Renal osteodystrophy, also known as uremic osteopathy, is a constellation of musculoskeletal abnormalities that occur in patients with chronic renal failure, due to concurrent and superimposed:
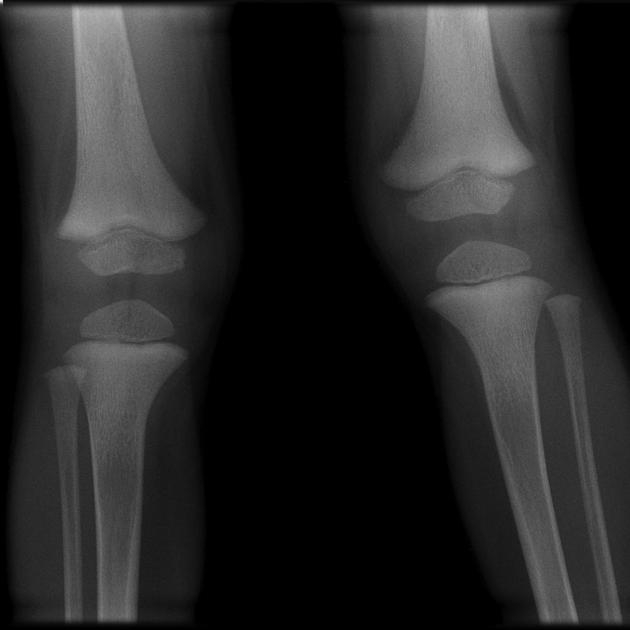
osteomalacia (adults) or rickets (children)
-
secondary hyperparathyroidism: abnormal calcium and phosphate metabolism
bone resorption
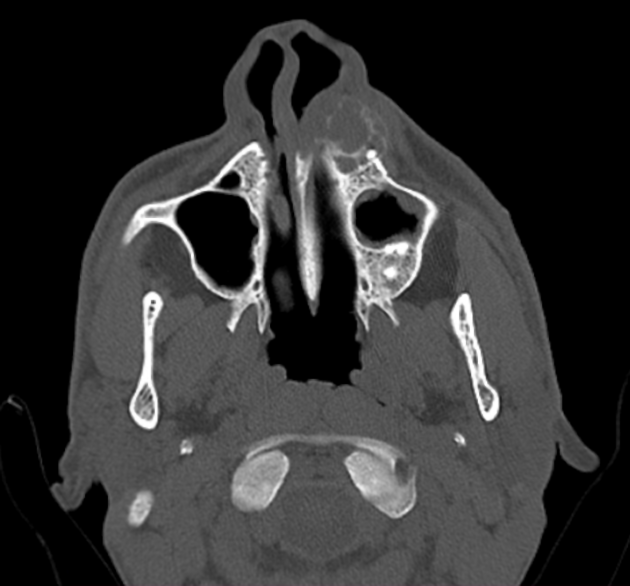
soft tissue and vascular calcifications
aluminum intoxication, e.g. if the patient is on hemodialysis
Radiographic features
Plain radiograph
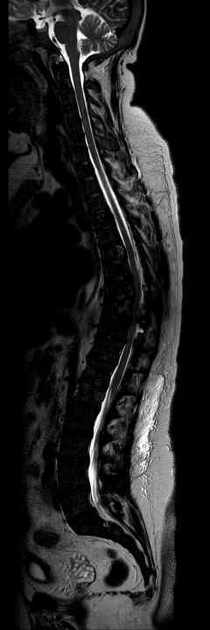
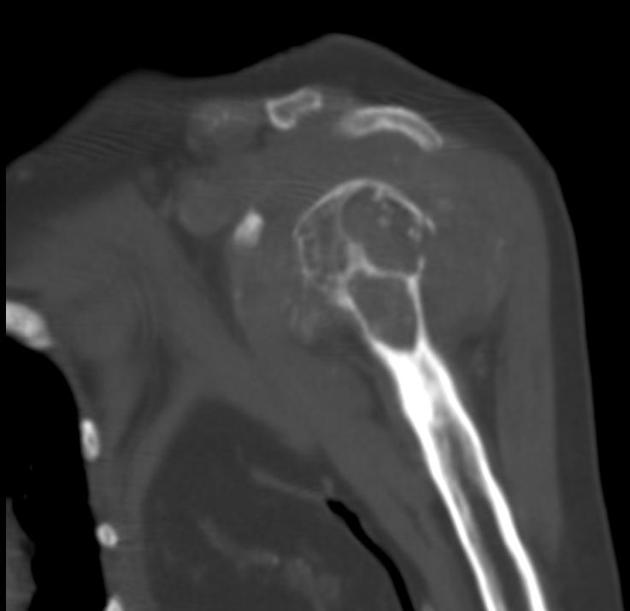
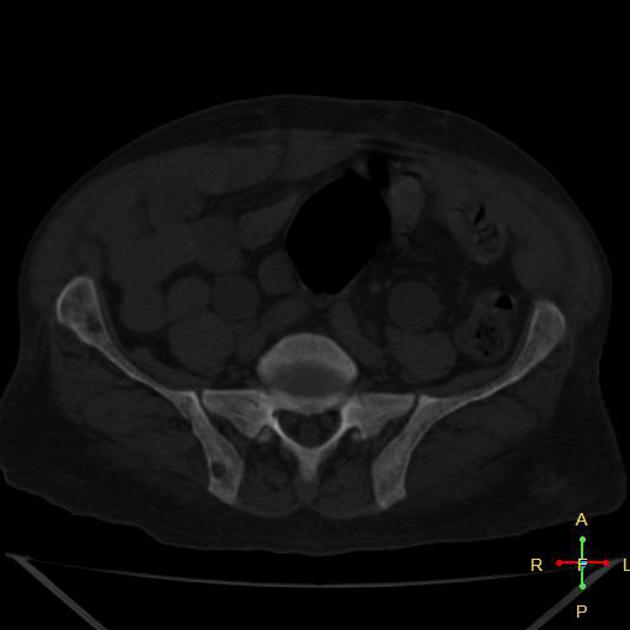
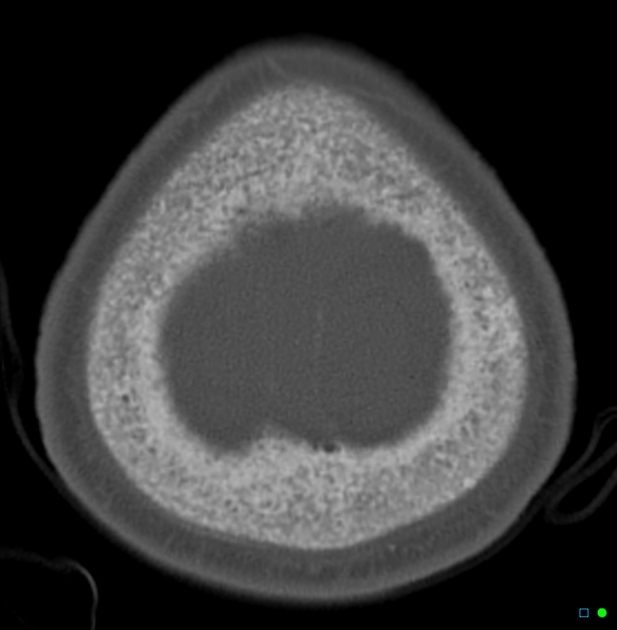
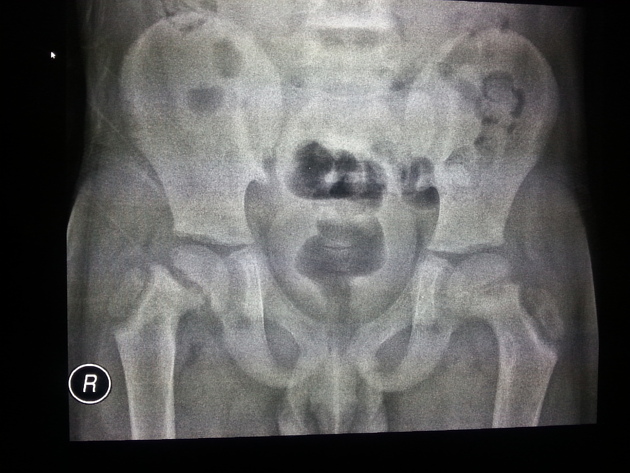
