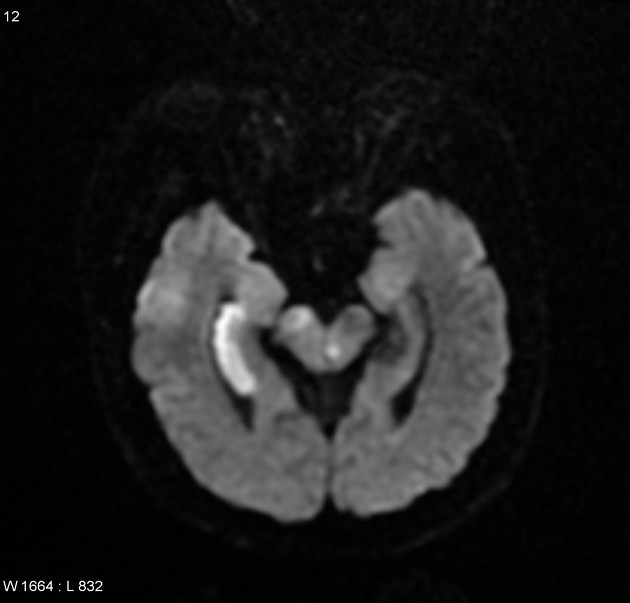
Posterior choroidal artery infarct
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Frank Gaillard had no recorded disclosures.
View Frank Gaillard's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Rohit Sharma had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Rohit Sharma's current disclosures- Posterior choroidal artery ischaemic stroke
- Posterior choroidal artery infarction
Posterior choroidal artery infarct is a rare isolated ischemic stroke syndrome due to occlusion of the posterior choroidal artery. It usually coexists with posterior cerebral artery, and often superior cerebellar artery, infarction.
Clinical presentation
When infarction is limited to to the lateral posterior choroidal artery territory, the most common clinical manifestations include:
homonymous quadrantanopia or homonymous horizontal sectoranopia (uncommon but highly suggestive of involvement of the lateral geniculate body)
hemisensory loss
neuropsychological dysfunction (transcortical aphasia, memory disturbances)
Medial posterior choroidal artery territory infarction is less frequent with Its neurologic presentation dominated by eye movement disorders.
Pathology
When seen in isolation, damage due to posterior choroidal artery infarction is characteristically limited to the:
pulvinar
posterior thalamus
References
- 1. Neau JP, Bogousslavsky J. The syndrome of posterior choroidal artery territory infarction. Ann. Neurol. 1996;39 (6): 779-88. doi:10.1002/ana.410390614 - Pubmed citation
Incoming Links
Related articles: Stroke and intracranial haemorrhage
-
stroke and intracranial hemorrhage
- general articles[+][+]
-
ischemic stroke
- general discussions[+][+]
- scoring and classification systems[+][+]
- Alberta stroke program early CT score (ASPECTS)
- ASCOD classification
- Canadian Neurological Scale
- Heidelberg bleeding classification
- NIH Stroke Scale
- Mathew stroke scale
- modified Rankin scale
- Orgogozo Stroke Scale
- Scandinavian Stroke Scale
- thrombolysis in cerebral infarction (TICI) scale
- TOAST classification
- collateral vessel scores
- signs[+][+]
- by region[+][+]
- hemispheric infarcts
- frontal lobe infarct
- parietal lobe infarct
- temporal lobe infarct
- occipital lobe infarct
- alexia without agraphia syndrome: PCA
- cortical blindness syndrome (Anton syndrome): top of basilar or bilateral PCA
- Balint syndrome: bilateral PCA
- lacunar infarct
-
thalamic infarct
- artery of Percheron infarct
- Déjerine-Roussy syndrome (thalamic pain syndrome): thalamoperforators of PCA
- top of the basilar syndrome
- striatocapsular infarct
- choroid plexus infarct
- cerebellar infarct
-
brainstem infarct
- midbrain infarct
- Benedikt syndrome: PCA
- Claude syndrome: PCA
- Nothnagel syndrome: PCA
- Weber syndrome: PCA
- Wernekink commissure syndrome
- pontine infarct
- Brissaud-Sicard syndrome
- facial colliculus syndrome
- Gasperini syndrome: basilar artery or AICA
- inferior medial pontine syndrome (Foville syndrome): basilar artery
- lateral pontine syndrome (Marie-Foix syndrome): basilar artery or AICA
- locked-in syndrome: basilar artery
- Millard-Gubler syndrome: basilar artery
- Raymond syndrome: basilar artery
- medullary infarct
- Babinski-Nageotte syndrome
- Cestan-Chenais syndrome
- hemimedullary syndrome (Reinhold syndrome)
- lateral medullary stroke syndrome (Wallenberg syndrome)
- medial medullary syndrome (Déjerine syndrome)
- Opalski syndrome
- midbrain infarct
- acute spinal cord ischemia syndrome
- hemispheric infarcts
- by vascular territory
- by vessel size[+][+]
- treatment options[+][+]
- complications[+][+]
-
intracranial hemorrhage[+][+]
-
intra-axial hemorrhage
- signs and formulas
- ABC/2 (volume estimation)
- black hole sign
- blend sign
- cashew nut sign
- CTA spot sign
- island sign
- satellite sign
- swirl sign
- zebra sign
- by type
- by location
- signs and formulas
- extra-axial hemorrhage
- extradural hemorrhage (EDH)
- intralaminar dural hemorrhage
- subdural hemorrhage (SDH)
-
subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH)
- types
- complications
- grading systems
- subpial hemorrhage
-
intra-axial hemorrhage




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.