Paragangliomas of the head and neck are rare, representing <0.5% of all head and neck tumors. They arise in a number of locations along the carotid sheath and middle ear including the carotid bifurcation, vagal ganglia, jugular bulb, and tympanic plexus.
For a general discussion of the pathology of these tumors please refer to the paraganglioma article.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Overall there is a 3:1 female predominance. Two-thirds of cases are diagnosed between the ages of 40 and 60. Approximately 25% are multicentric, and these tend to be familial.
Clinical presentation
Clinical presentation will depend on location.
When involving the middle ear cavity, the tumor may grow large and extend into the external ear: these may present with pulsatile tinnitus, cranial nerve palsies (typically IX-XI, Vernet syndrome), or conductive hearing loss. Direct otoscopic examination may reveal a retrotympanic vascular mass.
In the neck, the patient may present with a local mass.
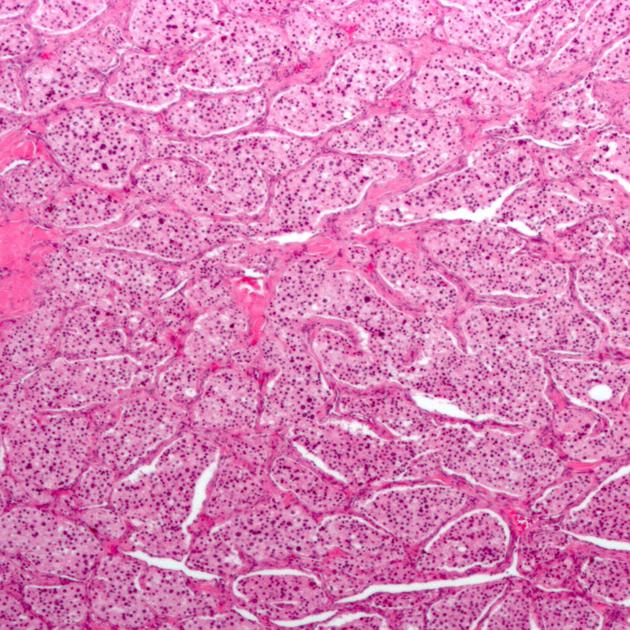
Pathology
Paragangliomas arise from neural crest cells, which can differentiate into cells of either the parasympathetic or sympathetic nervous system. In the head and neck, paragangliomas tend to be innervated by the parasympathetic system and do not secrete catecholamines and are thus termed nonchromaffin paragangliomas 10.
Multiple paragangliomas (both sporadic and familial subtypes) are commonly associated with mutations of the succinate dehydrogenase subunit genes 10.
Associations
Although often sporadically identified in otherwise normal individuals, paragangaliomas are seen associated with a number of systemic conditions including 10:
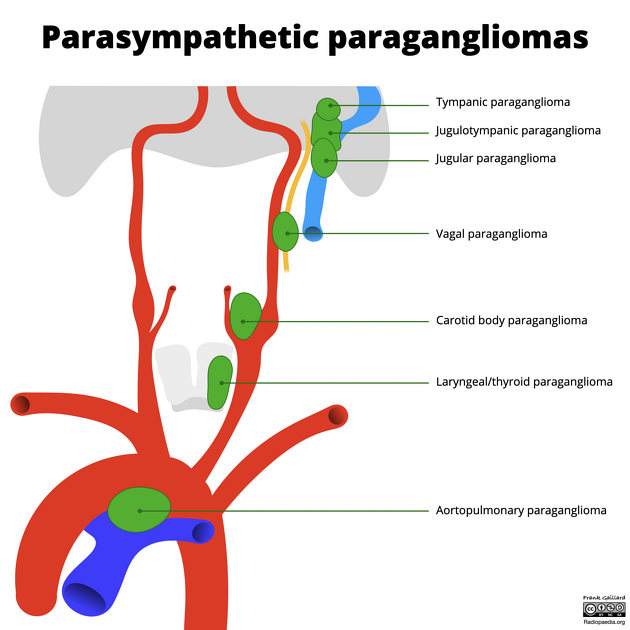
Location
They are divided according to location:
-
carotid body tumor (or chemodectoma)
located at the carotid body, and splaying the carotid bifurcation
most common paraganglioma of the head and neck (60-67% of total)
-
arise from the glomus tympanicum
confined to the middle ear overlying the cochlear promontory
arises from the inferior tympanic branch of glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) (or Jacobson's nerve)
