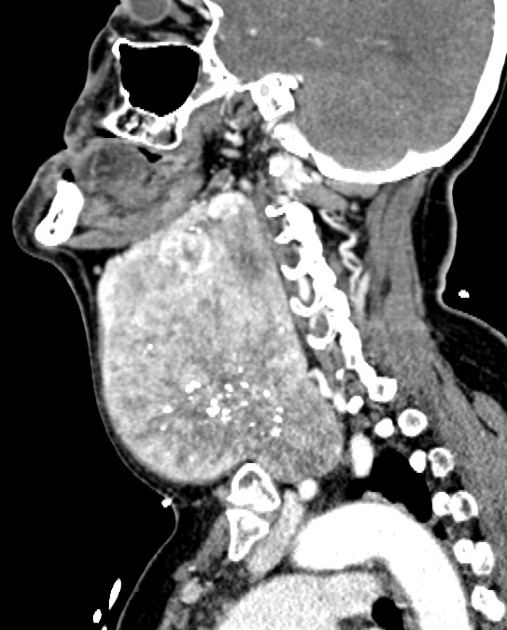
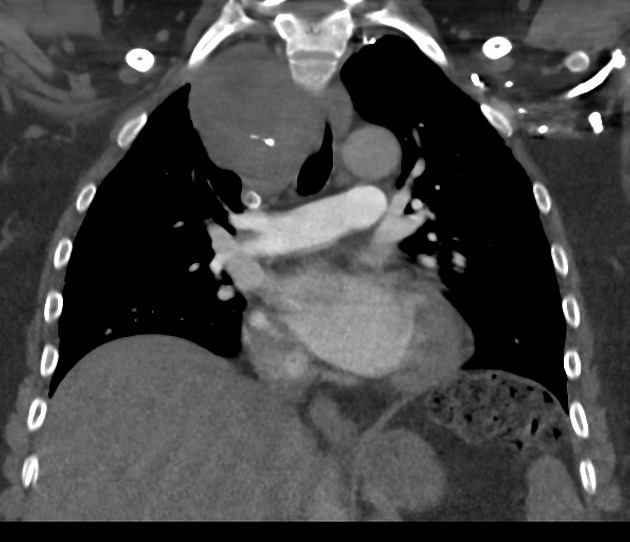
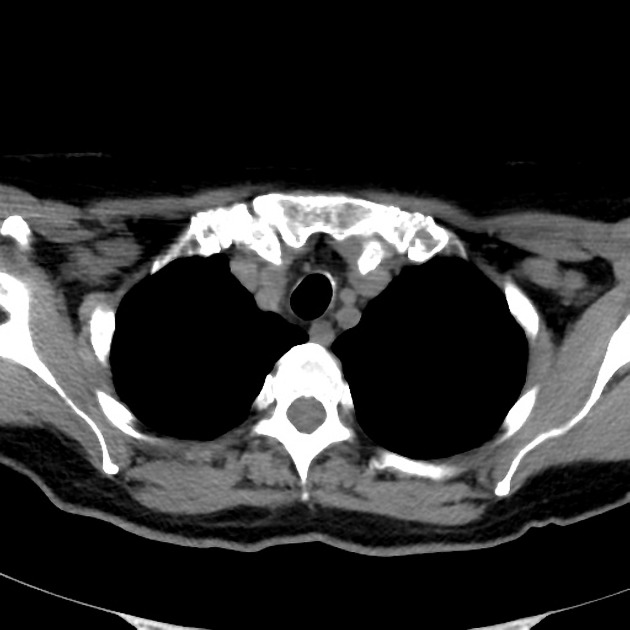
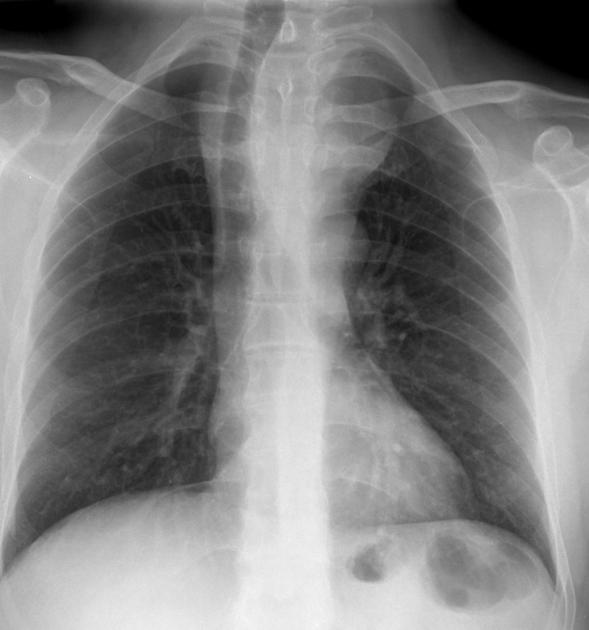
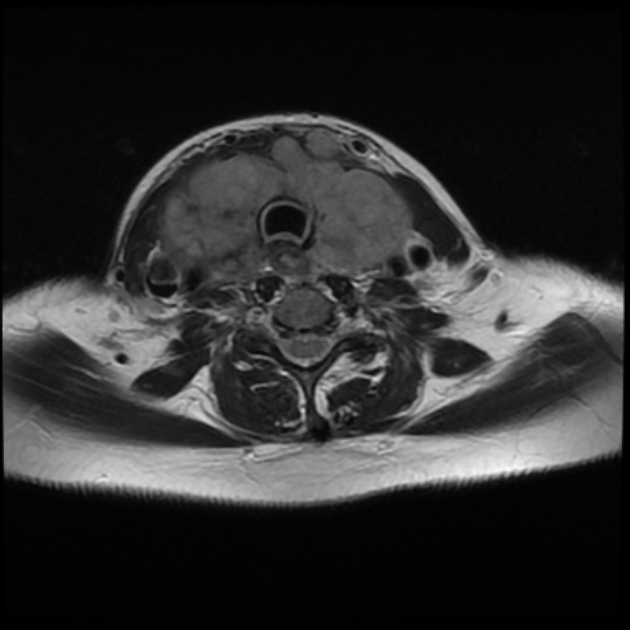
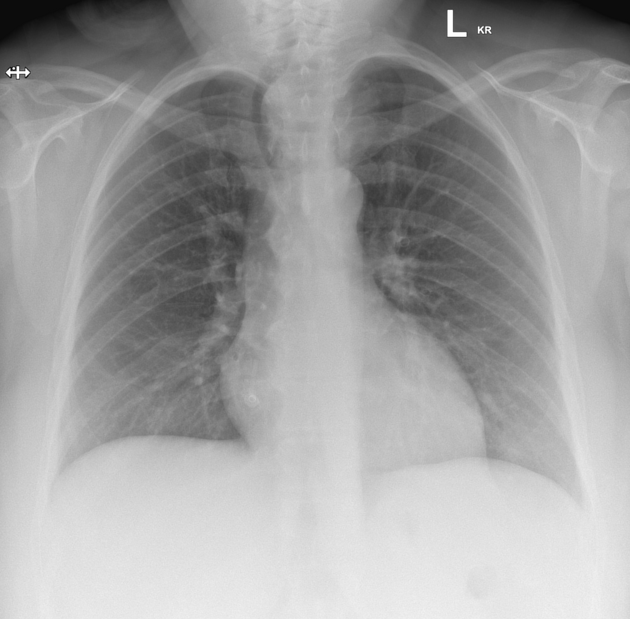
The thyroid gland may become so enlarged that it becomes a substernal (retrosternal) goiter.
Etiology
The causes of goiter are diverse 2,3:
non-toxic simple goiter, e.g. from iodine deficiency
-
goitrogens
drugs: lithium, amiodarone, etc.
diet: cabbage, sprouts, etc.
depositional disease, e.g. amyloidosis
miscellaneous, e.g. Plummer-Vinson syndrome
Radiographic features
