Mastitis (rare plural: mastitides) refers to inflammation of the breast parenchyma, of which there are a number of subtypes:
-
acute mastitis
puerperal mastitis usually occurs from infection with Staphylococcus spp. during lactation
non-puerperal mastitis: not related to lactation and usually occurs in older women
plasma cell mastitis (mammary duct ectasia): uncommon subareolar inflammation without associated bacterial infection
granulomatous mastitis: rare; usually occurs due to tuberculosis or sarcoidosis
On this page:
Clinical presentation
Clinically, the breast will be indurated, red and painful. Nipple retraction may also be evident. Nodal enlargement is common. The patient may often have systemic symptoms such as fever or leukocytosis.
Complications
breast abscess formation
Radiographic features
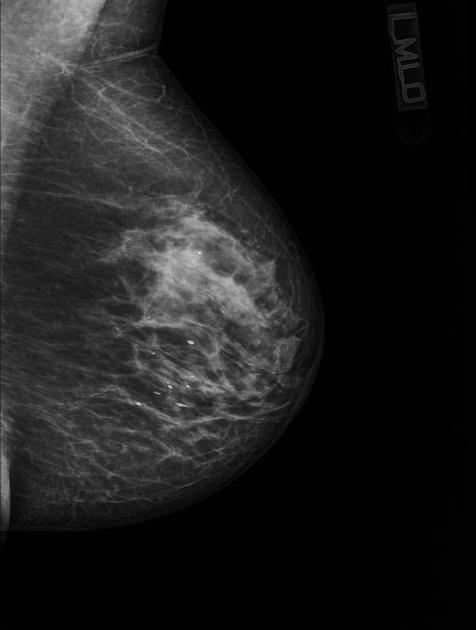
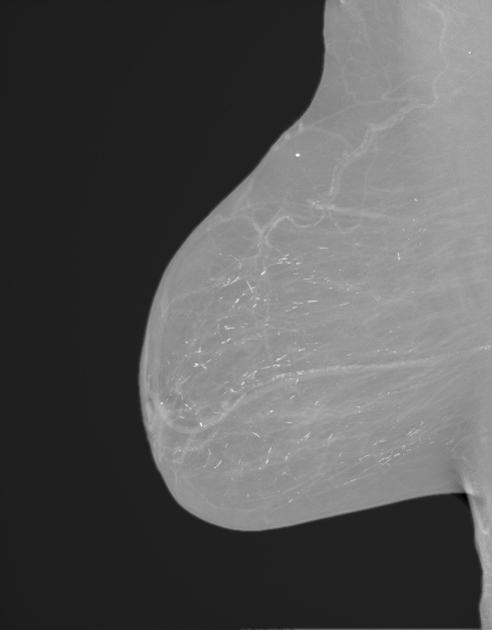
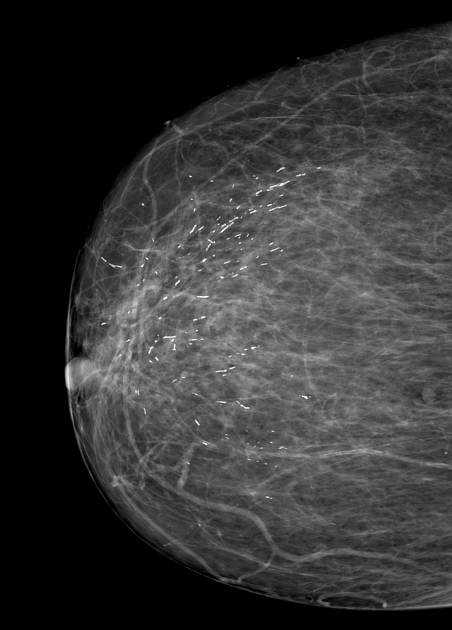
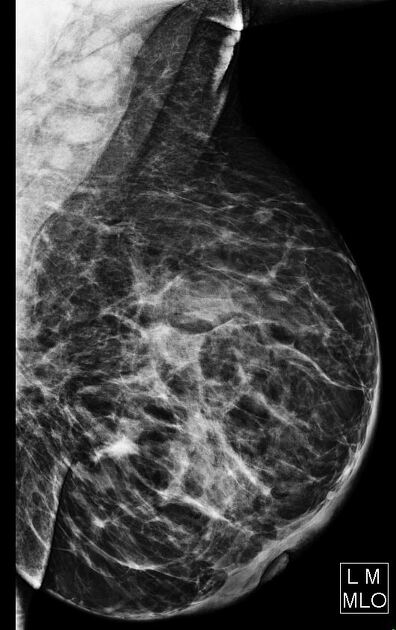
Mammography
On mammography, bacterial (puerperal or non-puerperal) mastitis usually features ill-defined regions of increased density and skin thickening.
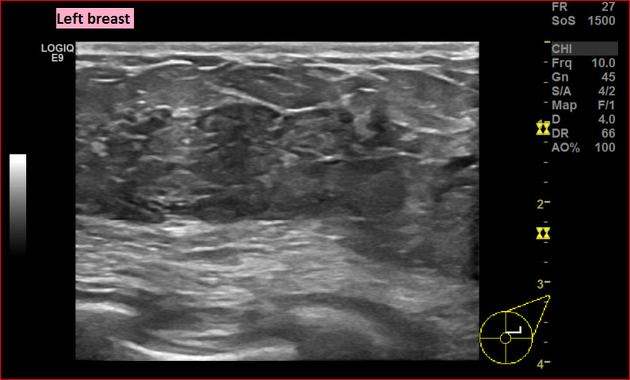
Ultrasound
On ultrasound, ill-defined areas of altered echotexture with hyperechogenicity representing infiltrated and inflamed fat lobules, hypoechoic areas in the glandular parenchyma, and associated mild skin thickening are seen. Inflammatory axillary lymph nodes may also be encountered. Occasionally, abscess formation may be visible.
Differential diagnosis
It is important to consider inflammatory breast cancer as a potential differential.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.