Breast sebaceous cyst, also known as, more correctly, an epidermal inclusion cyst or simply epidermoid cyst, is a benign breast lesion (BIRADS II).
For a general discussion of this entity outside the breast, please refer to epidermal inclusion cysts.
On this page:
Terminology
The two terms, breast sebaceous cyst and epidermal inclusion cyst, are not entirely synonymous as a sebaceous cyst has an epithelial lining as opposed to a epidermal inclusion cyst, which has an epidermal lining. As far as imaging is concerned, the two entities are indistinguishable from each other 6.
The sebaceous cyst implies that the lesion originates in the sebaceous glands, which is not the case and thus the term should be avoided. The epidermal inclusion cyst refers to an epidermoid cyst due to implantation of epidermal elements in the dermis. The preferred term is usually an epidermoid cyst. However, in reality, the terms are used interchangeably.
Pathology
A sebaceous cyst originates in the sebaceous gland while an epidermoid cyst, which is used interchangeably with the previous term, has its origin in the follicular infundibulum.
Location
These lesions are typically located in the skin or subcutaneous tissue. There may be a predilection towards the inframammary fold.
Radiographic features
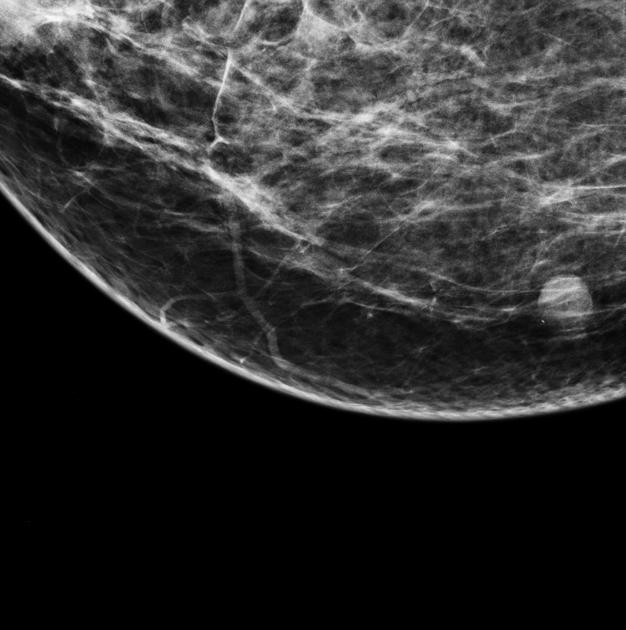
Mammography
They are usually seen as well-circumscribed rounded soft tissue density lesions close to the skin surface.
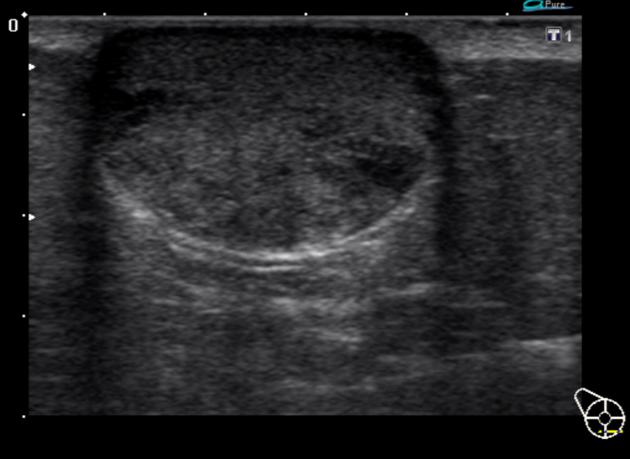
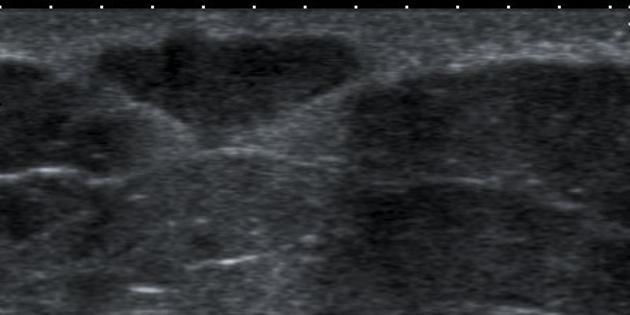
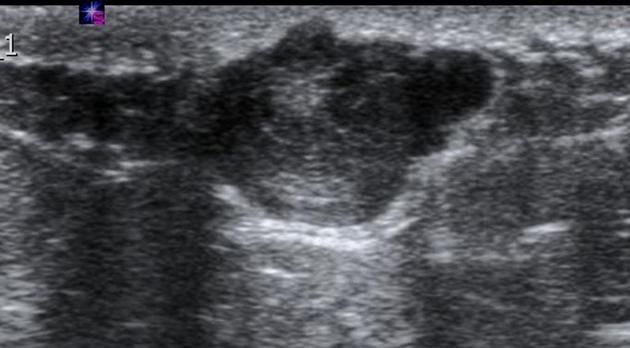
Breast ultrasound
They may be often seen as small and hypoechoic and again located close to the skin surface with through transmission and with no detectable vascular flow. Hypo- and hyperechoic alternating rings may sometimes be seen on sonography. In some occasions, a characteristic track may be seen extending into the skin surface.
Doppler imaging on ultrasound may on occasion show quite remarkable "flow". Possible low grade infection is not excluded.
Treatment and prognosis
When inflammation is present - both clinical and imaging follow up is advised 7.
Complications
infection: inflammation
cyst rupture causing a foreign body or granulomatous reaction, or abscess formation
malignant transformation into a low grade squamous cell carcinoma is extremely rare but has been reported
Differential diagnosis
Considerations on mammography include:
accessory nipple 5: particularly if along the milk line on breast tissue
On ultrasound also consider:
Montgomery tubercle: particularly if it is at the nipple-areolar region







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.