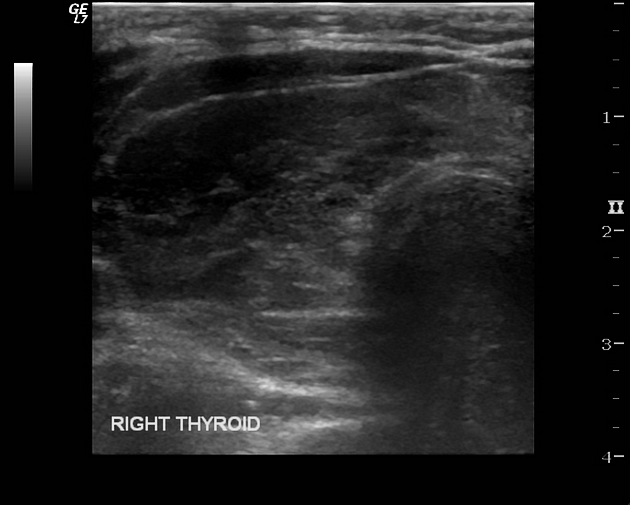
Ultrasound
-
each lobe normally measures 4,9:
length: 4-7 cm
depth: 1.3-2 cm
isthmus ≤0.5 cm deep
Thyroid volume can be estimated by measuring each lobe and applying the following correction factor for an ellipsoid formula 6:
height (cm) x width (cm) x depth (cm) x 0.529*
* various correction factors between 0.494-0.554 have been proposed 6,9
History and etymology
Goiter derives from the old French "goitron" meaning gullet. Goitron comes from the Latin "guttur" meaning throat.
Differential diagnosis
See main article: midline neck mass





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.