Imaging findings are many and varied:
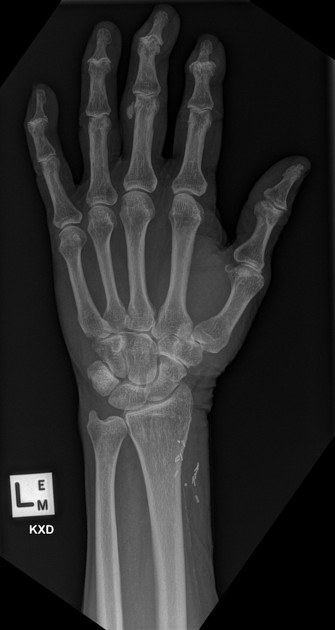
osteopenia: (often seen early) thinning of cortices and trabeculae
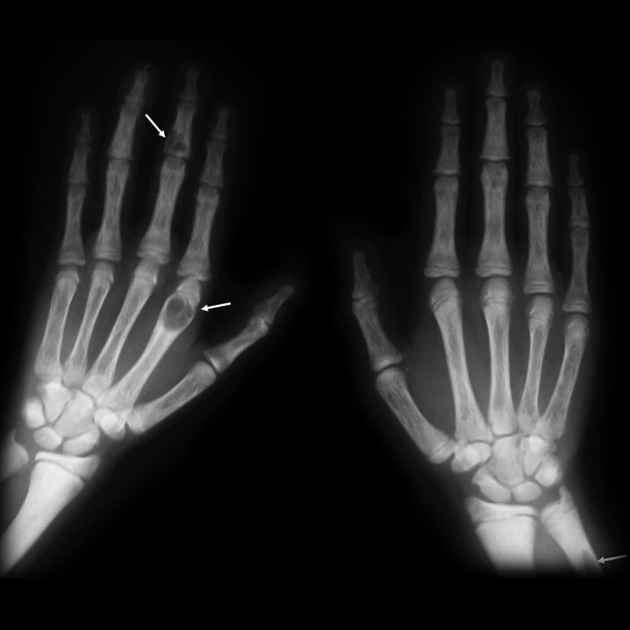
demineralization: usually subperiosteal, however, it may also involve joint margins, endosteal, subchondral, subligamentous areas, cortical bone, or trabeculae 5
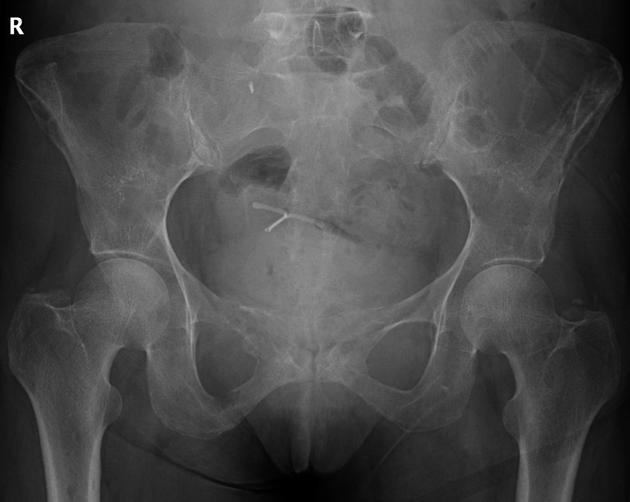
subperiosteal resorption: characteristic subperiosteal resorption may be seen on radial aspects of the middle phalanges of the index and long fingers
-
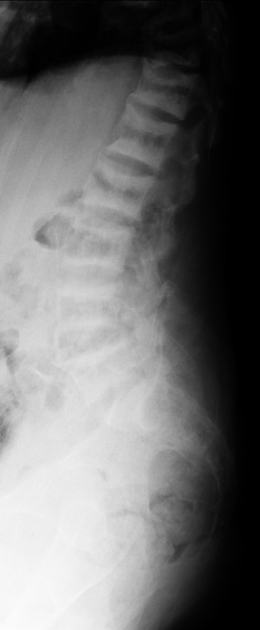
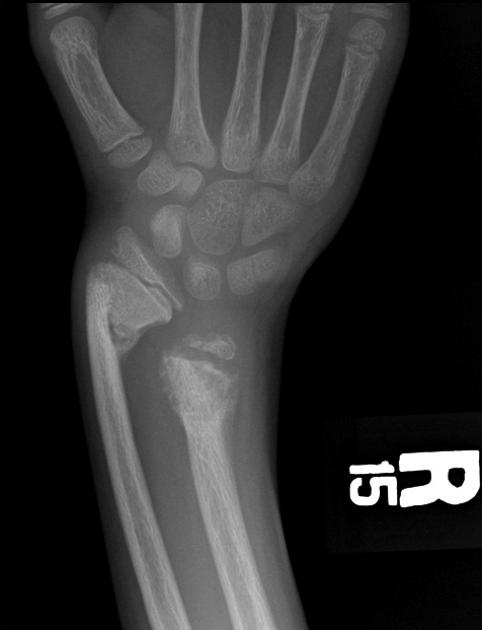
bone sclerosis
rugger jersey spine: sclerosis of the vertebral body endplates
amyloid deposition: erosion in and around joint
Bone scintigraphy
The bony skeleton has high affinity towards 99mTc- diphosphonate especially in the calvaria, and mandible. Beading of the costochondral junction (also known as "tie sternum") is also seen. The bone findings are usually due to secondary hyperparathyroidism but an osteomalacia component may contribute to some of its scintigraphy features. Meanwhile, kidneys and urinary bladder appear faint or not visualized 6.
Differential diagnosis
General imaging differential considerations include:
neoplasms: multiple myeloma, metastases; brown tumors can mimic primary malignant tumor of bone; amyloid deposition may mimic tenosynovial giant cell tumor or synovial chondromatosis
occult marrow abnormalities










 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.