second most common head and neck paraganglioma
-
arising from the glomus jugulotympanicum
extending between the cochlear promontory and jugular foramen
arising from Arnold's nerve, the mastoid branch of the vagus nerve (CN X)
-
arising from the glomus jugulare
confined to the jugular foramen
extending into the middle ear
-
arising from the glomus vagale associated with vagus nerve (CN X)
least common head and neck paraganglioma
-
laryngeal/thyroid paraganglioma 11,12
arising from the laryngeal paraganglia
may grow medially into the submucosal space or laterally into the thyroid bed
rare
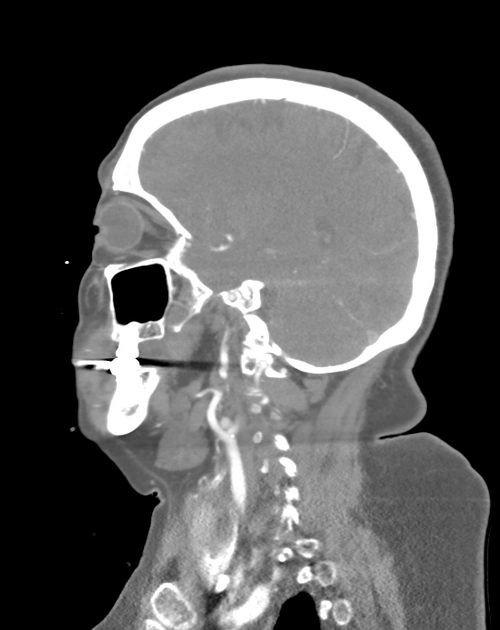
Radiographic features
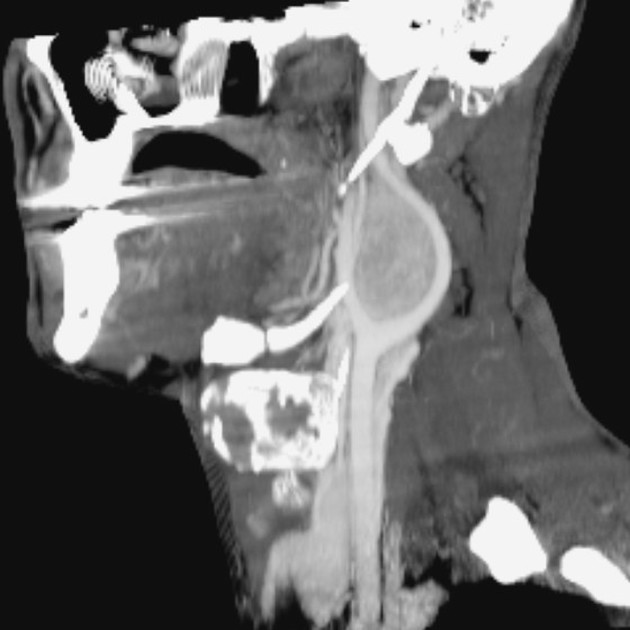
CT
useful when bone erosion occurs
a moth-eaten pattern is typical
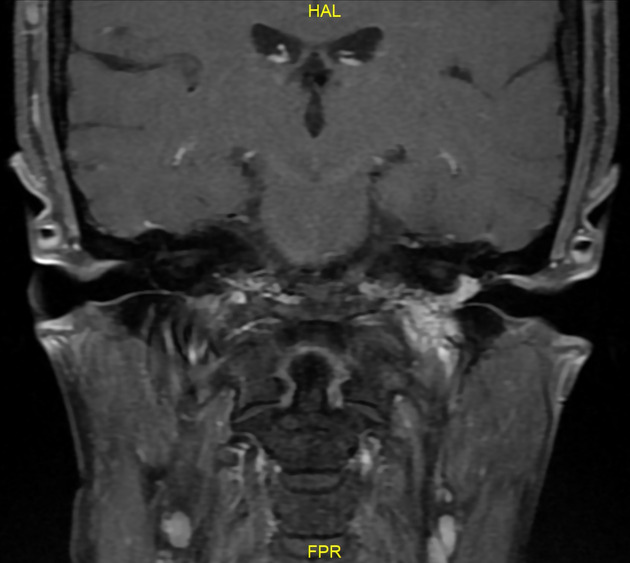
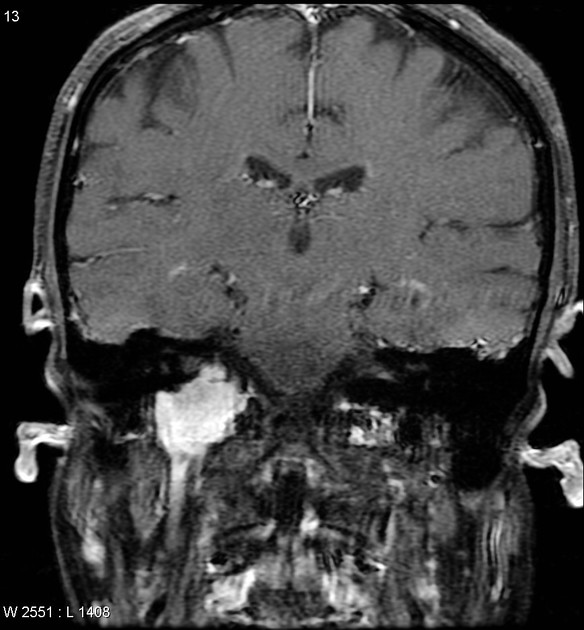
MRI
T1: may show a “salt and pepper” appearance; salt representing blood products from hemorrhage (uncommon) and pepper representing flow voids due to high vascularity (common)
T1C+ (Gd): demonstrate rapid wash-in and wash-out (as opposed to the more slow and steady enhancement of a schwannoma) 9
Angiography (DSA)
intense tumor blush
the most common feeding vessel is the ascending pharyngeal artery
Scintigraphy
high uptake on 111In labeled octreotide 7-8
Treatment and prognosis
Treatment is usually by excision. Preoperative endovascular embolization is often used to reduce tumor vascularity and aid excision. Radiotherapy may be used for palliation of unresectable lesions.
Malignant transformation is not terribly uncommon and has been reported in 16-19% of glomus vagale tumors, in 6% of carotid body tumors, and in 2-4% of glomus tympanicum tumors.
Differential diagnosis
When completely imaged with CT and contrast-enhanced MRI usually little differential is present. During work-up, however, numerous entities should be considered.
In the middle ear/petrous temporal bone consider:
In the jugular and carotid region consider:
lymph node metastasis/mass
sympathetic chain paraganglioma 13




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.